Apparatus for extracorporeal blood treatment
A technology of extracorporeal blood treatment and measuring devices, which is applied in the direction of pharmaceutical devices, other medical devices, suction devices, etc., and can solve problems such as the inability to distinguish uremic toxins and the inability to test the dialysis effect of dialysate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
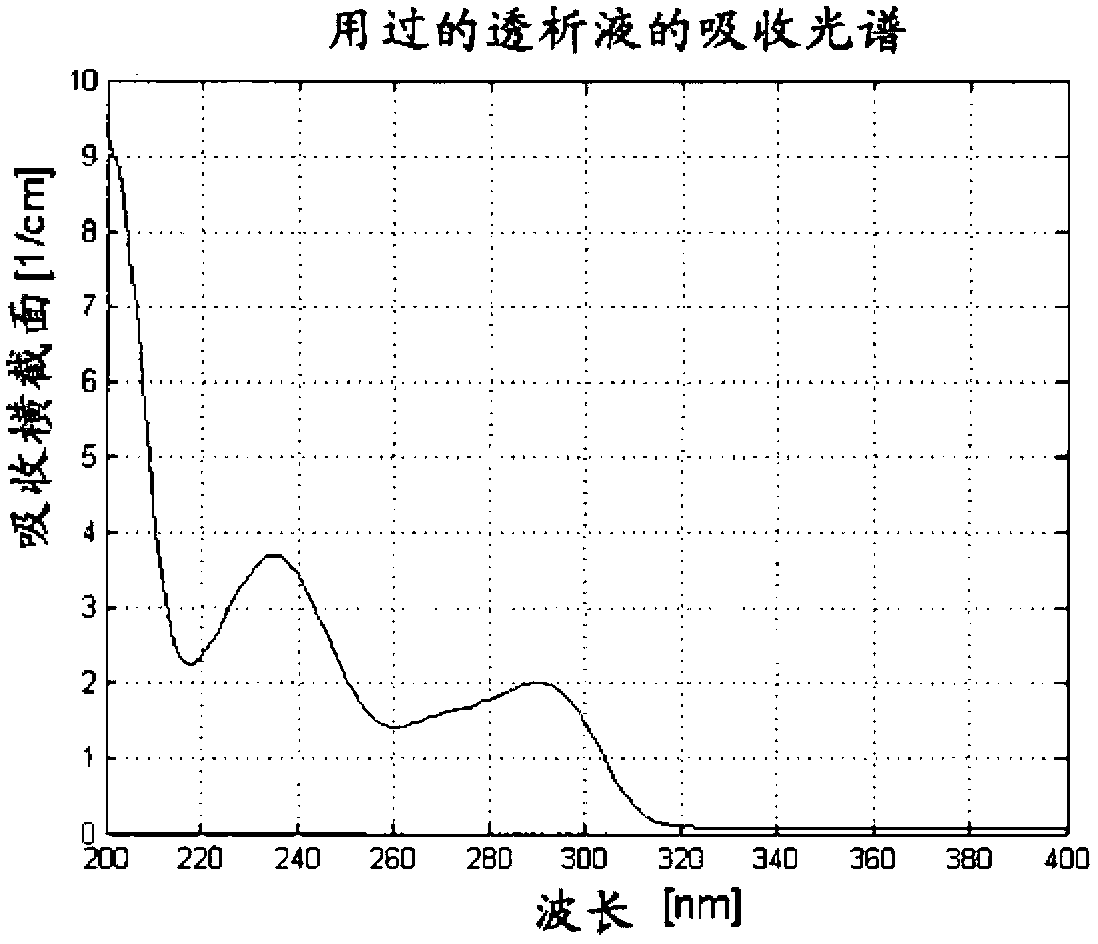
[0148] Dialysate samples from dialysis patients were drawn 10 minutes after treatment initiation and measured spectrophotometrically Absorbance in the wavelength range. In the present case, the absorbance is negligible for wavelengths greater than λ = 340 nm. In the range of λ=340 nm to λ=290 nm, the absorbance first rises sharply, then remains stable up to about λ=260 nm, and then rises sharply again. A local maximum is visible at λ=230nm. When the wavelength is less than λ=220nm, a further increase in absorbance can be observed. The dialysate spectra of different patients are generally distinguished from one another by their intensity and absorbance curves in the range between λ=290 nm to λ=255 nm. In the shown figures the curve in this range remains essentially constant, however local minima (e.g. A λ=260nm =0.5) or a strictly monotonically increasing function (such as A λ=260nm =1.5). figure 1 The spectrum of a dialysate sample of dialysate effluent from a dialysis ...
