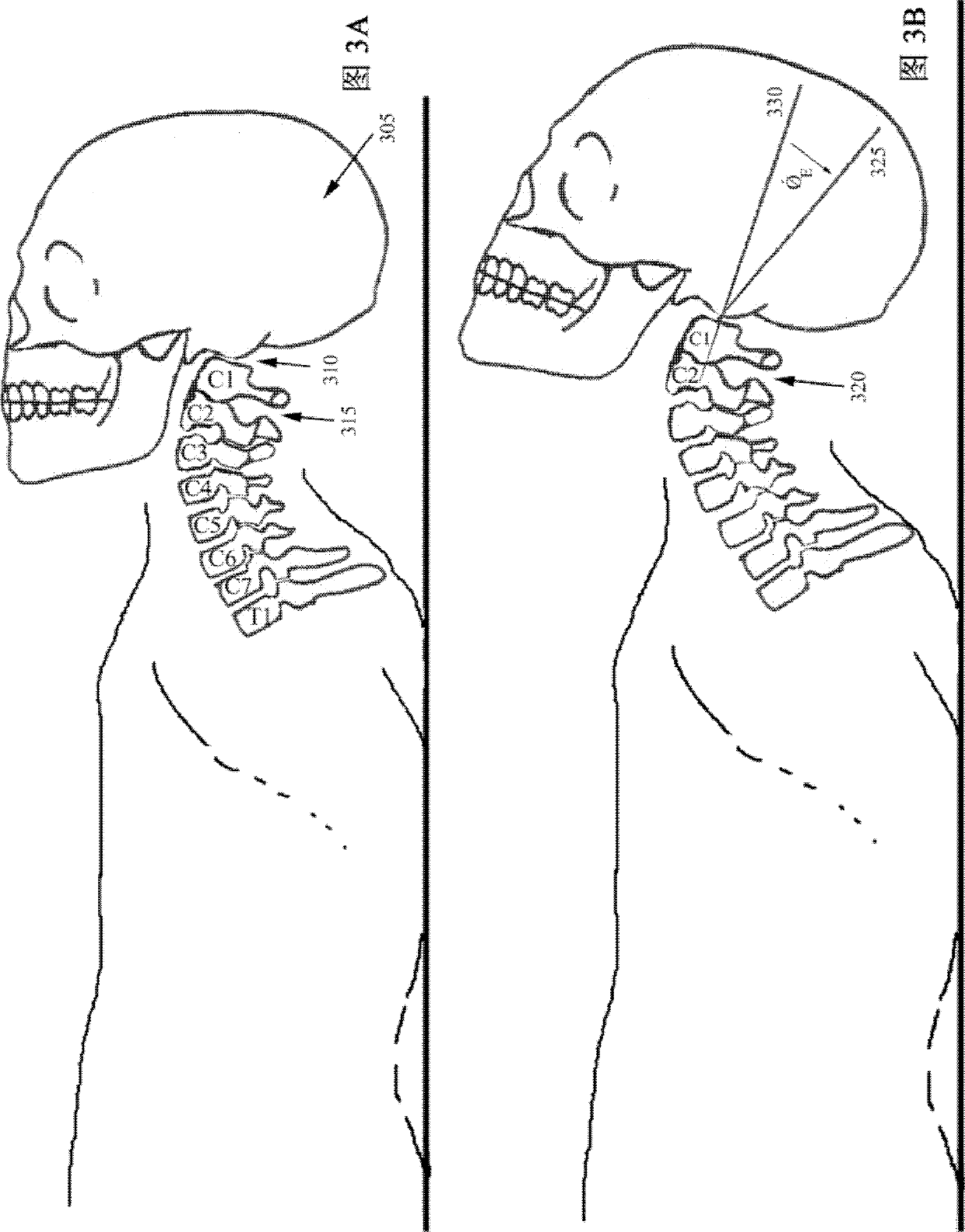
Patient interface equipment and method for aligning adjacent cervical vertebras by aid of same
A patient interface, patient technology, applied in fractures, non-surgical orthopedic operations, passive exercise equipment, etc., can solve problems such as discomfort, numbness, and deterioration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
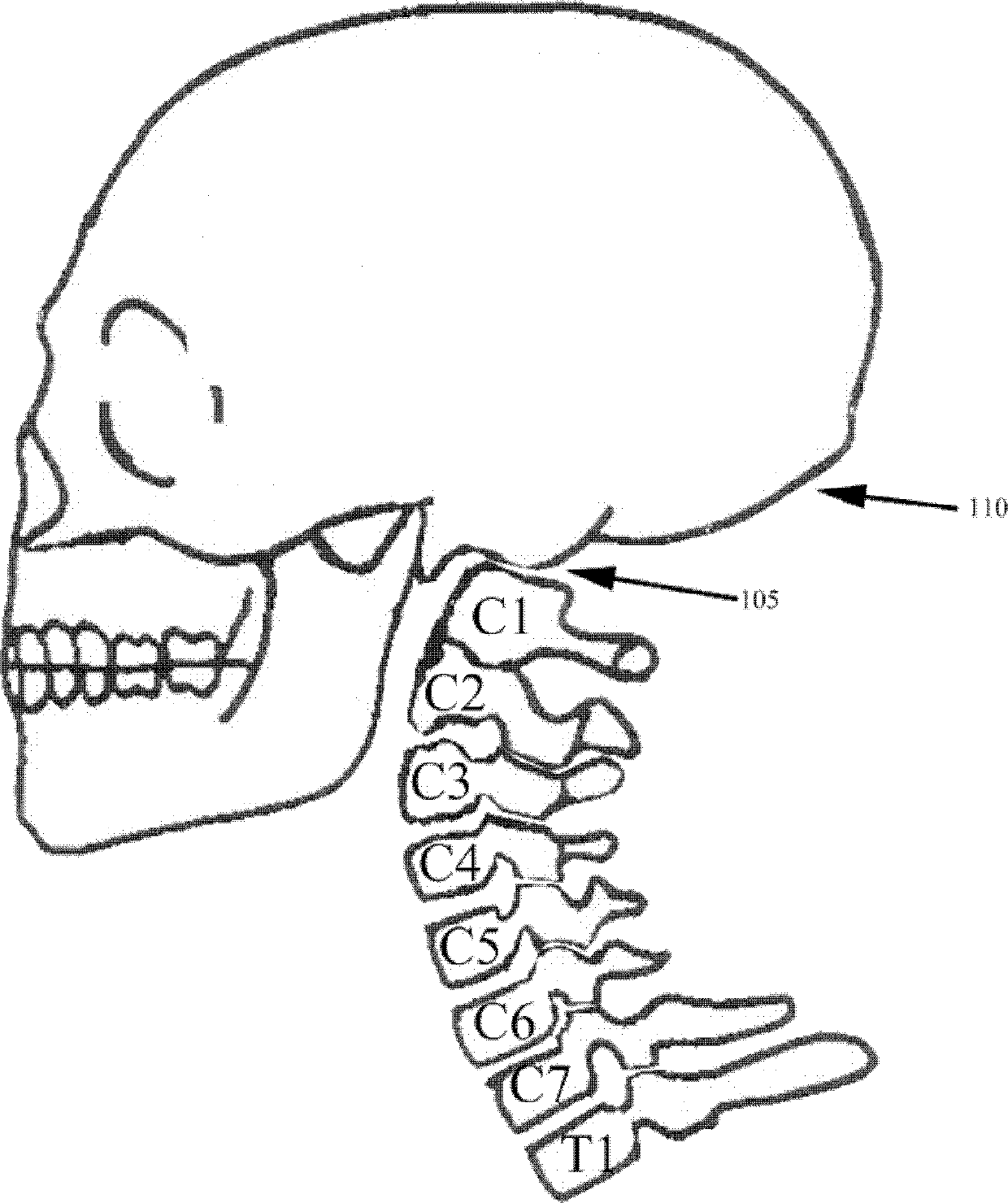
[0059] figure 1 A side view of the patient's skull 110 and cervical spine up to T1 is shown, with the cervical spine in a lordotic state and the skull 110 at a neutral angle, neither flexion nor extension. The base of the skull 110 and the occipital portion CO and the atlanto-occipital joint 105 are shown. The cervical vertebrae are labeled C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6 and C7. The first thoracic vertebra is labeled T1. In this regard, although the cervical spine and skull 110 are shown vertically, as if the patient were standing, the figure illustrates the plane that the back of the skull would be in if parallel to the patient's back.
