Thermal-image processing method capable of inhibiting effects of uneven thermal emissivity of material surface
A thermal emissivity and image processing technology, applied in image data processing, image enhancement, instruments, etc., to eliminate the interference of defect detection, improve detection accuracy, and suppress uneven thermal emissivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
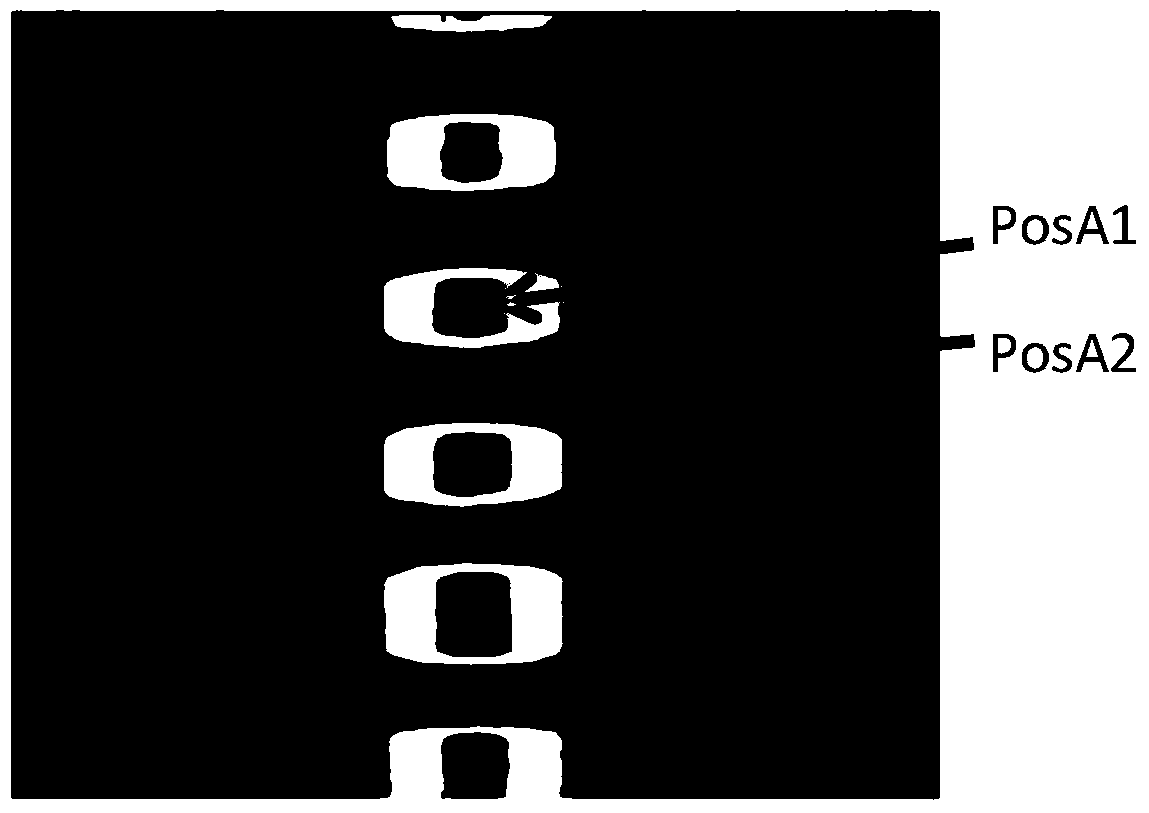
[0059] Figure 6 It is a photograph of stainless steel sample B. Such as Figure 6 As shown, the stainless steel sample B is the same as the stainless steel sample A, and the surface is equally spaced with light and dark stripes, and there is a crack in one of the bright stripes.
