A Microchannel Minimum Thermal Resistance Structure Optimization Method Based on Inlet Development Characteristics
A development characteristic, micro-channel technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems that do not conform to the actual situation, micro-scale heat exchanger design troubles, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Influence of embodiment 1 inlet effect on fluid flow
[0055] Because microchannel heat exchangers are limited in size, shorter channels need to be studied in order to meet actual needs, and the channel length has an important impact on the state of fluid flow.
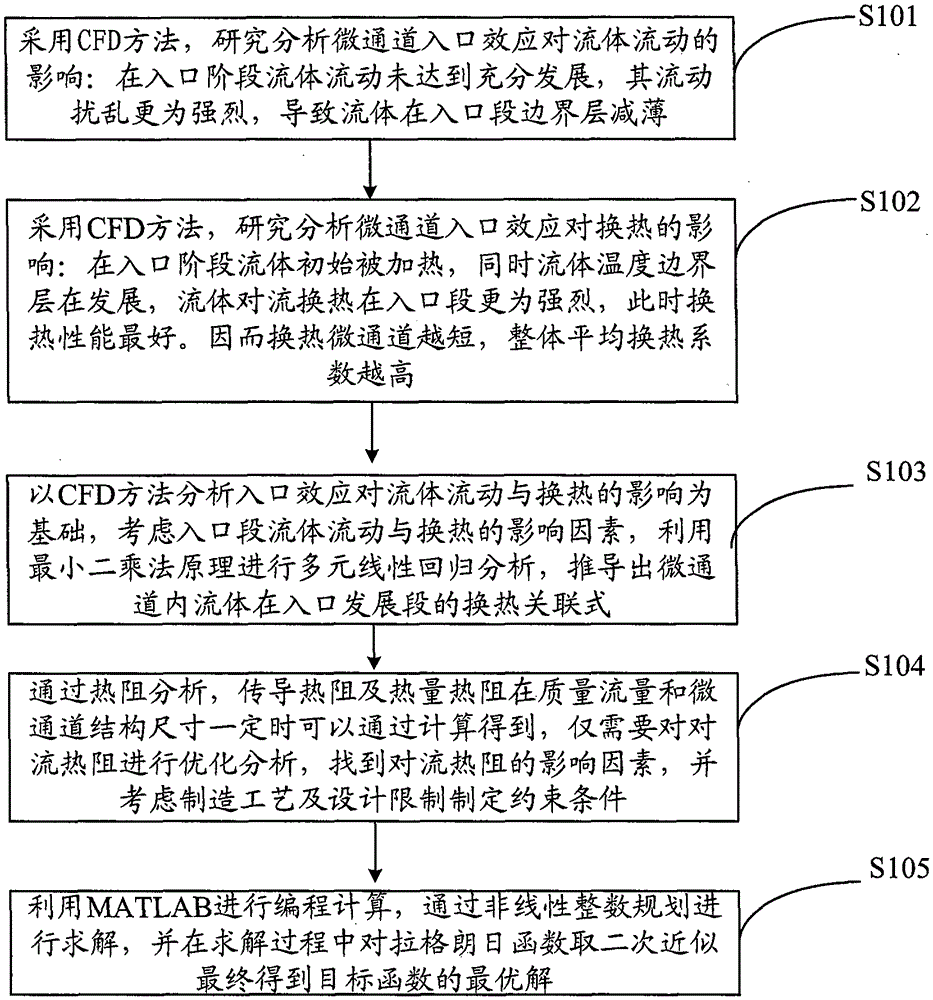
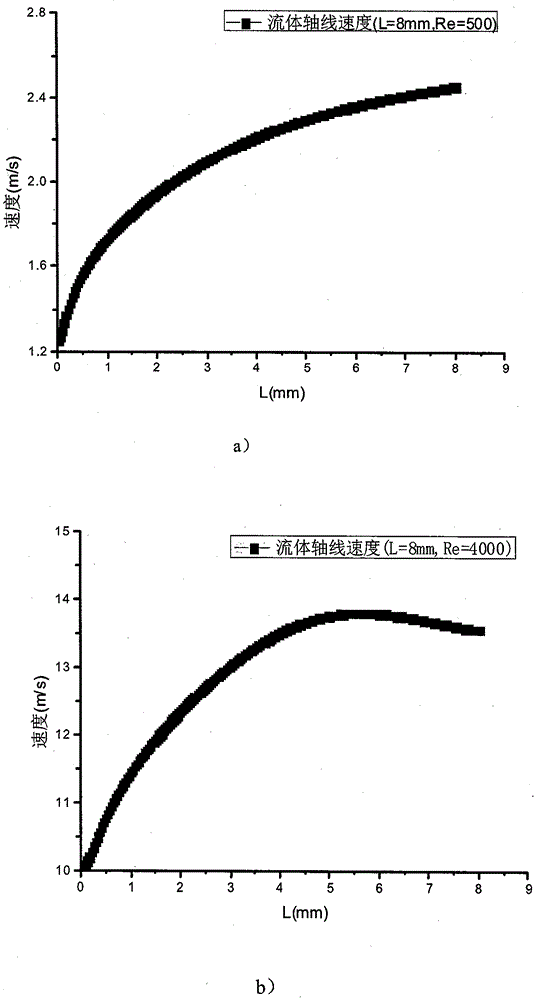
[0056] The velocity distribution of the central axis of the fluid (X=0~40mm, Y=0.4mm, Z=0mm) is analyzed for the rectangular channel with length L=8mm, Reynolds number Re=500, and aspect ratio α=1, such as figure 2 (a) shown. It can be seen that the velocity of the central axis of the fluid increases continuously with the flow direction, indicating that the channel flow has not been fully developed. The fluid flow range is in the inlet development section, and the degree of fluid flow is more disturbed, resulting in different flow characteristics from the scale of the fully developed section. Since the velocity boundary layer is thinner and the velocity gradient is larger in the flow inlet section, the fricti...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Embodiment 2 The influence of entrance effect on heat transfer
