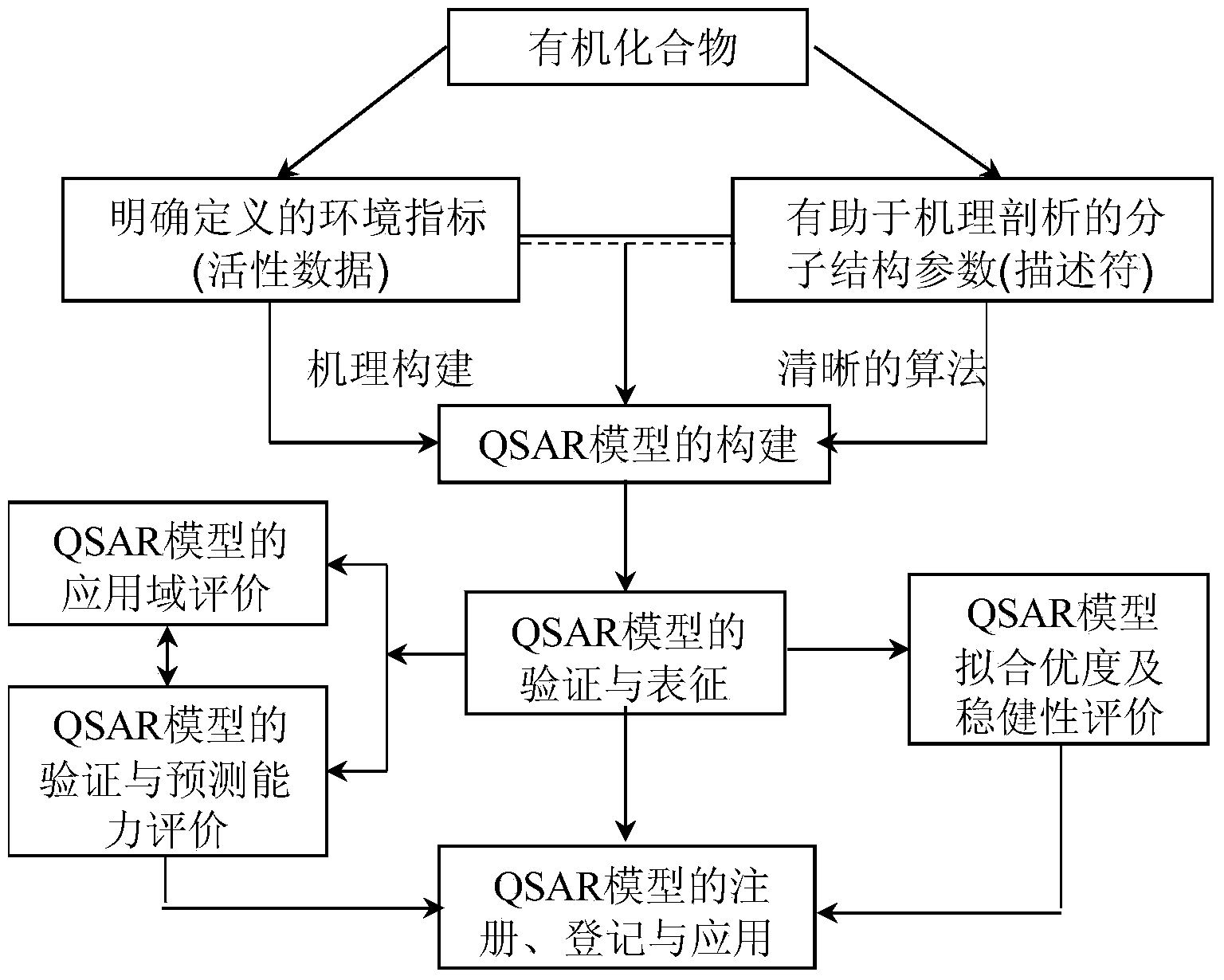
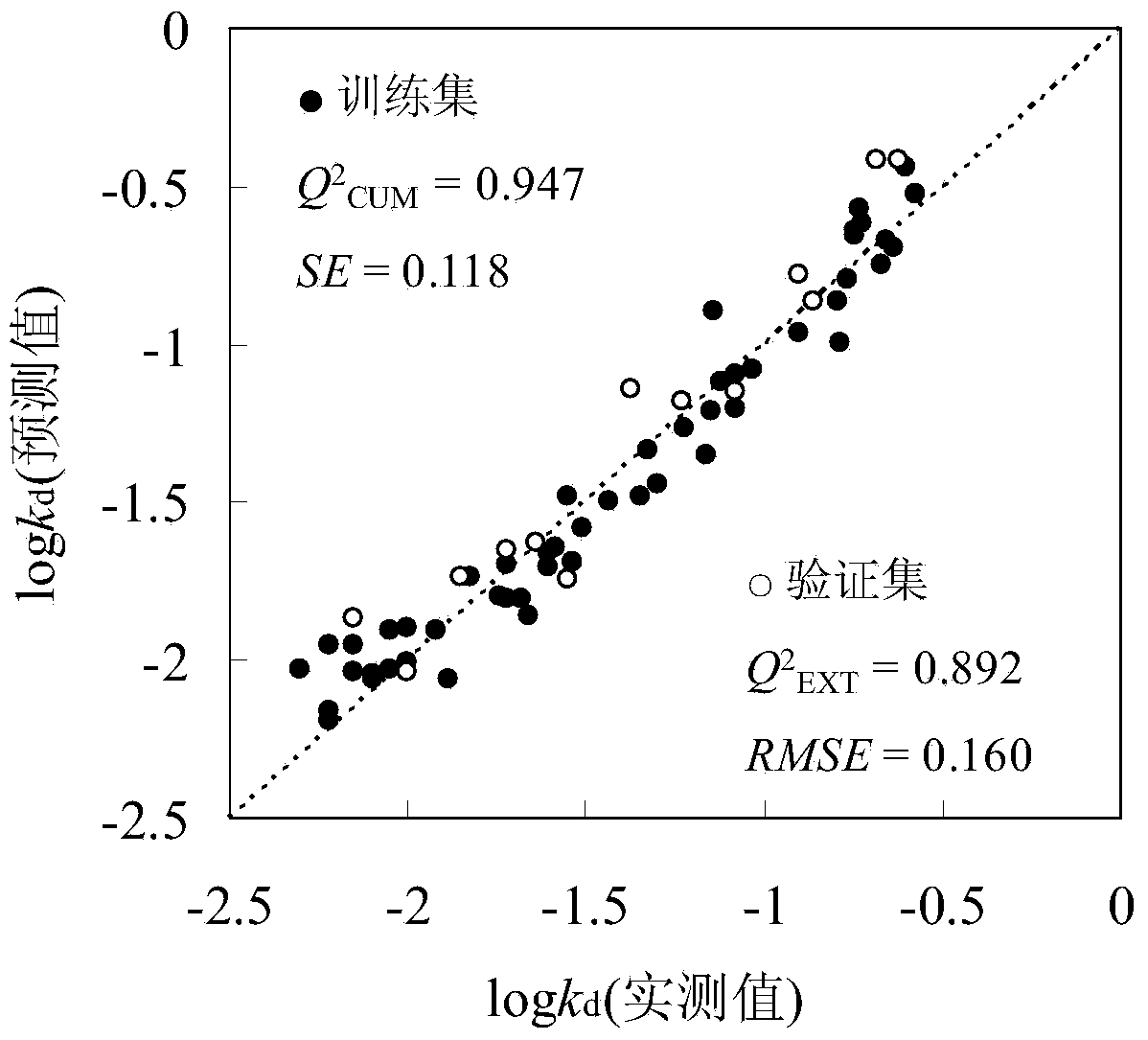
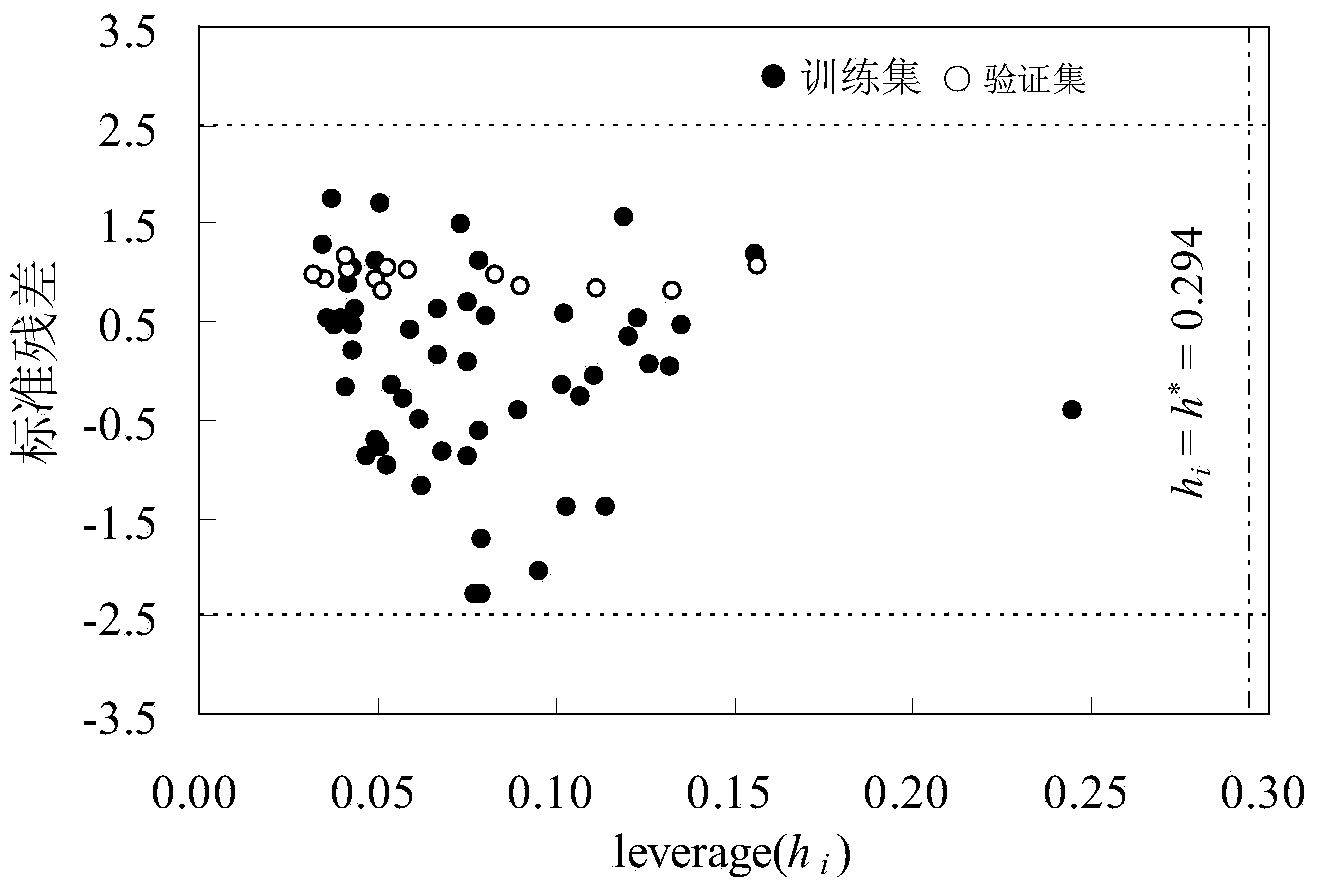
Method for predicting elimination speed of persistent organic pollutants on coastal zones
A technology of organic pollutants and persistence, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of no model application domain representation, etc., and achieve manpower saving, good fit, and low cost Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] 2,6-Dimethylnaphthalene: The leverage value calculated by Williams graph method is 0.2349* (warning value)=0.294, standard residual (SE)=-0.0288>-3, indicating that this compound is within the application domain of the QSAR model. Based on the mechanism of action, Gaussian09 software is used to calculate the four descriptor values in the model according to the method described in the invention.