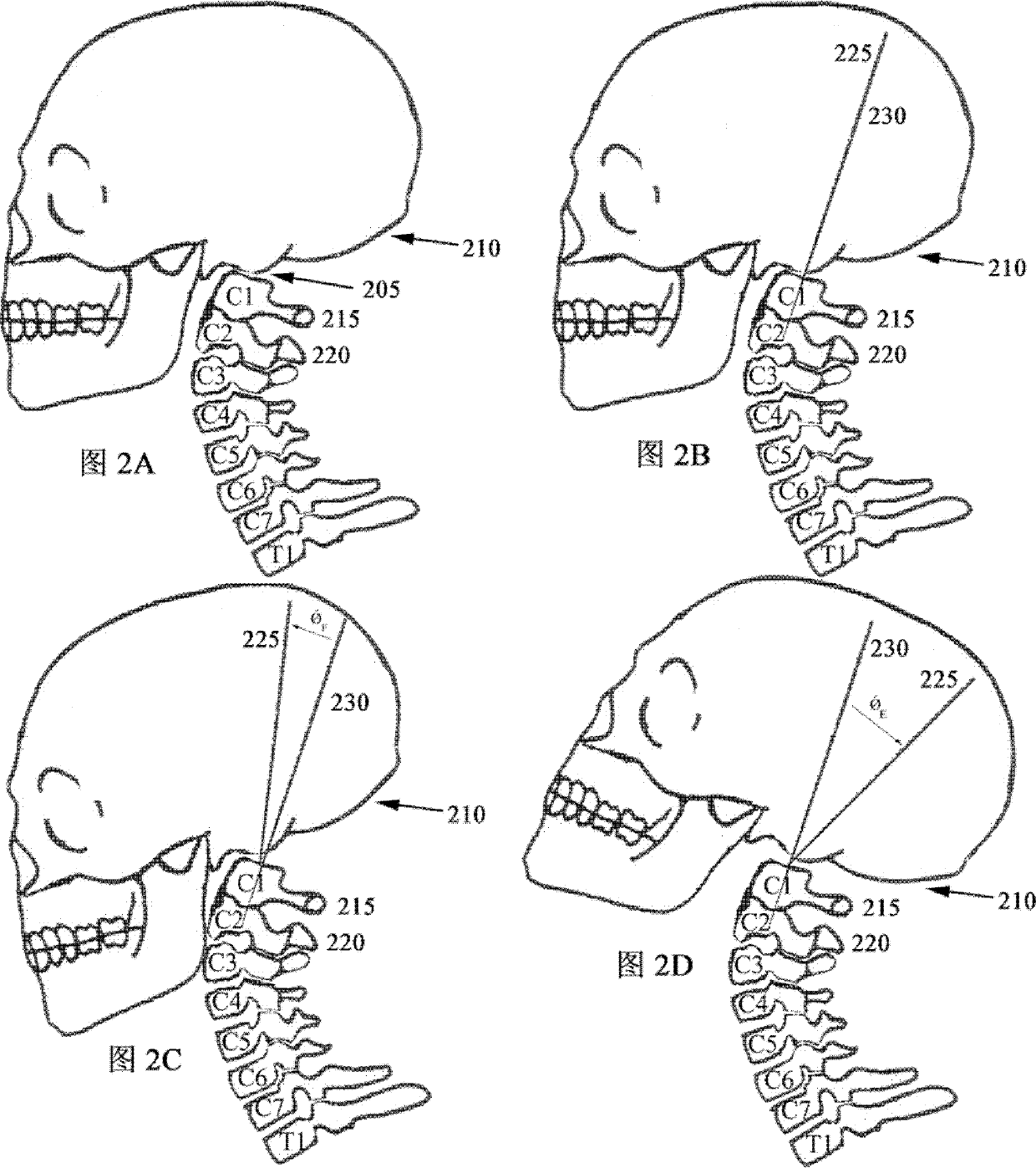
[0060] in the upper left corner of Figure 2A show figure 1 The skull 210 and cervical spine, atlanto-occipital joint 205 are at a neutral angle, neither flexing nor extending. in the upper right corner Figure 2B view with Figure 2A in the same. HPT line 230 is drawn parallel and collinear with C1-C2 215-220. HPT line 225 is drawn from atl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com