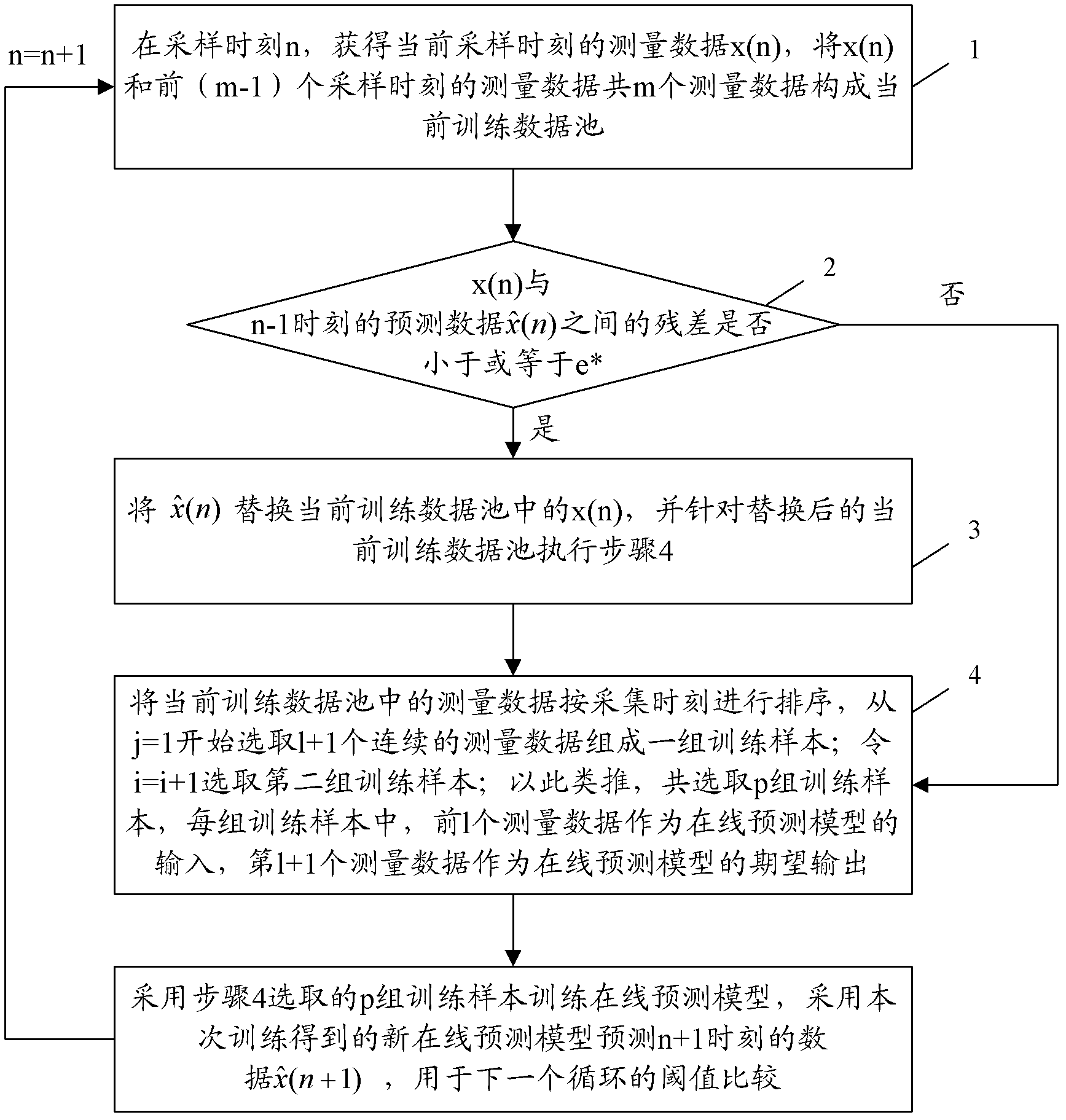
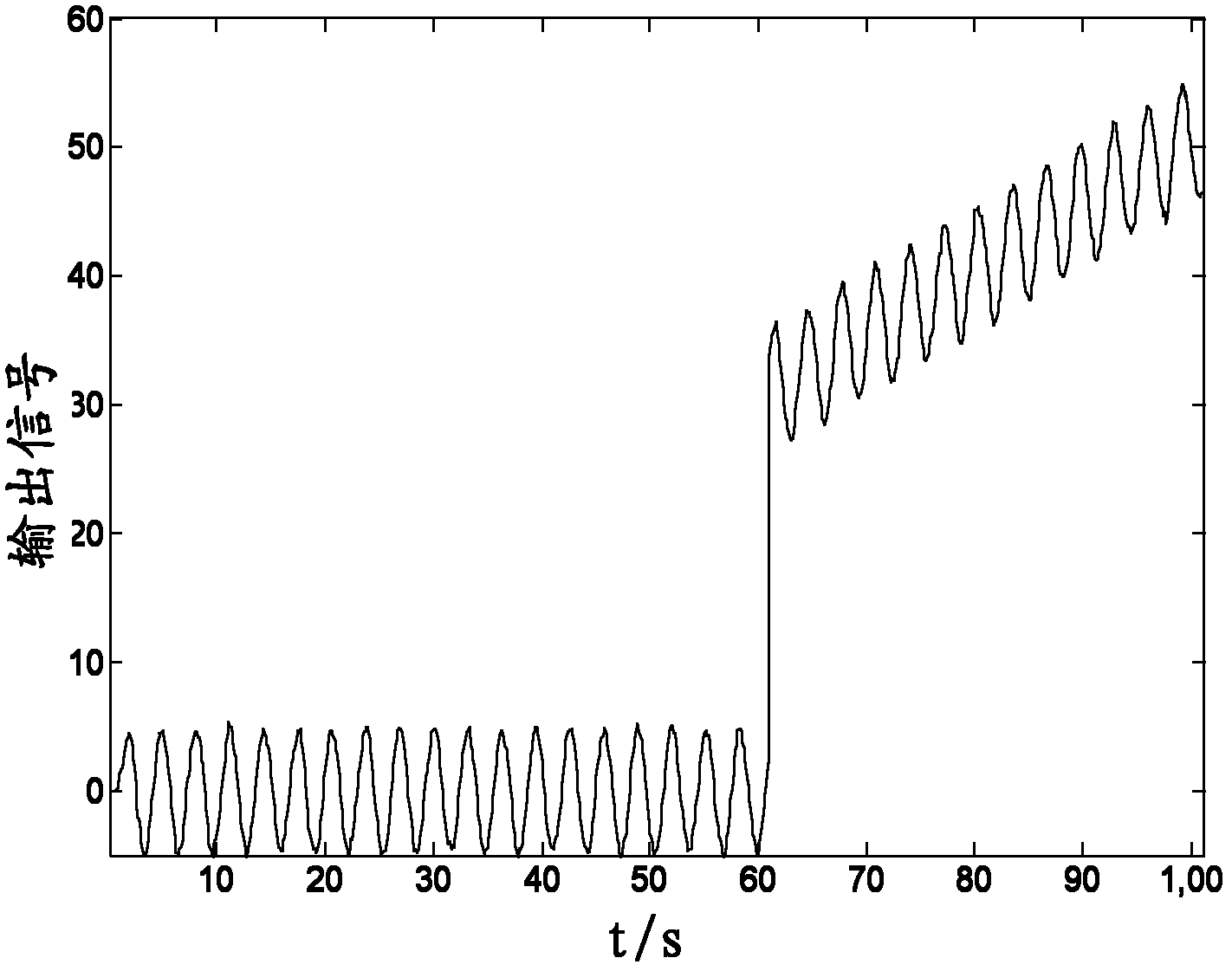
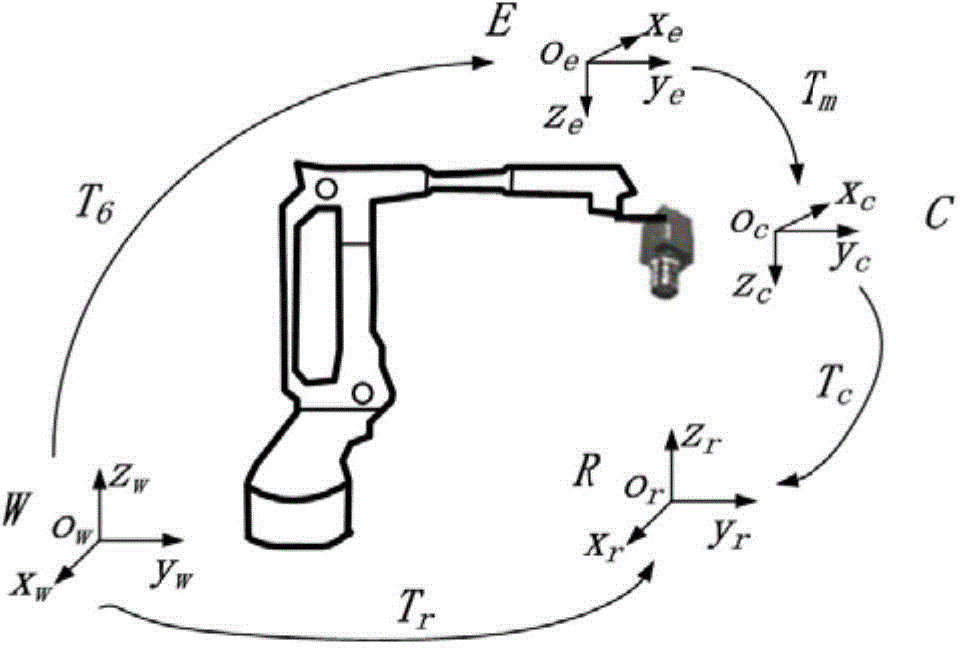
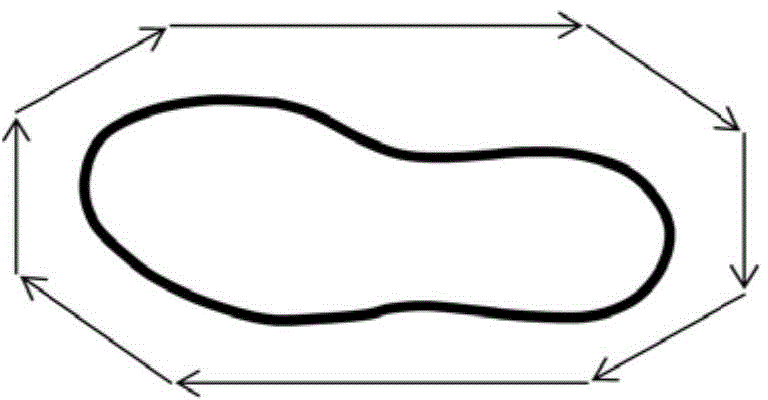
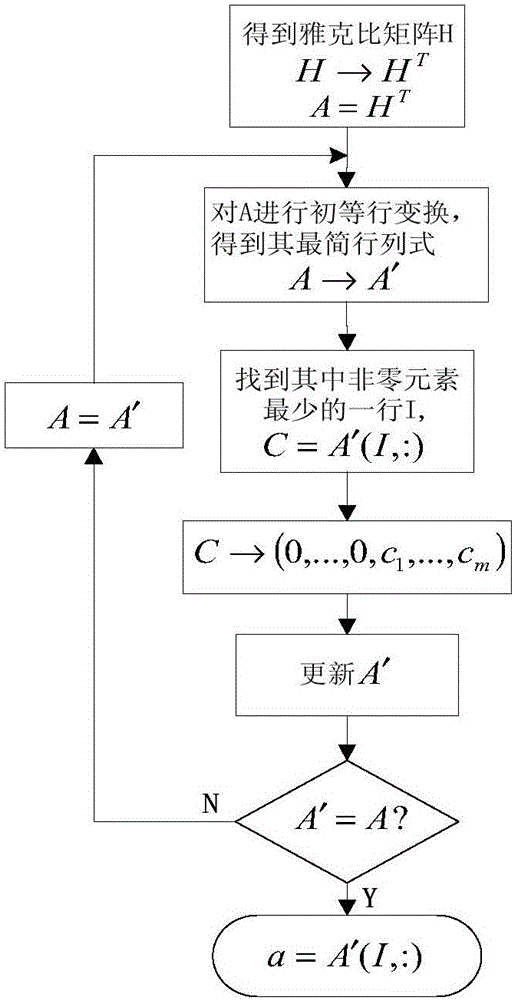
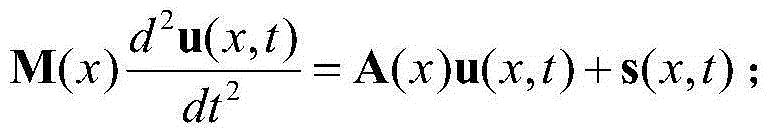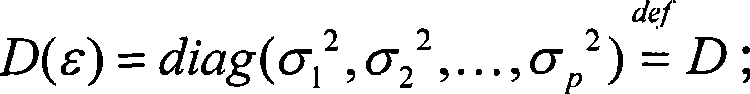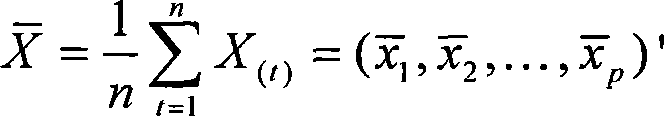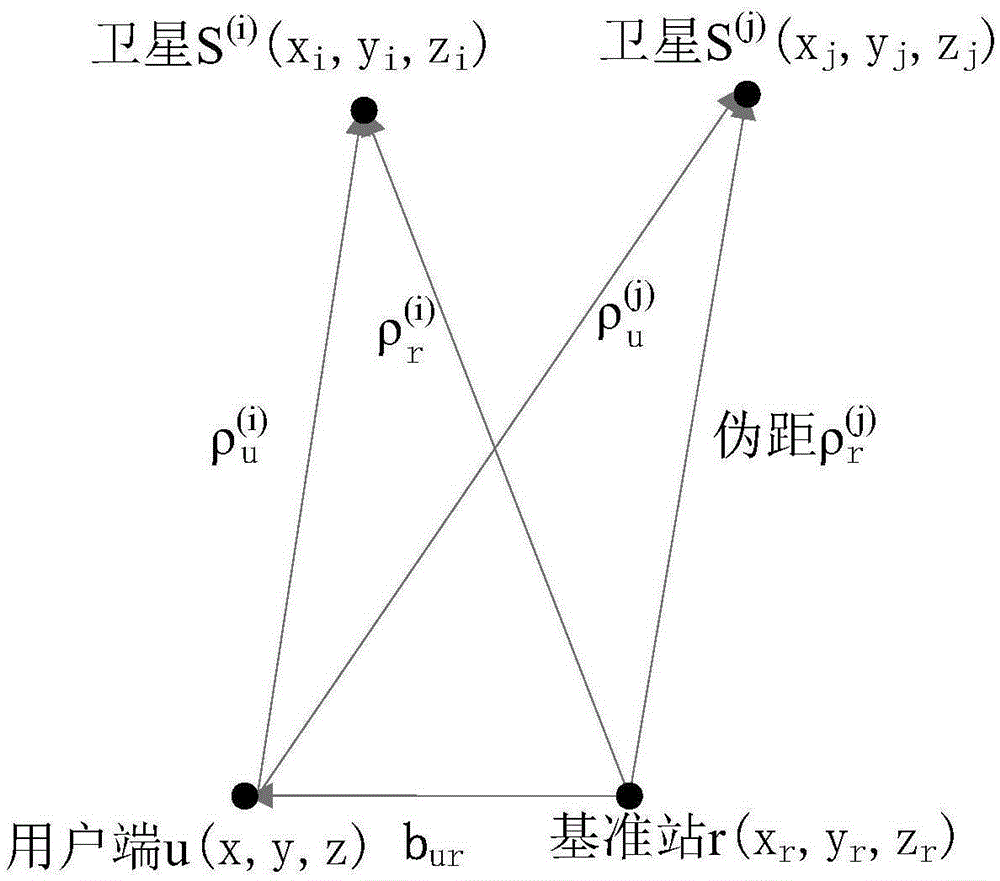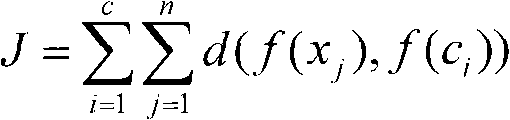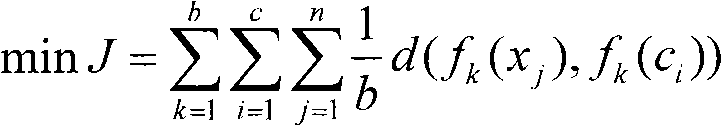Patents
