Single-stage bidirectional buck-boost inverter
A buck-boost and inverter technology, which is applied in the direction of converting AC power input to DC power output, output power conversion devices, electrical components, etc. , to simplify the structure and achieve the effect of two-way transmission of energy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
[0044] Specific embodiment 1: a single-stage single-phase bidirectional buck-boost inverter (1).
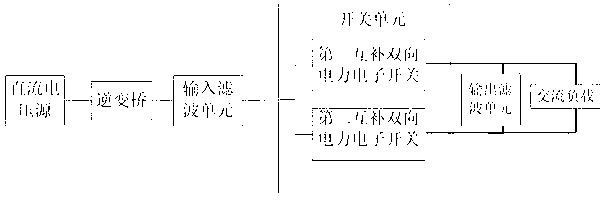
[0045] Such as figure 2 The shown single-stage single-phase bidirectional buck-boost inverter includes a single-phase inverter bridge, a filter inductor L, a switch unit, and a filter capacitor C.
[0046] The single-phase inverter bridge includes two bridge arms, the first bridge arm includes the fifth and sixth switching tubes Q 5 , Q 6 , the second bridge arm includes the seventh and eighth switching tubes Q 7 , Q 8 . Fifth switching tube Q 5 Cathode and sixth switching tube Q 6 The anode connection of the seventh switching tube Q 7 The cathode and the eighth switch tube Q 8 Anode connection, the fifth switching tube Q 5 Anode and the seventh switching tube Q 7 The connection point of the anode is the positive terminal of the single-phase inverter bridge, and the sixth switching tube Q 6 The cathode and the eighth switch tube Q 8The connection point of the cathode...
specific Embodiment 2
[0053] Specific embodiment 2, a single-stage single-phase bidirectional buck-boost inverter (2).
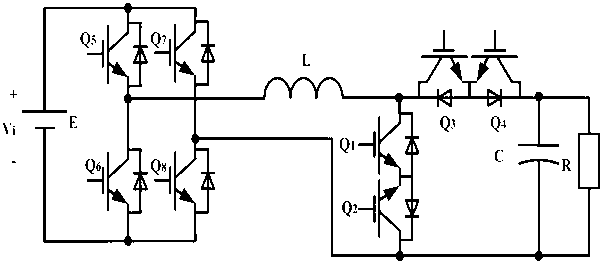
[0054] Such as Figure 5 The shown single-stage single-phase bidirectional buck-boost inverter includes a single-phase inverter bridge, a filter inductor L, a switch unit, and a filter capacitor C.
[0055] The single-phase inverter bridge is the same as the specific embodiment 1, consisting of fifth, sixth, seventh, and eighth switching tubes Q5, Q6, Q7, and Q8.
[0056] The switch unit includes a first complementary bidirectional power electronic switch and a second complementary bidirectional power electronic switch. The first complementary bidirectional power electronic switch includes a first switching tube Q1 and a second switching tube Q2. The second complementary bidirectional power electronic switch includes a third switch Tube Q3, fourth switching tube Q4;
[0057] One end of the filter inductance L is connected to the midpoint of a bridge arm of the single-phase inve...
specific Embodiment 3
[0060] Specific embodiment 3, a single-stage three-phase bidirectional buck-boost inverter.
[0061] Such as Image 6 The shown single-stage three-phase bidirectional buck-boost inverter includes: three-phase inverter bridge, A-phase filter inductor L a , B-phase filter inductance L b , C-phase filter inductor L c , the first complementary three-phase bidirectional power electronic switch, the second complementary three-phase bidirectional power electronic switch, A-phase filter capacitor C a , B-phase filter capacitor C b , C-phase filter capacitor C c .
[0062] The three-phase inverter bridge includes three bridge arms. The first bridge arm includes the seventh and eighth switching tubes Q7 and Q8, the second bridge arm includes the ninth and tenth switching tubes Q9 and Q10, and the third bridge arm includes the tenth switching tubes. 1. The twelfth switch tubes Q11 and Q12. The cathode of the seventh switching tube Q7 is connected to the anode of the eighth switch...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com