Solar cell module and method for manufacturing same
A solar cell and manufacturing method technology, which is applied to circuits, electrical components, photovoltaic power generation, etc., can solve the problems of thermal expansion difference, warpage and damage of solar cell components, and increase in manufacturing cost, and achieves the effect of small warpage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
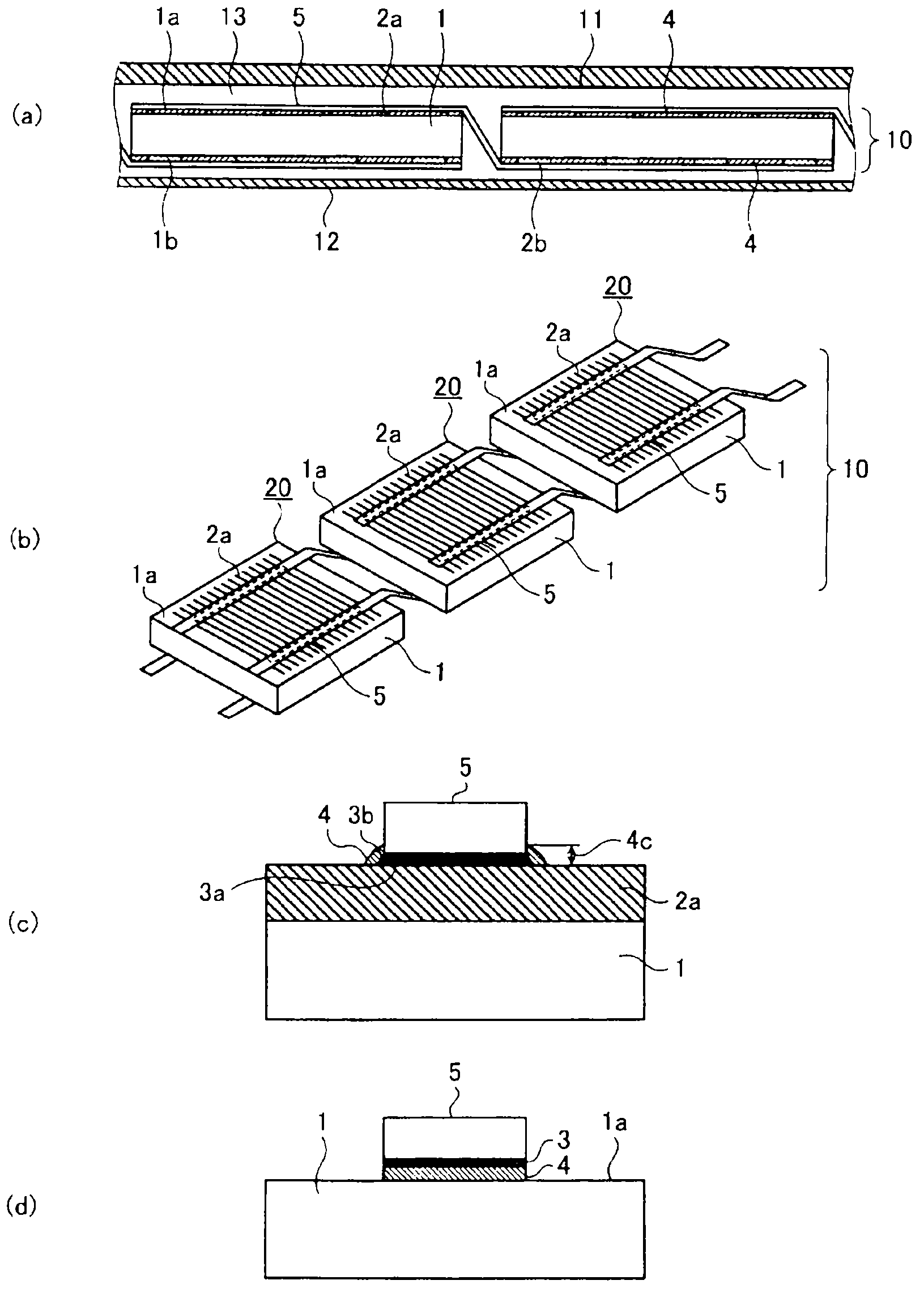
[0027] figure 1 is a diagram showing the structure of a solar cell module according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, figure 1 (a) is a cross-sectional view of the solar cell module, figure 1 (b) is a perspective view of a series group in which a plurality of solar cell elements 1 are connected by a wiring member 5 , figure 1 (c) is a cross-sectional view of the joint portion of the thin wire electrode (first collector electrode) 2 a and the wiring member 5 , figure 1 (d) is a cross-sectional view showing a junction between the light receiving surface 1 a and the wiring member 5 .
[0028] according to figure 1 (a), the solar battery module 100 is provided with a light-receiving surface protection member 11 on the light-receiving surface 1 a side of the solar battery series group 10 , and a rear surface protection member 12 is arranged on the back surface 1 b side, and between the solar battery series group 10 and the protection members 11 and 12 The sealing member...
