Constellation mapping method
A technology of constellation mapping and constellation diagram, which is applied in the field of digital information coding and transmission, can solve problems such as the absence of an ideal solution, and achieve the effects of improving hard decision capabilities, eliminating inter-subcarrier interference, and improving channel estimation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The input bit data is multiple sets of bit vectors with a length of M, and the constellation symbols obtained after mapping the bit data through an irregular constellation mapping method are output as real number vectors with a length of N. For example, the input kth bit vector is X k =[b k,0 , b k,1 ,...,b k,M-1 ], the output kth real vector is Y k =[y k,0 、y k,1 ,...,y k,M-1 ]. In this example, the X k map to Y k , so you can use a from {0,1} M to R N To describe the function F, where {0,1} M Represents an M-dimensional bit vector, which is represented by 0 and 1, such as 0011 (M=4), 0100010 (M=6), etc., R N Represents an N-dimensional real number vector, R is the Euclidean distance between the constellation point and the center of the constellation diagram, and R is a real number.
[0034] Among them, the function F satisfies the following two conditions:
[0035] 1. The function F will at least two different {0,1} M The vector in R maps to N The sa...
Embodiment 2
[0042] This embodiment is the same as the irregular constellation mapping method adopted in the first embodiment above, the difference is that in this embodiment, the function F will be {0,1} M map to R N Among them, M=6, N=2.
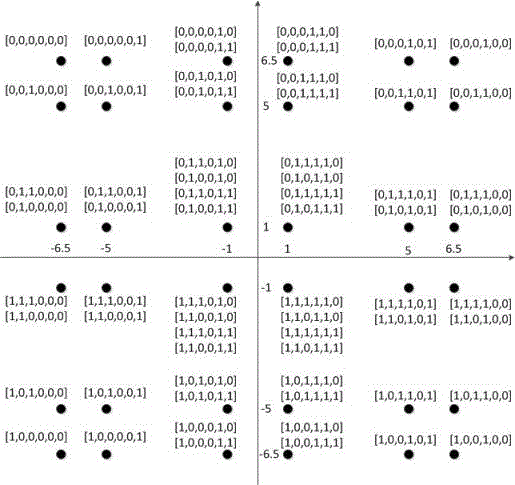
[0043] Such as figure 2 Shown is a constellation mapping diagram of a specific embodiment of a constellation mapping method.
[0044] refer to figure 2 , the function F maps [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] to [-6.5, 6.5], where two -6.5 and 6.5 correspond to figure 2 The abscissa and ordinate in .
[0045] From figure 2 As can be seen in the function F maps [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0] and [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1] to the same constellation point (ie [-1, 6.5]) superior. Function F takes [0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1] and [0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1] are mapped to the same constellation point (ie [-1, 1]).
[0046] At the same time, the closest constellation point to [-6.5, -6.5] (including [-6.5, -5] and [-5, -6.5]) has a Euclidean distance of 1.5,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com