Method for recognizing cloud based on mie-scattering laser radar with equalized value distribution
A lidar and meter scattering technology, applied in the re-radiation of electromagnetic waves, the use of re-radiation, measurement devices, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete detection of near-field signals, difficulty in distinguishing cloud signals from aerosol signals, and increased misjudgment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0073] In order to make the purpose, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention more clear, the embodiments of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. Here, the exemplary embodiments and descriptions of the present invention are used to explain the present invention, but not to limit the present invention.
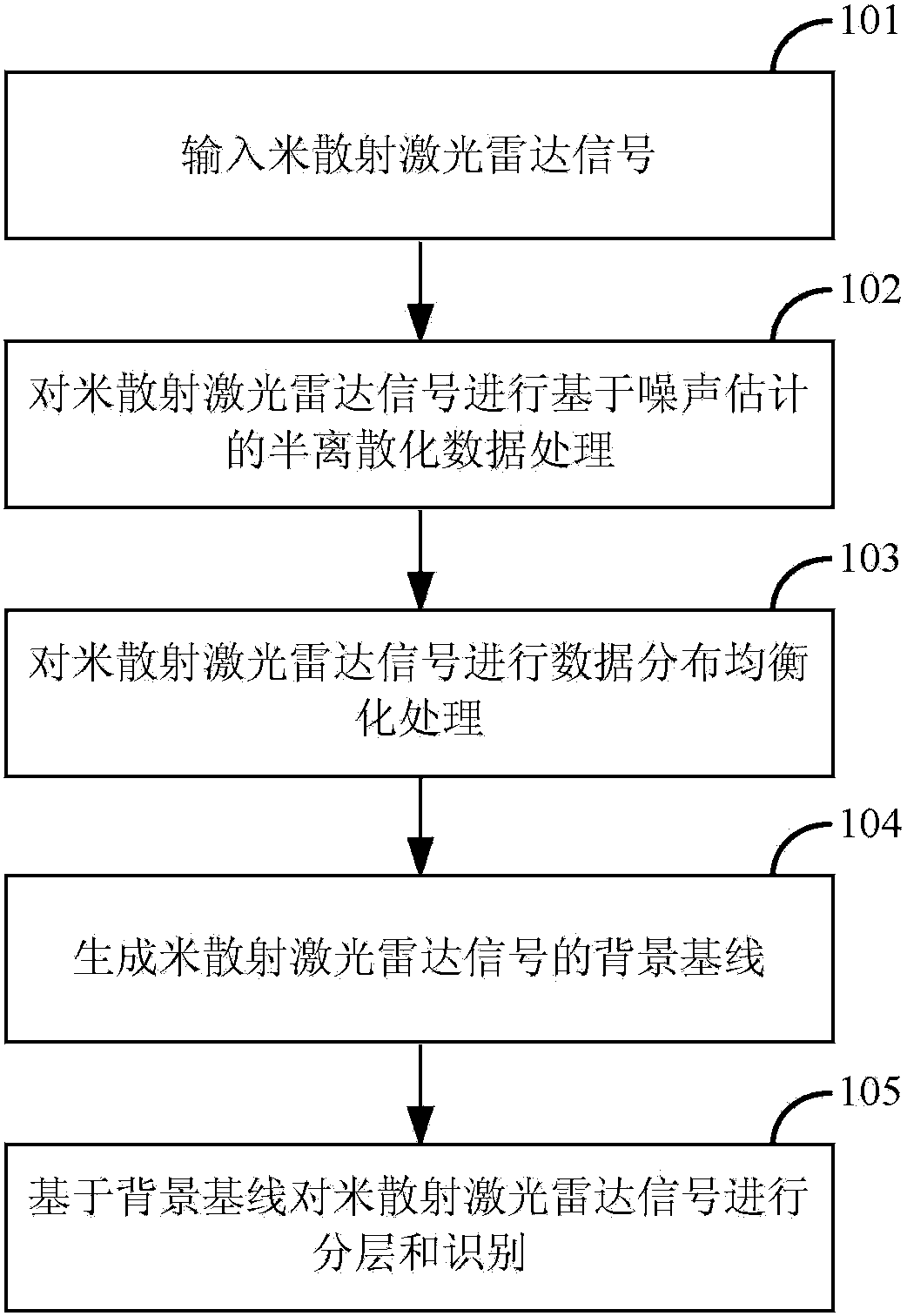
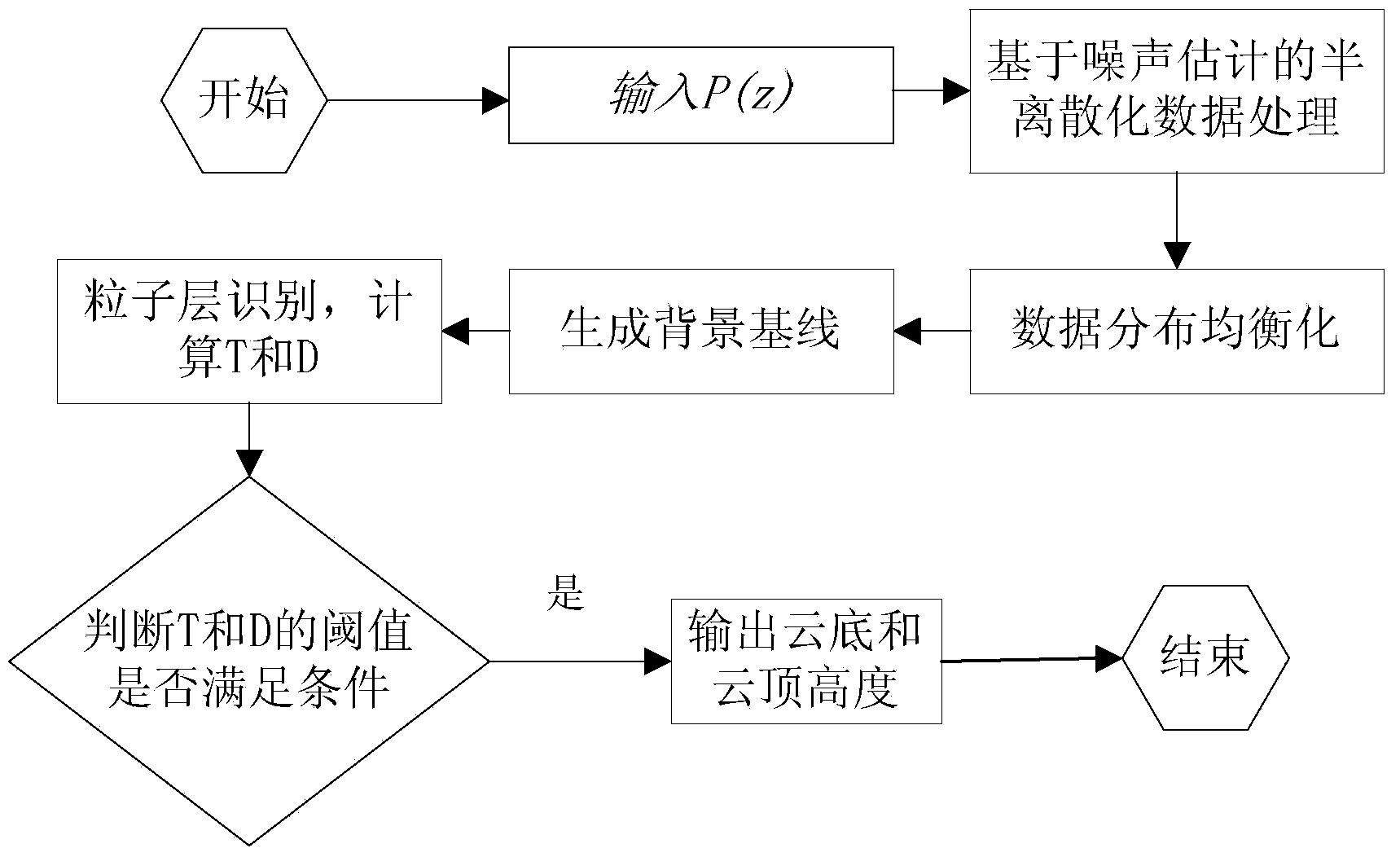
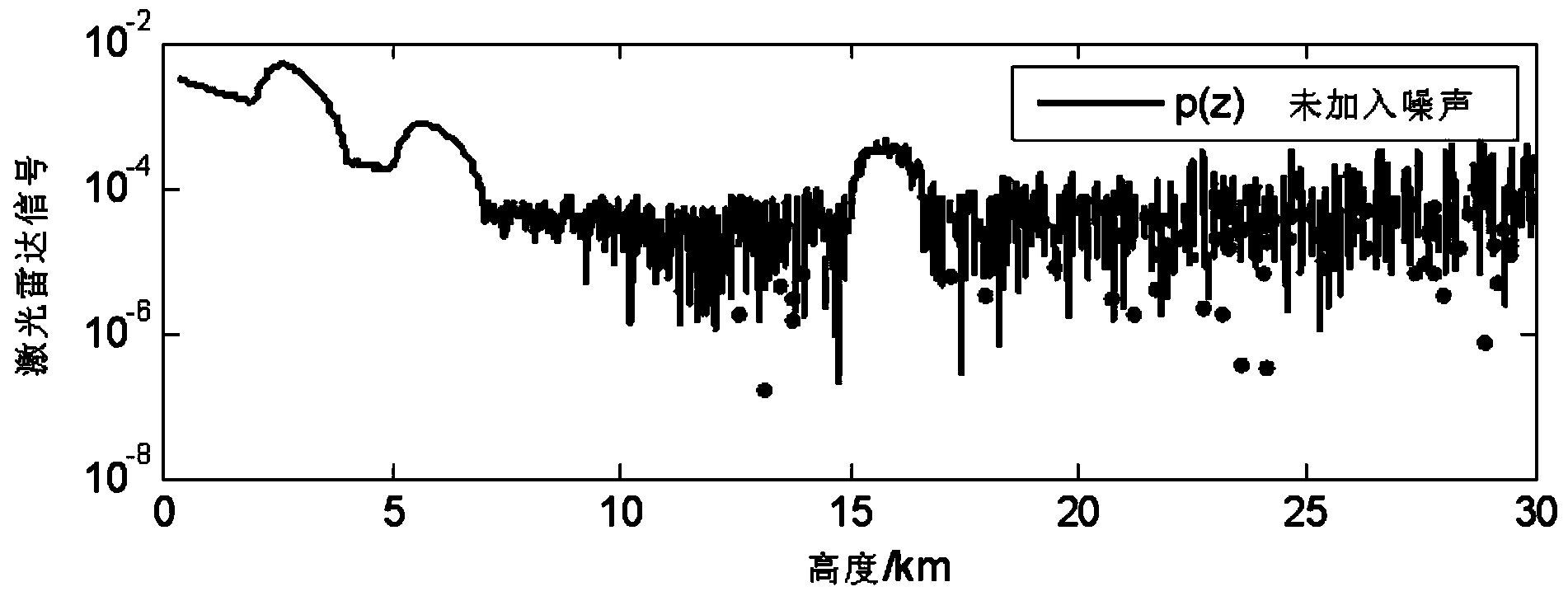
[0074] In order to weaken the importance of the smoothing problem in the cloud identification process, find out the background baseline adaptive to signal changes, thereby solving the problem that the current algorithm relies too much on smoothing or misses detection of weaker cloud echo signals, the present invention implements This example provides a cloud identification method based on numerical distribution equalization of meter-scattering lidar, which realizes the identification of cloud signals from lidar signals. figure 1 It is the processing flowchart of the m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com