Embodiment approach 2
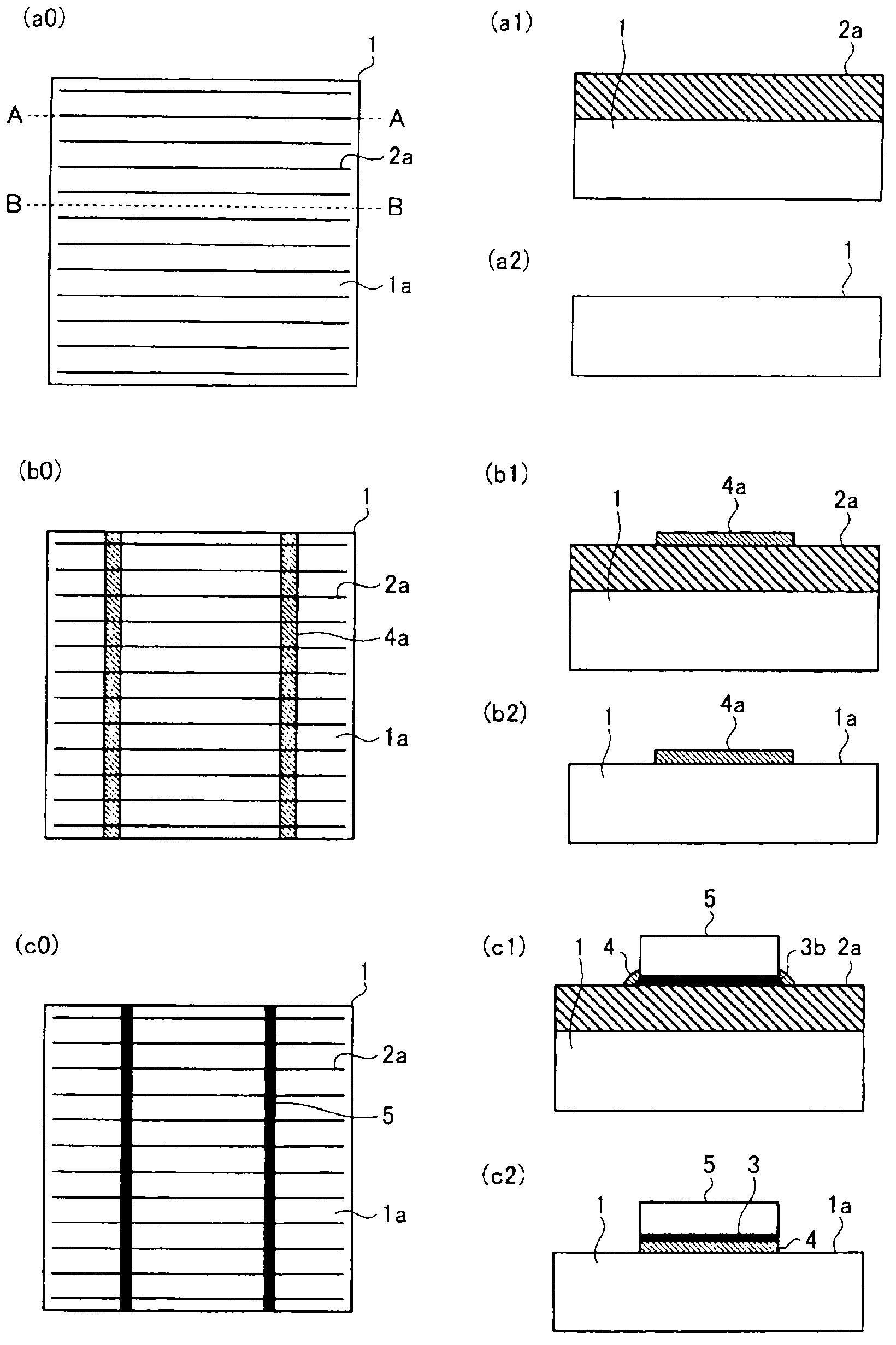
[0039] figure 2 It is a figure which shows the solar cell module of Embodiment 2 of this invention, and is for demonstrating the method of bonding the solar cell element 1 and the wiring member 5 in order. figure 2 ( a0 ) is a plan view of the light receiving surface 1 a of the solar cell element 1 . A plurality of thin wire electrodes 2a are formed in parallel on the light receiving surface 1a. figure 2 (a1) is figure 2 The cross-sectional view along line AA of ( a0 ) shows a cross-section of the thin wire electrode 2 a in a direction intersecting the wiring member 5 . figure 2 (a2) is figure 2 The cross-sectional view along line BB of ( a0 ) shows the cross-section of the region other than the thin wire electrode 2 a.
[0040] figure 2 (b0) is a plan view of the light-receiving surface 1a in a state where the thermosetting epoxy resin composition 4a before curing is arranged, and the above-mentioned thermosetting epoxy resin composition 4a contains an organic aci...
