Actuator, robot hand, robot, electronic component carrying device, and printer
A technology of actuators and piezoelectric elements, applied in the direction of robots, piezoelectric devices/electrostrictive devices, manipulators, etc., can solve the problems of loss of driving energy of the driving body, vibration leakage, driving energy loss of the driven body, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach )
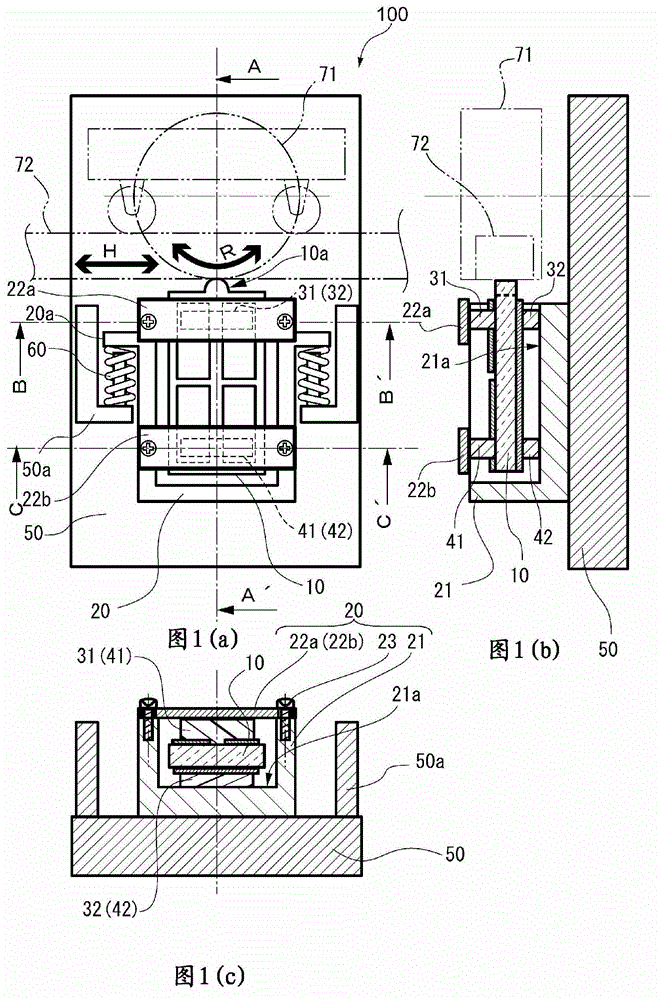
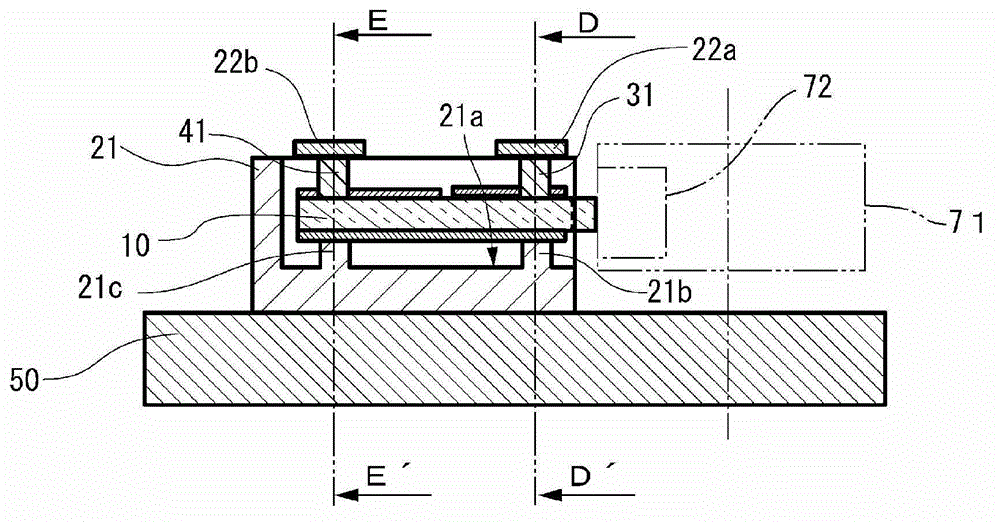
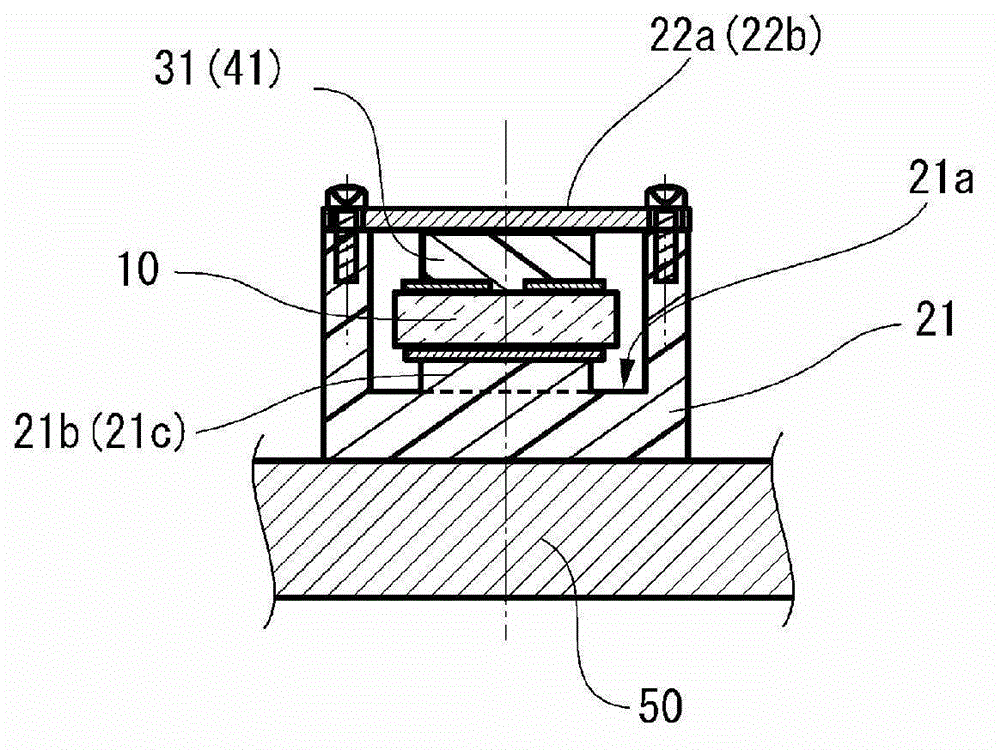
[0054] Fig. 1 shows the actuator of the first embodiment, Fig. 1(a) is a plan view, Fig. 1(b) is a cross-sectional view of the A-A' part shown in Fig. 1(a), Fig. 1(c) is Fig. 1(a) ) Sectional views of B-B' and C-C' parts. As shown in FIG. 1( a ), the actuator 100 includes a holding case 20 as a holding member, a piezoelectric element 10 held by the holding case 20 , and a spring serving as a biasing mechanism for the holding case 20 The base 50 and the driven body 71 or the driven body 72 of the spring fixing part 50a installed at 60.
[0055] The driven body 71 is driven to rotate in the illustrated R direction, and the driven body 72 is linearly driven in the illustrated H direction. In the actuator 100 according to the present embodiment, linear driving of the driven body 72 in the illustrated H direction is described, but the driven body 71 which is rotationally driven may also be described. The biasing portion 20 a of the holding case 20 is biased by the spring 60 relat...
no. 2 approach )