[0062] The heat transfer characteristics of rectangular channels with an equivalent diameter of 0.4mm, an aspect ratio of 1, and lengths of L=8mm, 20mm, and 40mm were studied, and the following results were obtained: Image 6 The results shown. It can be seen that Nu decreases with the increase of the length. Under the same Reynolds number, the heat transfer performance of the fluid in the microchannel when L=8mm is about twice that of L=40mm, indicating that the shorter the length of the microchannel, the better the heat transfer performance. The higher the performance. This is because the fluid is heated from the inlet of the pipe, and the temperature boundary layer in the pipe is developing at the same time. Nu is the largest at the inlet, and then decreases greatly in the short flow length, and then slows down with the flow direction decrease, such as Figure 7 shown. This shows that the convective...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Heat transfer correlation formula under the inlet effect of embodiment 3
[0065] For microchannel heat exchangers with length L=8mm, 10mm, 15mm, equivalent diameter of 0.4mm, and different aspect ratios (α=1, 2, 4, 5), the fluids in the channels are all in the inlet development stage, respectively The heat transfer coefficient Nu is calculated under the conditions of laminar flow (Re<2000) and turbulent flow (2000≤Re≤6000), and the correlation formula for the heat transfer coefficient Nu of the fluid in the inlet development section of the microchannel is obtained by fitting, which is relatively With a 15% error:
[0066] Nu=1.183Re 0.350 alpha 0.242 (L / D h ) -0.216 PR 1 / 3 (Re<2000);(1)
[0067] Nu=10.664Re 0.269 alpha -0.074 (L / D h ) -0.402 PR 1 / 3 (2000≤Re≤6000)(2)
[0068] From Equation 1 and Equation 2, it can be seen that when the fluid in the microchannel is in the development stage of the laminar flow inlet, Nu increases with the increase of the aspec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com