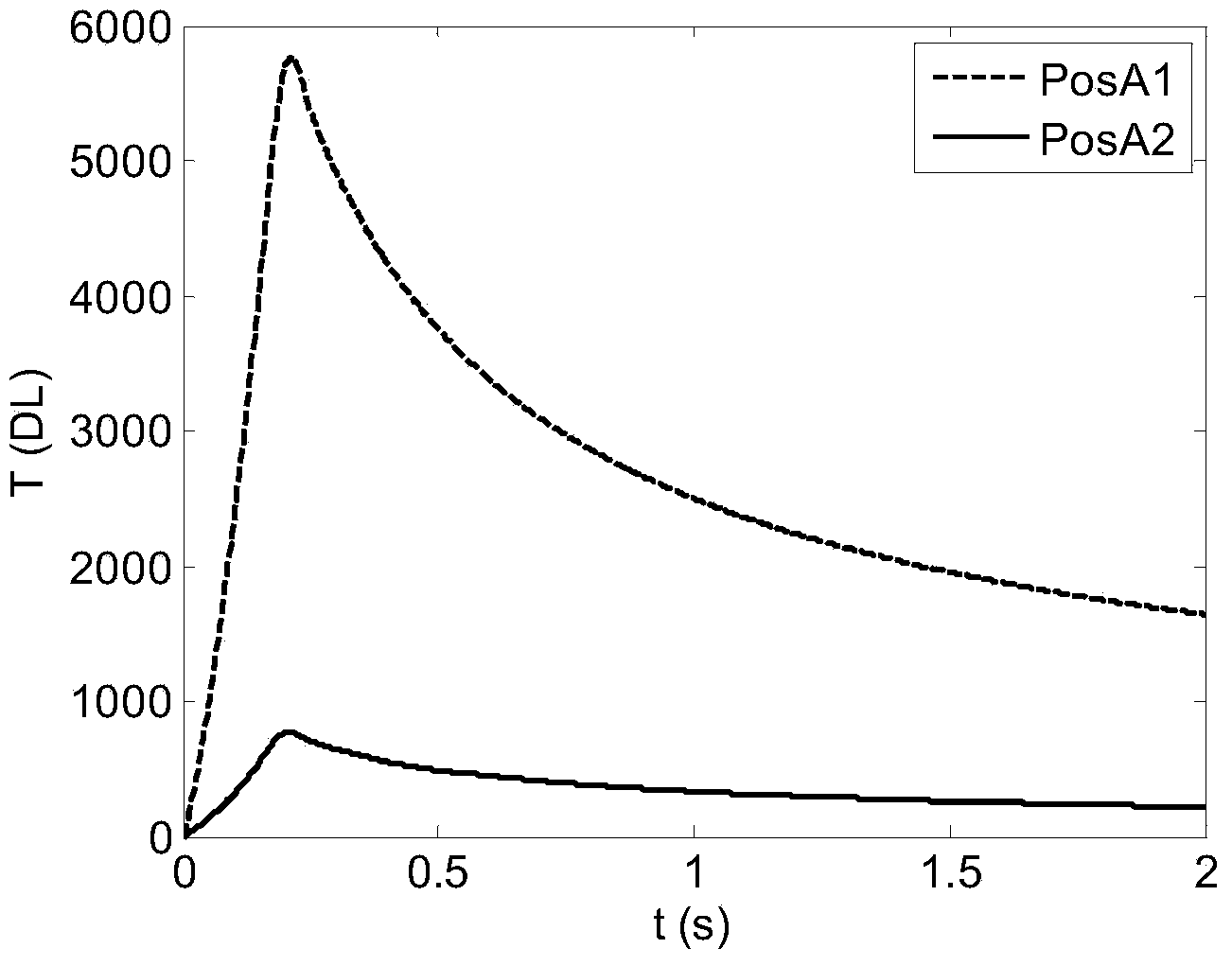
[0060] In this embodiment, eddy current is still used to heat the stainless steel sample B. Figure 7 is the infrared thermal image of stainless steel sample B at the end of heating. Such as Figure 7 As shown, the crack edge and the inside of the stainless steel sample B present different temperature states due to their own temperature differences, for example, the region PosB1 at the end of the crack and the region PosB2 at the side of the crack present a higher temperature than the inside of the crack; As in sample A, PosB4 in the black stripe area has a higher thermal emissivity, and the infrared thermal image brightness is higher, showing a high temperature, while the bright stripe area Pos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com