Literature
344 results about "Galerkin least squares" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
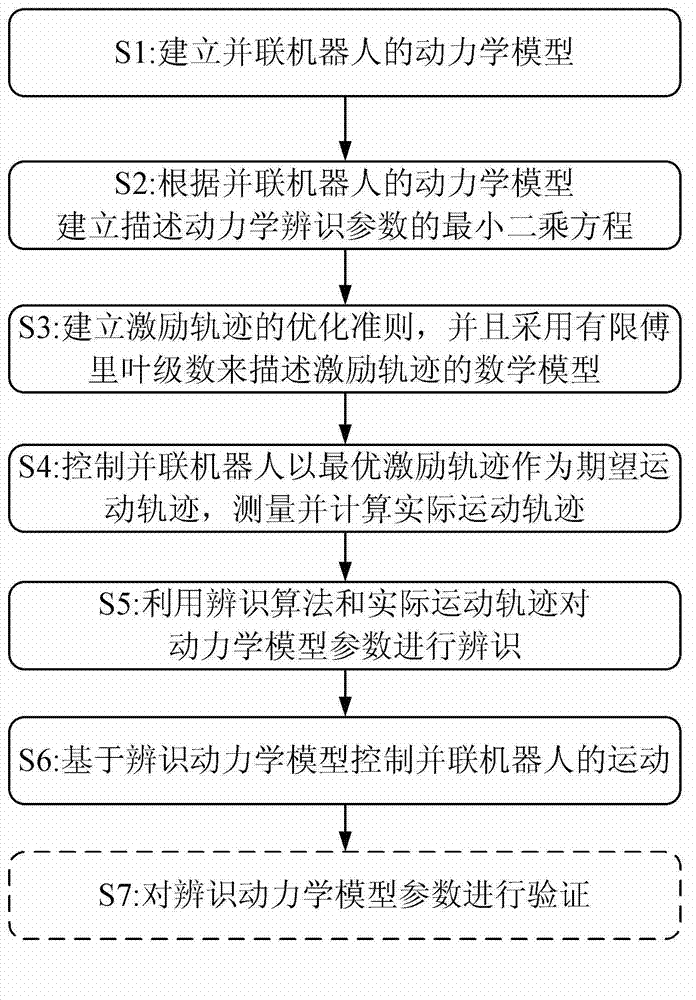
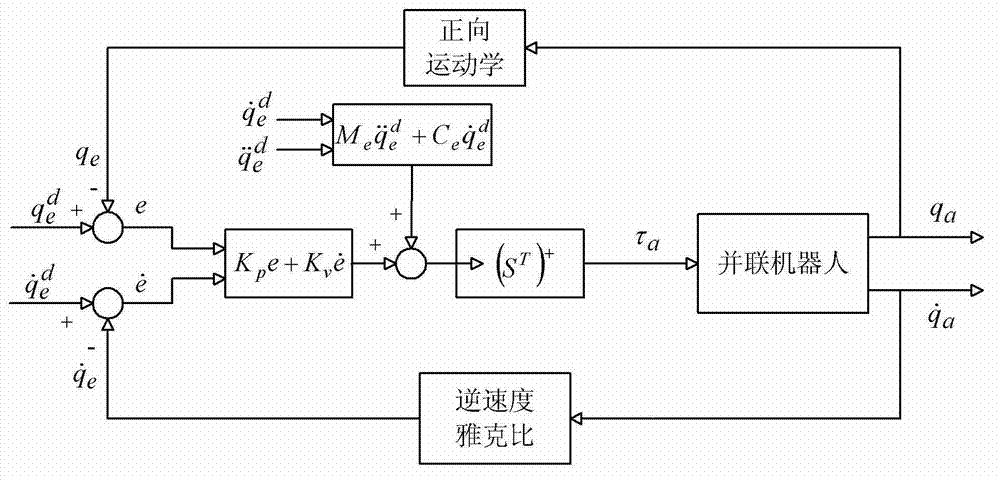
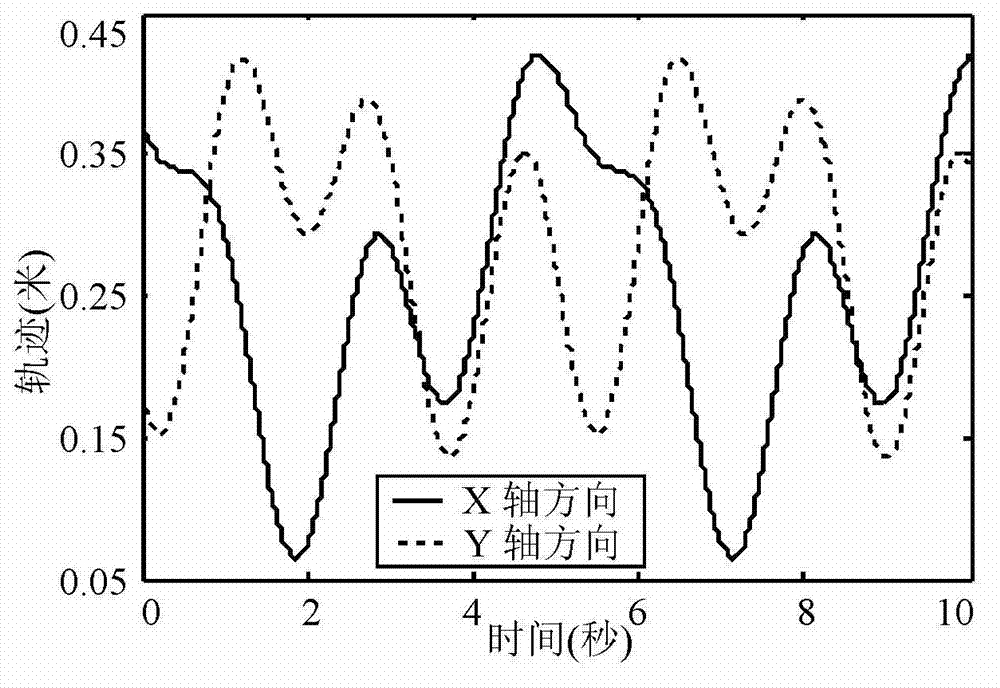
Dynamic model parameter identification based parallel robot control method