Embodiment approach 3
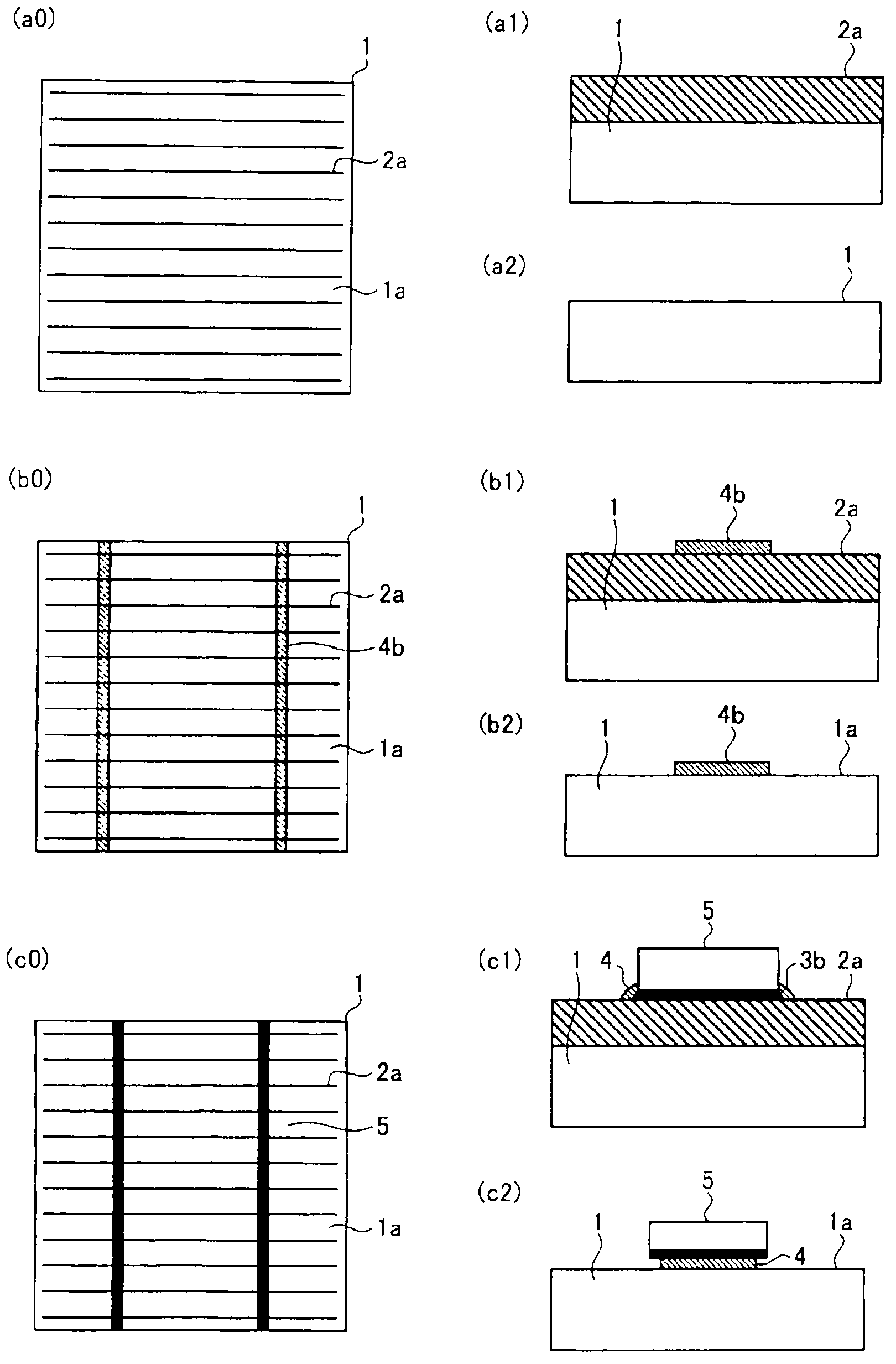
[0048] image 3 It is a figure which shows the solar cell module of Embodiment 3 of this invention, and is used for demonstrating the bonding method of the solar cell element 1 and the wiring member 5. image 3 (a0) is a figure for demonstrating the method of joining the wiring member 5 of the solar cell element 1. image 3 (a1) is image 3 (a0) A cross-sectional view corresponding to the line A-A. image 3 (a2) is image 3 (a0) Cross-sectional view corresponding to line BB. A plurality of thin wire electrodes 2a are formed in parallel on the light receiving surface 1a of the solar cell element 1 .
[0049] image 3 (b0) is a diagram showing the state where the thermosetting epoxy resin composition 4b before curing is arranged. The thermosetting epoxy resin composition 4b is narrower than the width of the wiring member 5 and contains an organic acid or Organic acids are used in hardeners. image 3 (b1) is image 3 (b0) A cross-sectional view corresponding to the line A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com