Method and system for serving slave clocks by master clock
A master clock, clock technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as no solutions, and achieve the effect of increasing the number
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
[0049] This example uses the synchronization process of the master clock and a slave clock it serves as an example to illustrate. In fact, the master clock can perform the relevant process of this example simultaneously with any slave clock it serves to increase the number of slave clocks it serves. The specific implementation scheme of this example is as follows:
[0050] Step 1, the master clock sets the service slave clock number threshold to Nmax according to its own processing capability.
[0051] Step 2: The slave clock initiates a unicast Sync negotiation message to the master clock, specifying a sending frequency.
[0052] Step 3. After receiving the message, the master clock judges whether there are Nmax number of slave clocks N, and if so, then sends a Grant message to reject the unicast to the slave clock, otherwise the master clock records the information of the slave clock to the slave clock list, and update the number N of current service slave clocks to N+1.
...
example 3
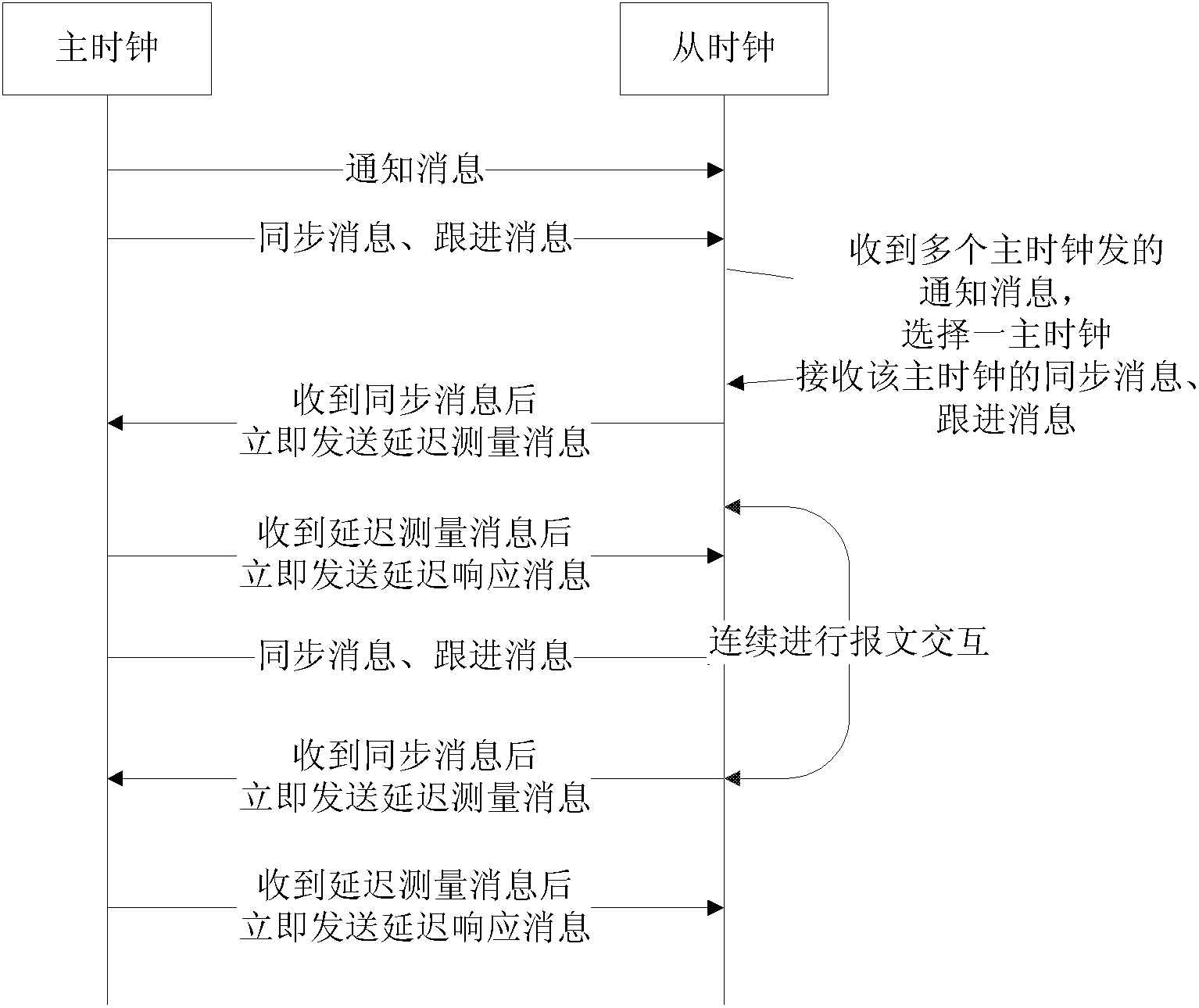
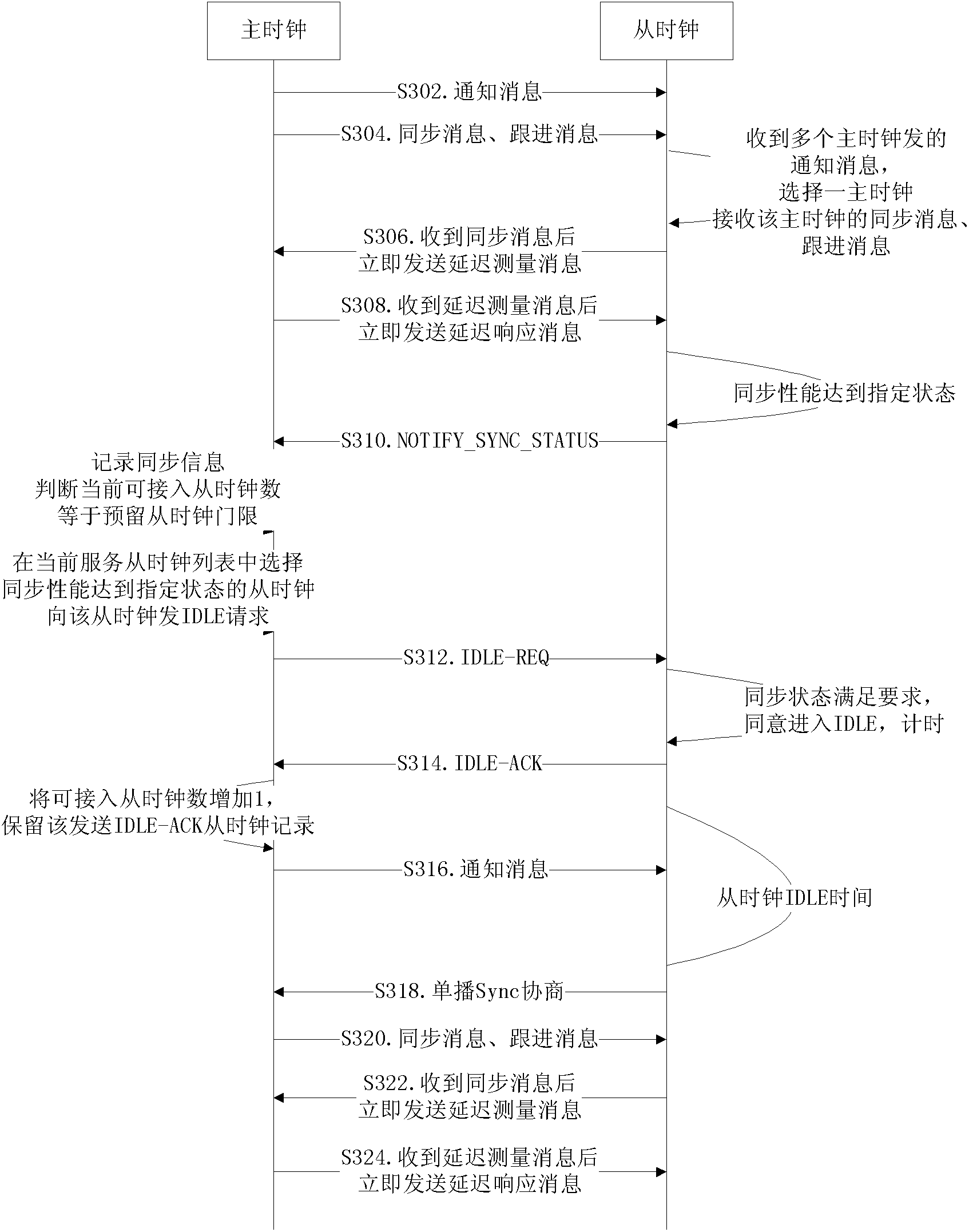
[0111] image 3 A schematic flowchart of a method for serving a slave clock for a master clock when joining IDLE according to Example 3 of the present invention. Such as image 3 As shown, the method includes:
[0112] Step S302, the master clock sends a notification message to the slave clock;
[0113] Step S304, the master clock sends a synchronization message and a follow-up message to the slave clock;
[0114] Step S306, the slave clock receives notification messages sent by multiple master clocks, selects a master clock, and receives the synchronization message and follow-up message of the master clock; after the slave clock receives the synchronization message, it immediately sends a delay measurement message;
[0115] Step S308, after the master clock receives the delay measurement message, it immediately sends a delay response message;
[0116] Step S310, the slave clock sends NOTIFY-SYNC-STATUS to the master clock after determining that the synchronization perform...
