Systems and methods for reducing parasitic losses in wireless power systems
A wireless power, power technology, applied in the field of electronics, can solve problems such as short range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] Embodiments of the invention will be described more fully hereinafter with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which like reference numerals refer to like elements throughout the seven views, and in which example embodiments are shown. Embodiments of the claims may, however, be implemented in many different ways and should not be construed as limited to the embodiments set forth herein. The embodiments set forth herein are non-limiting examples and, among other possible examples, only examples.
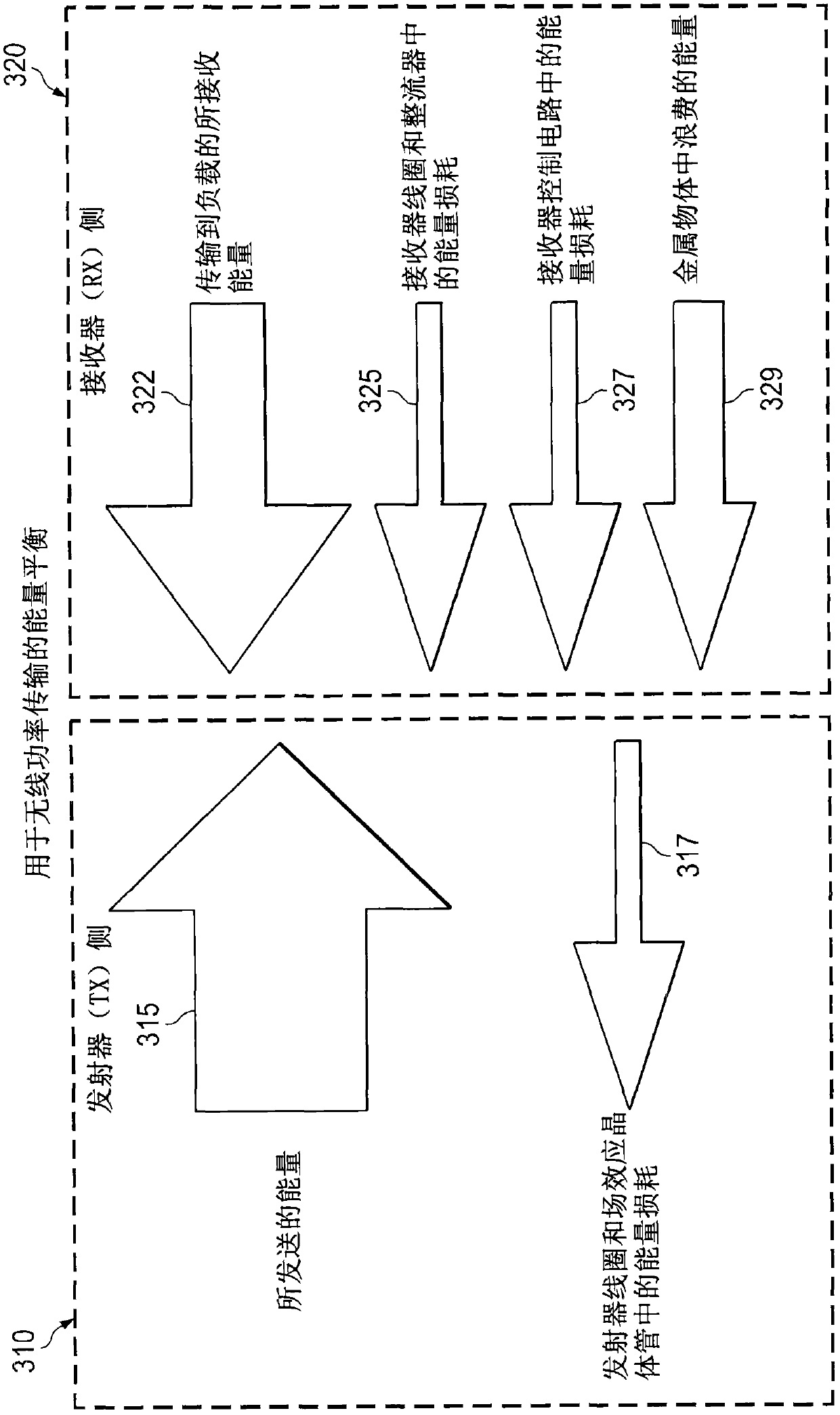
[0020] With wireless charging, the receiving part of the system can periodically send to the primary side, for example, the voltage, current and power levels it is operating at and the corrective actions required by the primary side to keep the secondary side power parameters at the desired within the operating range. The performance of such systems can be significantly degraded when parasitic metallic objects are accidentally or intentionally brought close to the trans...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com