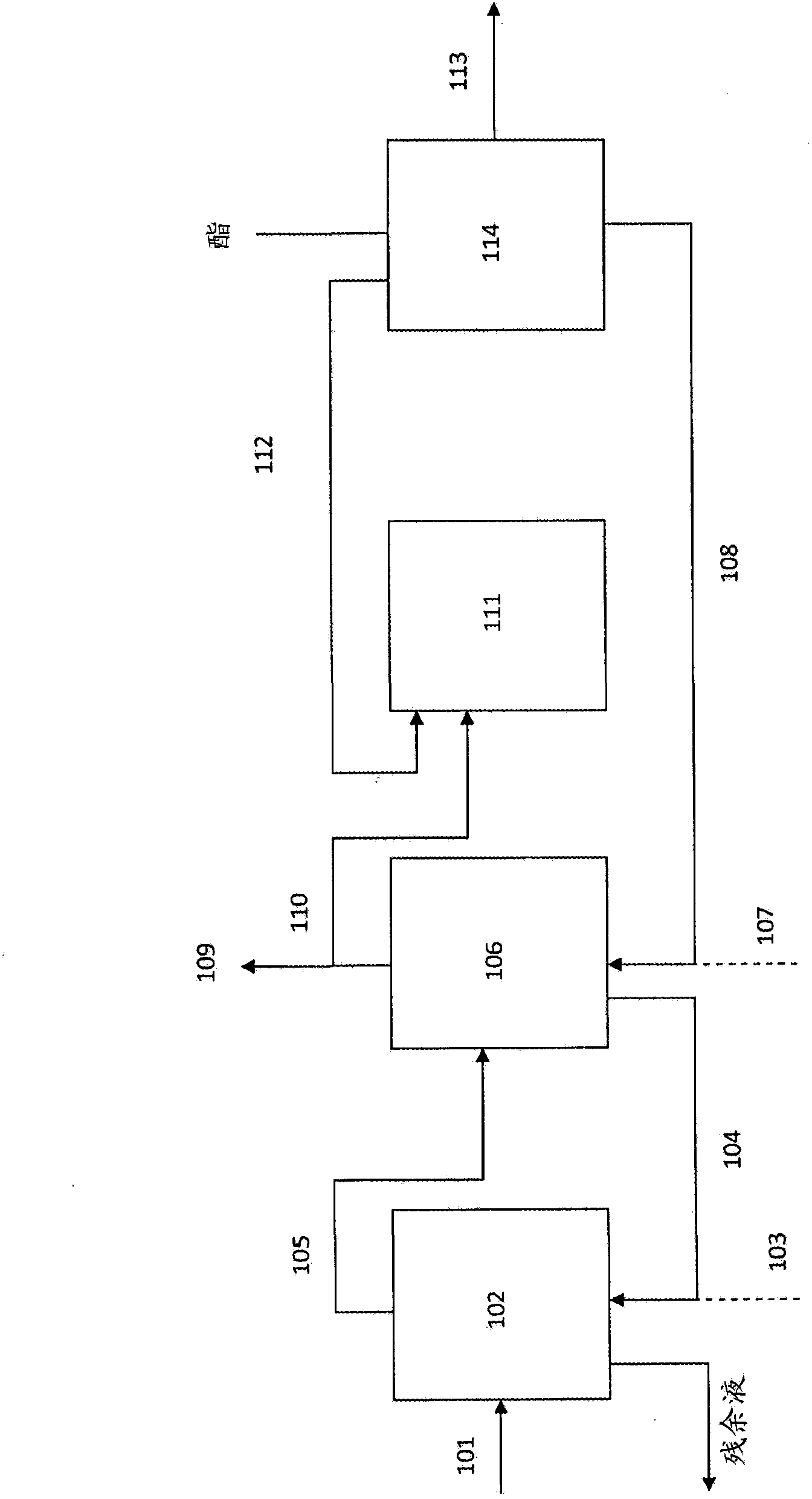
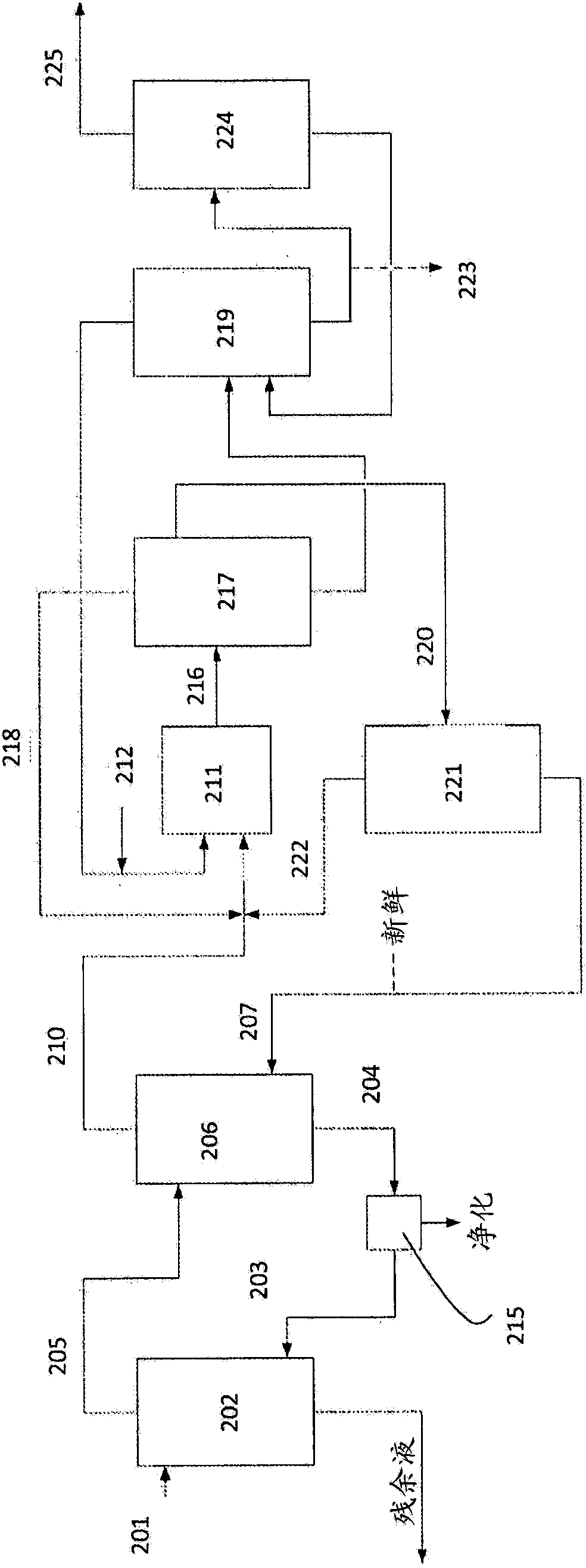
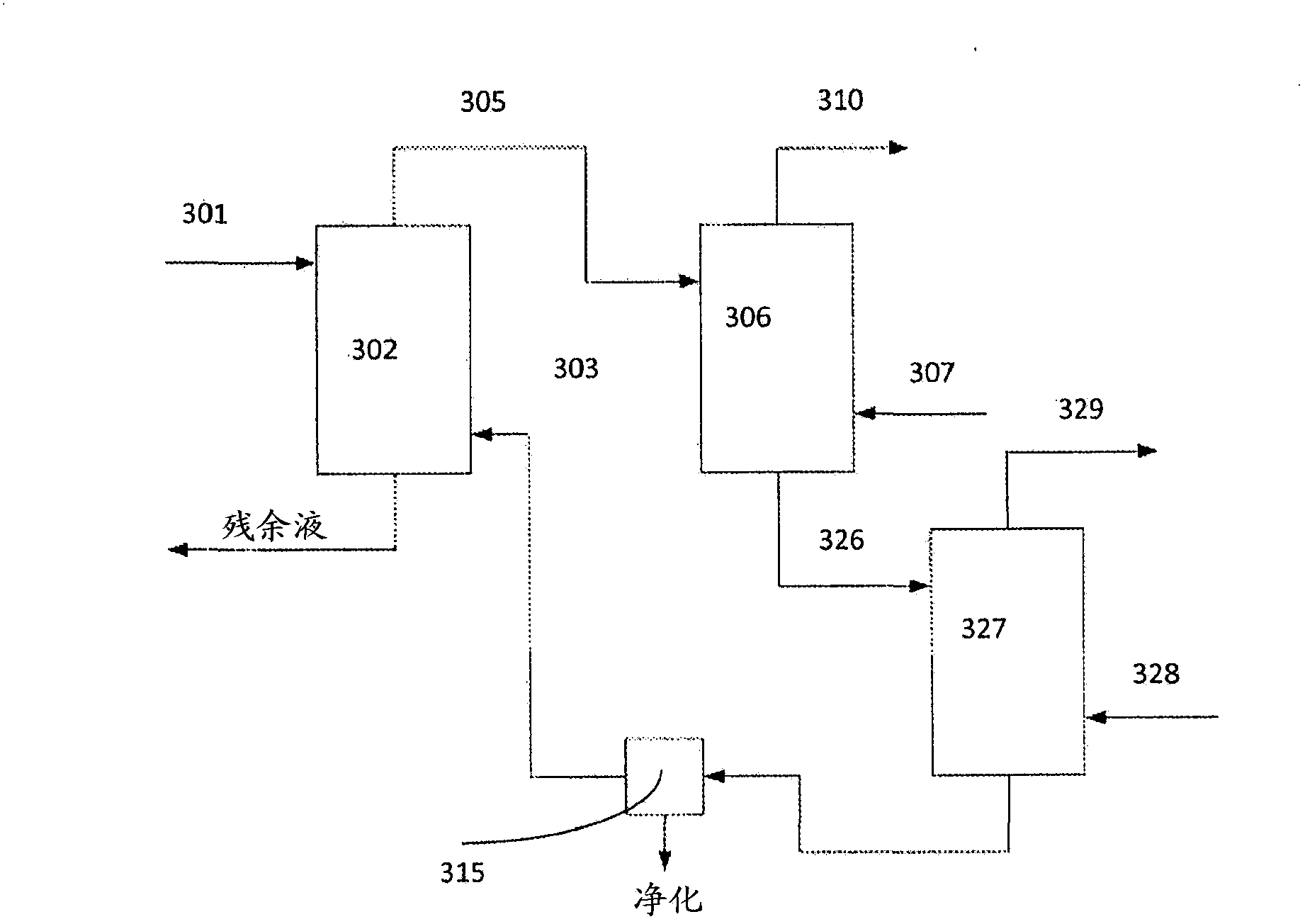
Method for recovery of organic acid from dilute aqueous solution
A technology of organic acid and aqueous solution, applied in the field of separation and recovery of one or more organic acids, to achieve the effect of high carboxylic acid yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] The boiling points of the free acid and methyl ester forms of selected water-soluble C1-C5 carboxylic acids are depicted in Table 1 for the pure compounds. At atmospheric pressure, the boiling point interval within the mixture is 84°C for the free acid form and 95°C for the methyl ester form, indicating the greater separation achievable for the latter group. Acid recovery in the methyl ester form was achieved at lower temperatures and with better separation compared to recovery of the free acid form, even without complexation with the extractant.
[0073] This is evidence for a significantly more energetically favorable recovery of acid in the ester form compared to the recovery of the acid form.