example 2
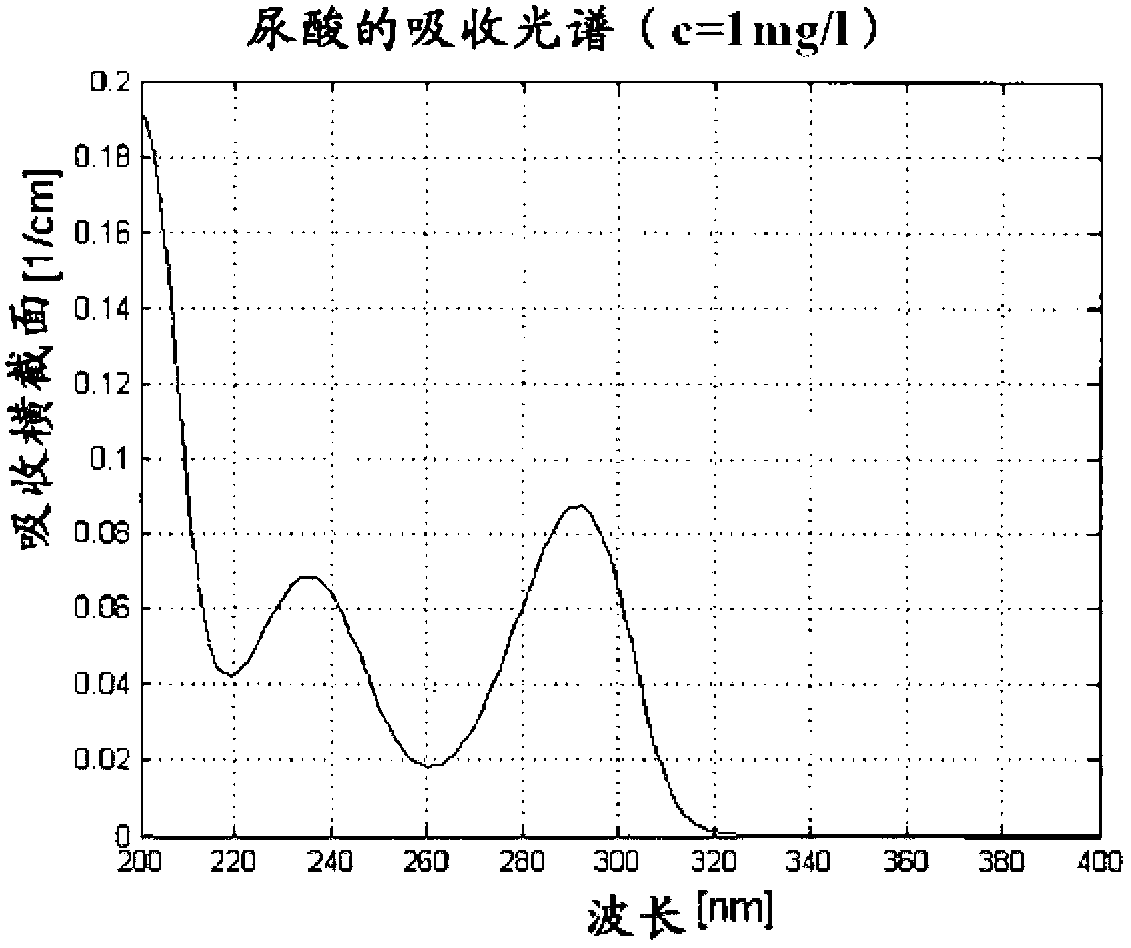
[0150] The absorption properties of uric acid at a concentration c=1 mg / l were determined spectrophotometrically in water for a wavelength range of 200 to 400 nm. figure 2 Qualitatively illustrate the absorption characteristics of uric acid in the range of λ=400nm to λ=200nm. Three local maxima at λ=290nm, λ=235nm and λ=205nm are clearly visible, among which the maximum absorbance (A λ=205nm =1.5 or A λ=290nm =0.7).
