Oxide superconductivity wire material and method of manufacturing thereof
A superconducting wire, oxide technology, applied in cable/conductor manufacturing, chemical instruments and methods, copper compounds, etc., can solve the problems of inability to obtain superconducting properties, Ic reduction, etc., to ensure superconducting properties, high superconductivity Effects of Features
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0098] In the same manufacturing method as in Example 1, Sn was used instead of the added element (added metal) Zr, and a superconducting raw material solution in which 1 wt% of Sn was added to the superconducting raw material solution was used, and the same method as in Example 1 was used. A superconducting wire in which oxide particles containing Sn were formed as magnetic flux pinning in a superconducting layer was produced.
[0099] Figure 7 A is a TEM image of a vertical section of the superconducting layer of Example 2, Figure 7 B is the element map image of the same section. also, Figure 7 also with Figure 6 same in Figure 7 Shown in A as a flux pinning point 145 in the superconducting layer, Figure 7 In B, the magnetic flux pinning point appears in the light and medium part. such as these Figure 7 A. Figure 7 As shown in B, BaSnO, which is an oxide particle containing Sn, is uniformly dispersed and formed in the superconducting layer as the magnetic flu...
Embodiment 3
[0101] In the same manufacturing method as in Example 1, Nb was used instead of the added element (added metal) Zr, and a superconducting raw material solution in which 1 wt% of Nb was added to the superconducting raw material solution was used. A superconducting wire in which oxide particles containing Nb were formed as magnetic flux pinning points in the superconducting layer was produced.
[0102] Figure 8 A is a TEM image of a vertical section of the superconducting layer of Example 3, Figure 8 B is the element map image of the same section. also, Figure 8 also with Figure 6 same in Figure 8 Shown in A as a flux pinning point 145 in the superconducting layer, Figure 8 In B, the magnetic flux pinning point appears in the light and medium part. Such as Figure 8 A. Figure 8 As shown in B, oxide particles containing Nb, that is, YNbBa, are uniformly dispersed and formed in the superconducting layer as magnetic flux pinning points. 2 o 6 , BaNb 2 o 6 . In a...
Embodiment 4
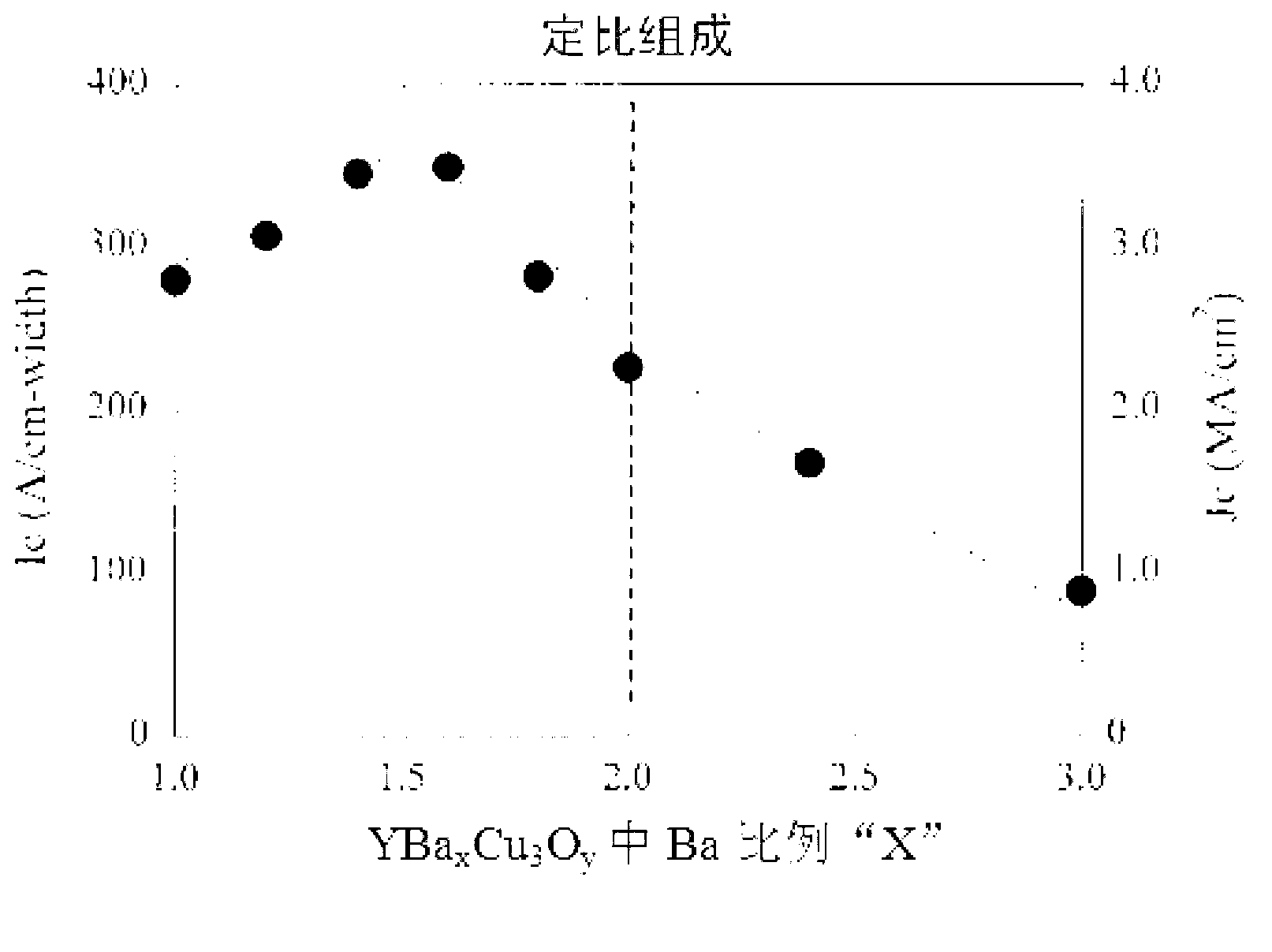
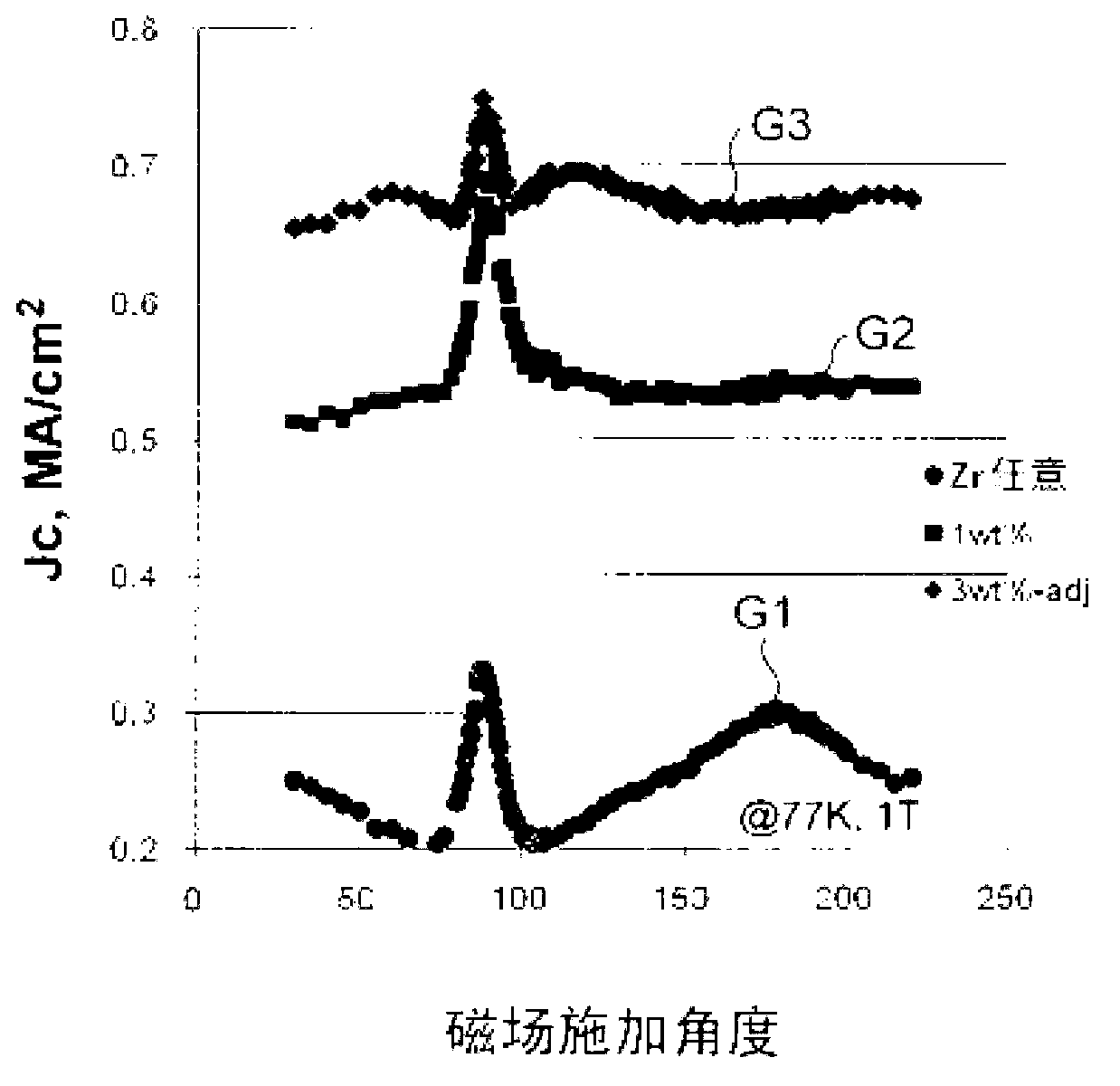
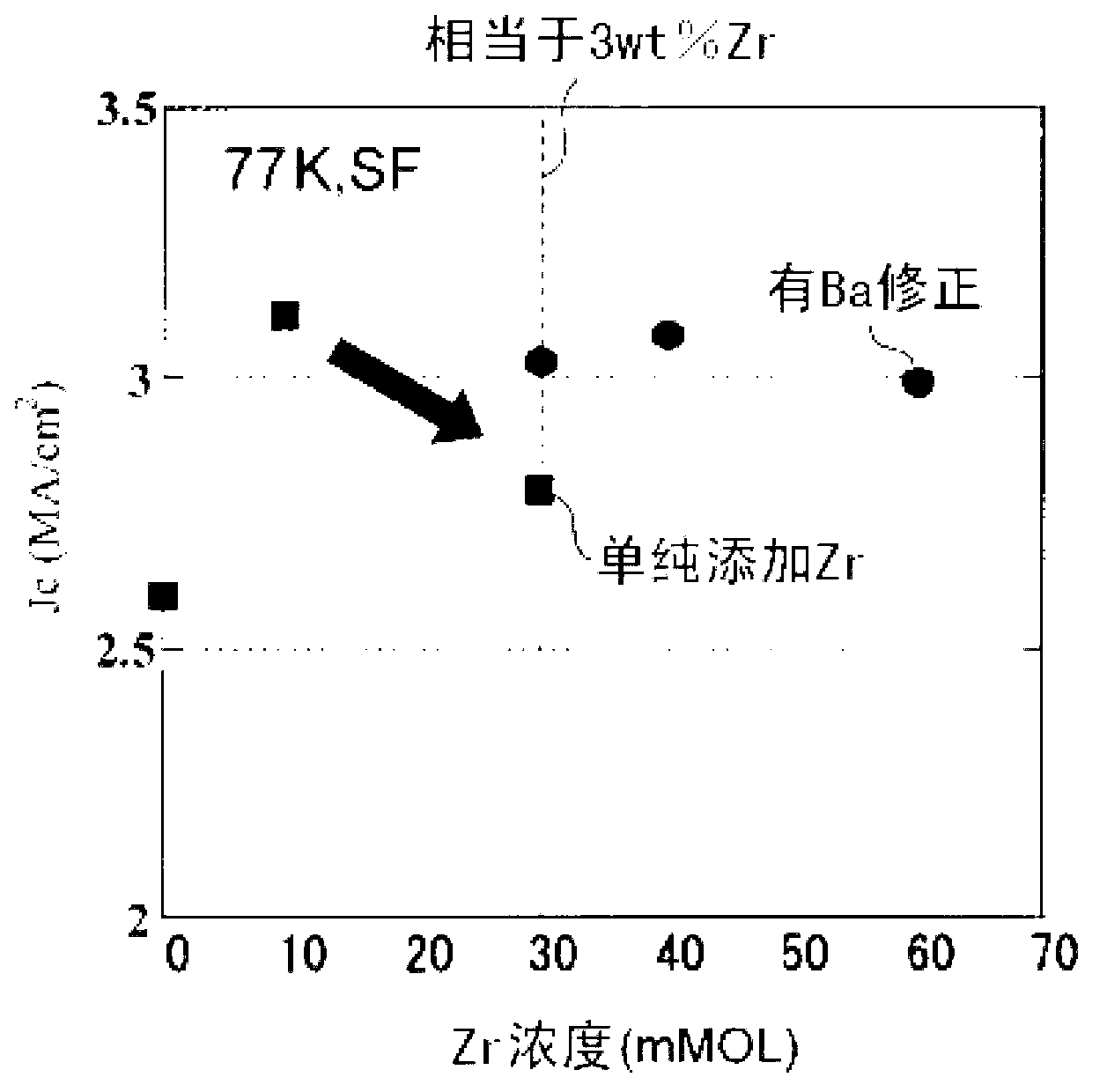
[0104] In the same manufacturing method as in Example 1, a Zr-containing naphthenate with Zr as an additional element (addition metal) was used to add 3% (3wt%) in terms of metal weight ratio, and additional The amount of Ba in the Zr reaction, and thus, the superconducting raw material solution prepared in such a manner that the molar ratio of Y:Gd:Ba:Cu is maintained at 0.77:0.23:1.5:3 is prepared to have A superconducting wire including a superconducting layer of oxide particles of Zr. That is, the superconducting wire of Example 4 has oxide particles BaZrO containing Zr uniformly dispersed as magnetic flux pinning points. 3 the superconducting layer. In the superconducting wire of Example 4, Jc was 3.0 [MA / cm 2 ] (@77K, from the magnetic field), Jc, min is 0.66 [MA / cm 2 ] (@77K, 1T).
[0105]
[0106] In this comparative example, a superconducting wire was produced by the same production method as in Example 1 without adding an additive element (additional metal) Zr....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com