[0074] Table 1
[0075] sour
Embodiment 2-5
[0077] extract
[0078] The Scheibel column was filled with an aqueous solution containing 3.5 wt-% formic acid (Kemira) from the top of the column at a rate of 3.93 kg / h. Cyanex 932 (Cytec) solution was fed to the bottom of the column at a rate of 0.998 kg / h. The stirring speed was 350 rpm, and the column temperature range was 25-28°C. The extraction solution was separated and withdrawn from the column at a rate of 1.08 kg / h. In Cyanex 923, it contains 9.9 wt-% formic acid (in pure form) and 3.4 wt-% water. The recovery rate of formic acid in Cyanex923 was 78%.
[0079] Esterification
[0080] In a glass reactor heated with circulating silicone oil, 500.23 g of the resulting extraction solution were mixed with 105.73 g of methanol. The reactor was equipped with a fractionation column with structured packing and a cooler with isopropanol. The solution was warmed to 70°C with continuous mixing at ambient pressure. The distillate containing methyl formate in methanol was ...
Embodiment 3
[0092] extract
[0093] Similar to Example 2, the extraction was carried out.
[0094] The extraction solution coming out of the column contained 9.0 wt-% formic acid (in pure form) and 3.1 wt-% water in Cyanex 923.
[0095] Esterification
[0096] Similar to Example 2, 500.00 g of the obtained extraction solution was mixed with 96.0 g of methanol. The solution was warmed to 90°C at ambient pressure with continuous mixing. A distillate containing methyl formate in methanol was collected and more methanol was gradually introduced into the reactor below the liquid level. Keep the solution at about 90°C and continue the distillation until a distillate is obtained.
[0097] The consumption of methanol was recorded and the formation of methyl formate was quantified using GC both from the distillate and from the distillation bottoms. Table 4 shows the homogeneous quality of the distillate and Table 5 shows the final results.
[0098] Table 4
[0099]
[0100] table 5
[0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com