Radial logarithmic spiral micro-stripe slow wave line
A logarithmic spiral and slow wave line technology, applied in the field of microwave vacuum electronic devices, can solve the problems that the DC input power of the traveling wave tube cannot be too large, the output power is limited, and the working voltage can be increased.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] Specific embodiments of the present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, so that those skilled in the art can better understand the present invention. It should be noted that in the following description, when detailed descriptions of known functions and designs may dilute the main content of the present invention, these descriptions will be omitted here.
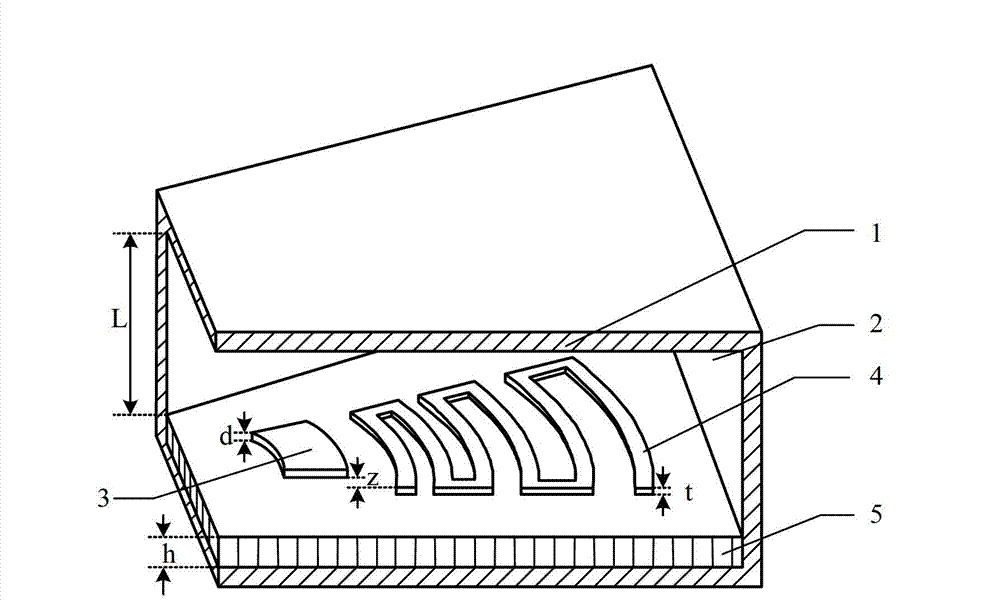
[0022] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of a specific embodiment of the radial logarithmic spiral microstrip slow wave line of the present invention.
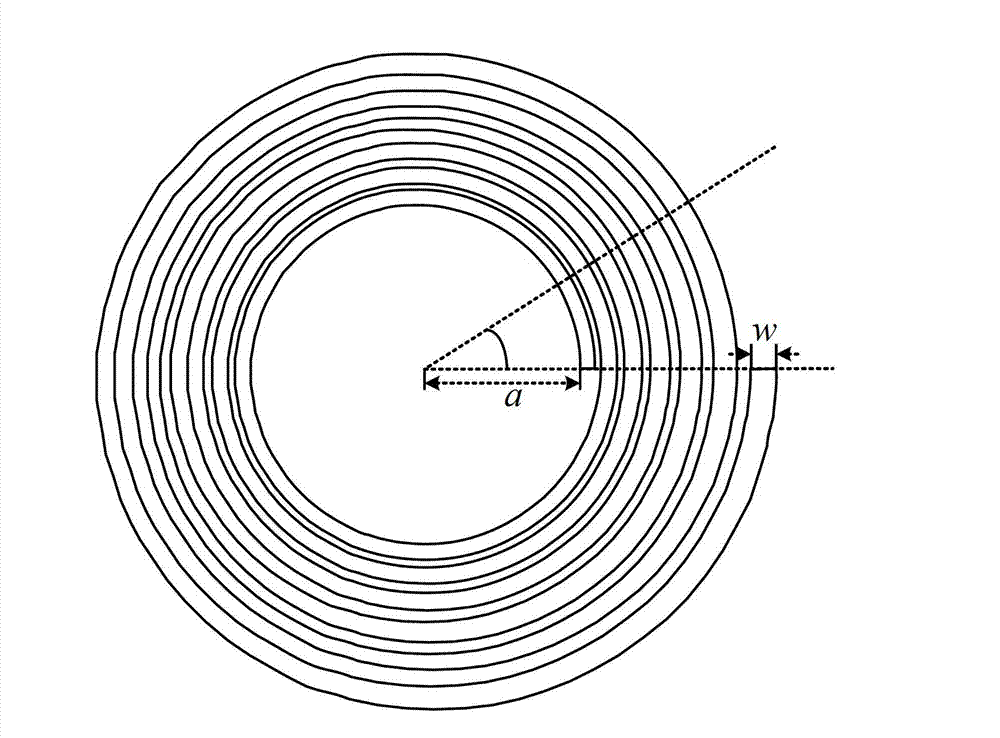
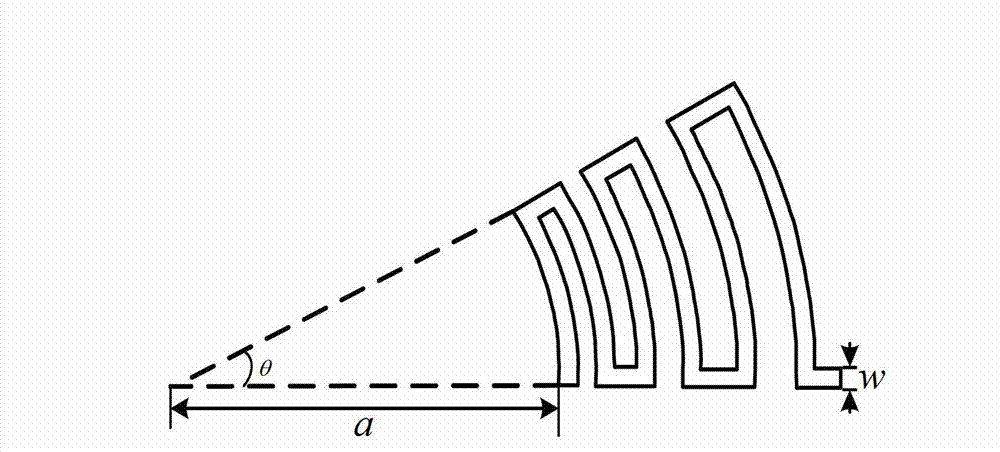
[0023] In this example, if figure 1 As shown, the radial logarithmic spiral microstrip slow wave line of the present invention is a quasi-periodic structure along the radial direction, and uses a plane fan-shaped electron beam to work. It can be regarded as composed of four parts, from top to bottom: fan-shaped vacuum chamber 2, angular radial logarithmic spiral metal belt 4, fan-shaped dielectric plate 5 and ...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap