Fixed-length time slot based dynamic channel allocation method for time division duplex/time division multiple access
A time division multiple access and time division duplex technology, applied in local area network and access network, communication fields, can solve the problems of low channel utilization, high complexity of channel allocation scheduling algorithm, large data transmission waiting time, etc. Requirements for equipment operating speed, requirements for reducing complexity, and the effect of high channel utilization efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] In this example, the network is composed of central node 0 and slave nodes 1 and 2; the physical layer is modulated by OFDM, the duration of one OFDM symbol is 18us, the length of the physical frame header is 2us, and the time slots between adjacent uplink (or downlink) time slots The interval between time slots is 2us, and the frame interval between sending and receiving transitions between the down (up) time slot and the adjacent up (down) time slot is 50 us.
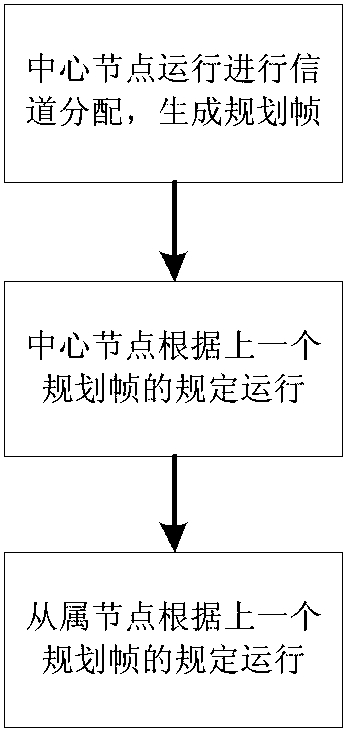
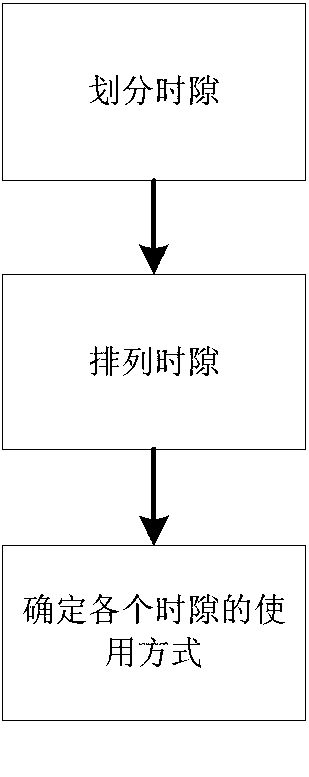
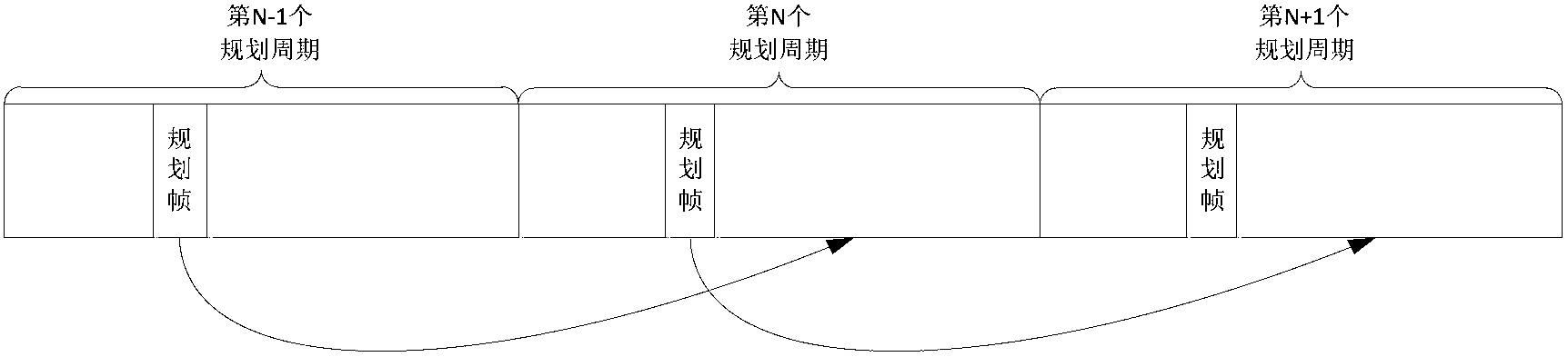
[0029] The planning frame is sent by the central node, which contains the channel allocation scheme in the next planning period and the confirmation information of the uplink data frame in the previous planning period. The planning frame is carried by a physical frame of one OFDM symbol and broadcast by the central node to all slave nodes .
[0030] The report frame is sent by the slave node, which contains the local queue information of the slave node and the confirmation information of the downlink data frame...
Embodiment 2
[0123] Embodiment 2 In this example, the network is composed of central node 0 and slave nodes 1 and 2; the physical layer is modulated by OFDM, the duration of one OFDM symbol is 18us, the length of the physical frame header is 2us, and the adjacent uplink (or downlink) each The time slot interval between the slots is 2us, and the frame interval between sending and receiving conversion between the down (up) line time slot and the adjacent up (down) line time slot is 50 us.
[0124] The planning frame is sent by the central node, which contains the channel allocation scheme in the next planning period and the confirmation information of the uplink data frame in the previous planning period. The planning frame is carried by a physical frame of one OFDM symbol and broadcast by the central node to all slave nodes .
[0125] The report frame is sent by the slave node, which contains the local queue information of the slave node and the confirmation information of the downlink data...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com