example 3
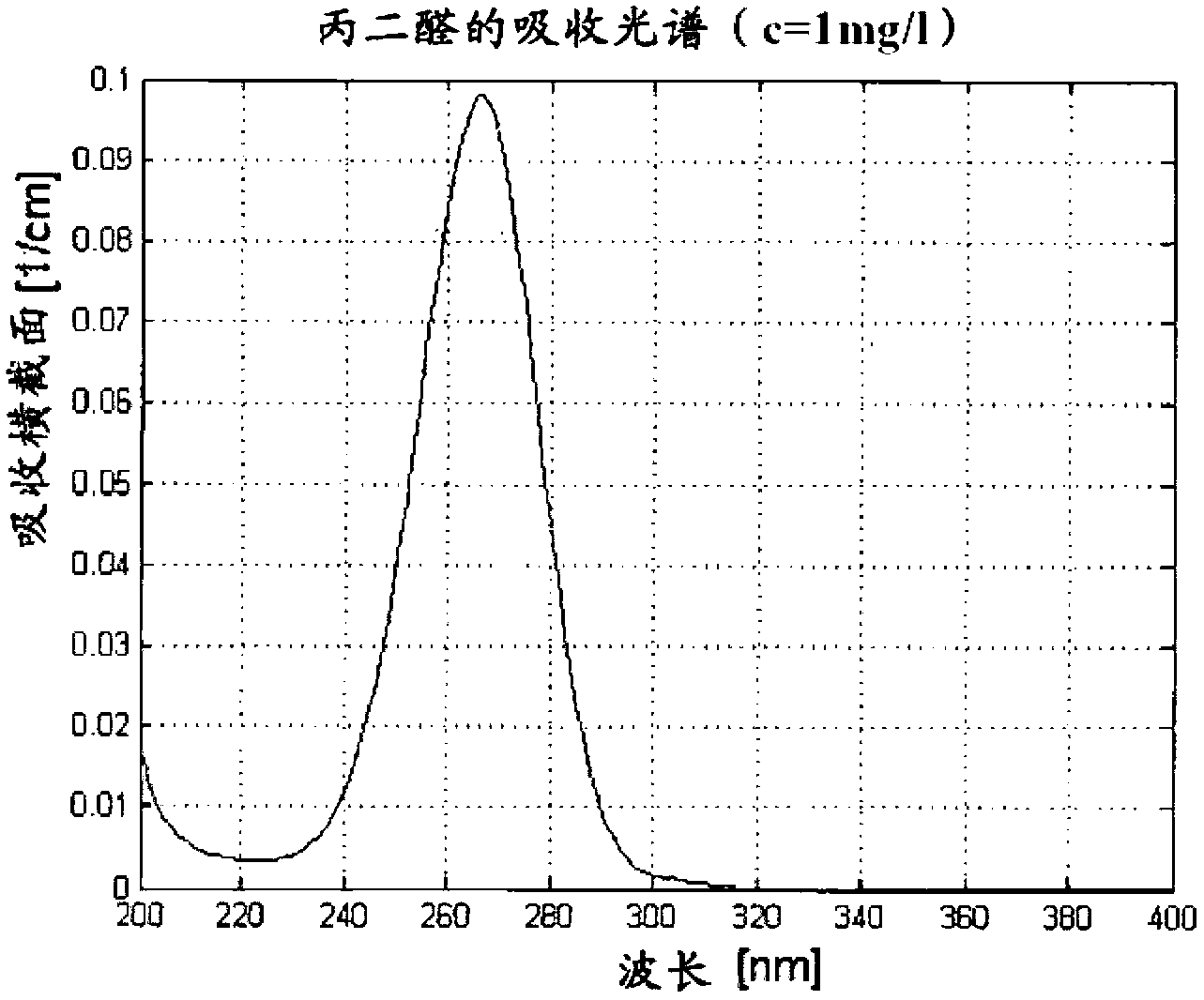
[0152] The absorption properties of malondialdehyde at a concentration c=1 mg / l were determined spectrophotometrically in water for a wavelength range from 200 to 400 nm. image 3 Qualitatively illustrate the absorption characteristics of malondialdehyde in the range of λ=400nm to λ=200nm. The local maximum at λ=266nm is clearly visible (A λ=266nm =1.005).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com