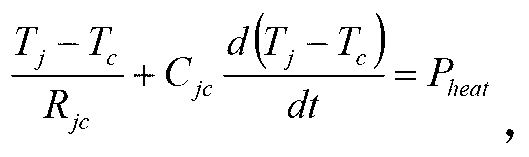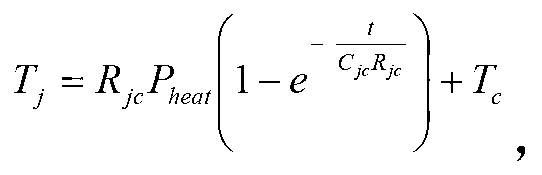Novel method for extracting heat capacity and thermal time constant of light-emitting diode (LED) system
A thermal time constant and LED system technology, applied in the field of LED lighting, can solve the problem that the thermal resistance, thermal capacity and thermal time constant cannot be given at one time, and the overall thermal resistance and overall thermal capacity of the device cannot be obtained at one time. The process of differential structure function method is complicated, etc., to achieve the effect of simple operation, simplified extraction process, and accurate parameter results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] The following takes the extraction of the thermal time constant and heat capacity of Philip-Luxeon LED, and the LED model is LXHL-PW01 as an example to illustrate this method and its extraction results.
[0055] The power supply of this LED is 1 watt, and the initial temperature of the bottom shell is T c is 30°C. When the LED junction temperature rises to the steady-state temperature, the power supply is removed, and the LED junction temperature begins to drop naturally. From the measured curve, the maximum steady-state temperature T can be read jss at 41°C.
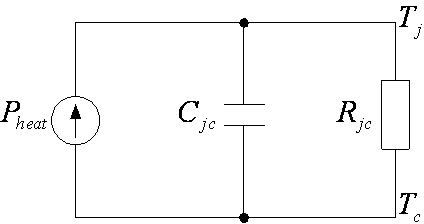
[0056] Thus, the thermal resistance of this LED is: where P heat =k h *P d , k h is the heat dissipation coefficient of the device, for this device, the heat dissipation coefficient k h =0.87,P d Power supply for LED.
[0057] Going back to the measured LED junction temperature rise and natural fall curves, according to the method of extracting the thermal time constant provided by this patent, read th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com