example 4
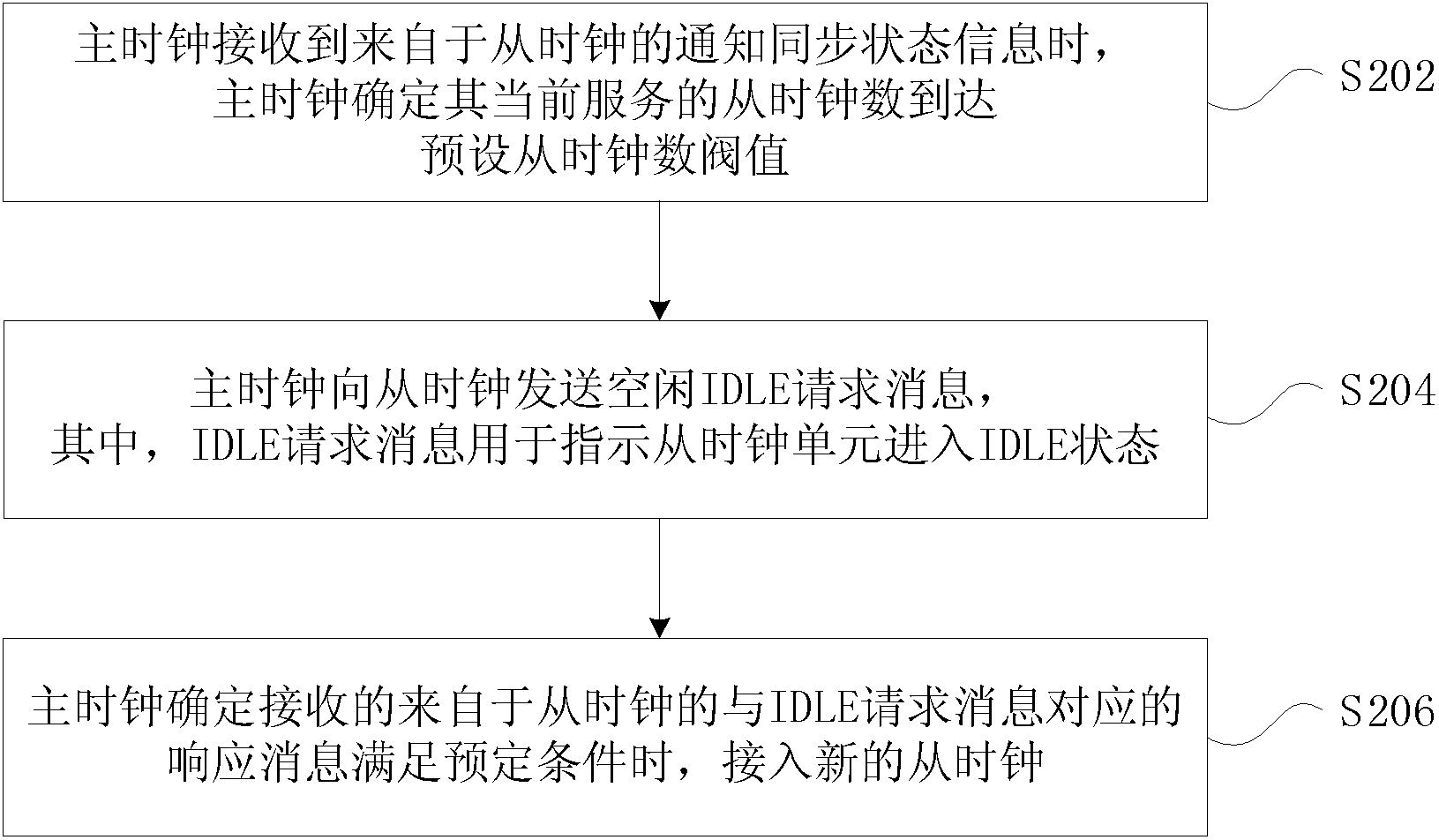
[0125] Figure 4a It is a schematic diagram of the processing flow of the master clock according to Example 4 of the present invention. Such as Figure 4a As shown, the processing flow includes:
[0126] Step S402, preset the maximum number of service slave clocks Nmax, reserve the number of access slave clocks Nres, and the synchronization holding time Lsync;
[0127] Step S404, after receiving the slave clock unicast negotiation message, check whether the number N of the current serving slave clocks is less than Nmax; if yes, go to step S406, otherwise, go to step S410;
[0128] Step S406, after receiving the slave clock unicast negotiation message, check the number N of slave clocks currently serving, if it is less than Nmax, update N=N+1;
[0129] Step S408, send Announce, Sync, FollowUp to the above slave clock, and respond to Delay-Req, that is, send Delay-resp;
[0130] Step S410, the master clock judges whether there is SyncHoldTime>Lsync in its list of slave clock...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com