[0079] Contamination elimination rate logk of 2,6-dimethylnaphthalene in mussels d The measured value of is: -0.577. The prediction steps based on the QSAR model are as follows:
[0080] logk d =0.134–1070×(0.000674)–0.00486×(174.4643)–76.5×(-0.01197)–0.0431×(0.018006)=-0.527. The predicted values are in good agreement with the measured values.
Embodiment 2
[0082] Dibenzofuran: the leverage value calculated by Williams graph method is 0.1335* (warning value)=0.294, standard residual (SE)=0.2374<3, indicating that this compound is within the application domain of the QSAR model. Based on the mechanism of action, Gaussian09 software is used to calculate the four descriptor values in the model according to the method described in the invention.
[0083] Pollution elimination rate logk of dibenzofuran in mussels d The measured value of is: -0.635. The prediction steps based on the QSAR model are as follows:
[0084] logk d =0.134–1070×(0.000815)–0.00486×(169.273)–76.5×(-0.012547)–0.0431×(0.208105)=-0.527. The predicted values are in good agreement with the measured values.
Embodiment 3
[0086] 1-Methylphenanthrene: The leverage value calculated by Williams graph method is 0.0414* (warning value)=0.294, standard residual (SE)=0.3421<3, indicating that this compound is within the application domain of the QSAR model. Based on the mechanism of action, Gaussian09 software is used to calculate the four descriptor values in the model according to the method described in the invention.
[0087] Contamination elimination rate logk of 1-methylphenanthrene in mussel d The measured value of is: -0.858. The prediction steps based on the QSAR model are as follows:
[0088] logk d =0.134–1070×(0.000699)–0.00486×(224.2747)–76.5×(-0.0117)–0.0431×(0.120829)=-0.860. The predicted values are in good agreement with the measured values.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com