[0080] FIG. 9 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a portion B-B' and a portion C-C' indicated in FIG. 1( a ) of the support portion of the actuator according to the second embodiment. In addition, the actuator according to the second embodiment is different from the actuator 100 according to the first embodiment in that the supporting parts 31, 32, 41, 42 include elastic members, and the other structures are the same. Therefore, the same structures as those of the actuator 100 according to the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals and description thereof will be omitted.
[0081] The actuator 300 shown in FIG. 9( a ) includes: a disc spring 91 serving as an elastic member in the first support portion 31 and the second support portion 41 , and a buffer member 81 . The disc spring 91 sandwiches the piezoelectric element 10 between the third support portion 32 and the fourth support portion 42 and the buffer member 81 and is disposed between the pressing ...
no. 3 approach )
[0087] Figure 10 It is an external view showing a robot hand 1000 including the actuator 100 or 300 according to the first embodiment. Figure 10 The actuator 100 included in the shown robot hand 1000 is the actuator 100 according to the first embodiment, and is in the form of a driven body 71 (see FIG. 1000 rotation drive motors for the joints are used. The robot hand 1000 includes fingers 1200 connected to a base 1100 . The actuator 100 as a rotation drive motor is provided at the connection part 1300 of the base part 1100 and the finger part 1200 and the joint part 1400 of the finger part 1200 . In addition, a control unit 1500 is provided on the robot hand 1000, and the actuator 100 is driven by the control unit 1500, so that the connection unit 1300 and the joint unit 1400 can be rotated, and the fingers 1200 can be deformed as desired like a human finger. status.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com