The invention provides a parallel robot control method which comprises the following steps: S1, building a dynamic model of a parallel robot; S2, establishing a least square equation used for describing dynamic parameter identification according to the dynamic model of the parallel robot; S3, establishing an optimization criterion of a motivation track according to the least square equation, and describing a mathematical model of the motivation track with the adoption of finite fourier series; S4, controlling the parallel robot to take an optimal motivation track as the expected motion track, and measuring and calculating a practical motion track; S5, identifying dynamic model parameters with the utilization of an identification algorithm and the practical motion track; and S6, controlling the motion of the parallel robot based on the identification dynamic model. The dynamic model parameter identification based parallel robot control method is capable of enabling the precise and intact dynamic model to be established, and precisely controlling the motion of the parallel robot.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
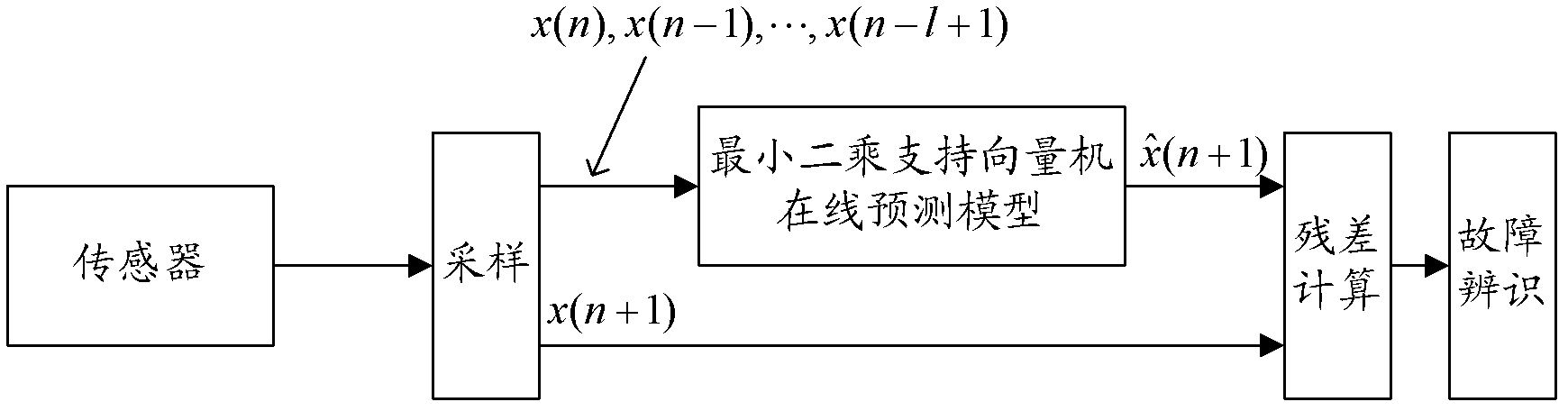
Sensor-fault diagnosing method based on online prediction of least-squares support-vector machine
ActiveCN102324034APredicted output valueCharacter and pattern recognitionLeast squares support vector machineLinear regression
The invention discloses a sensor-fault diagnosing method based on the online prediction of a least-squares support-vector machine. In the method, a least-squares support-vector machine online-predicting model is established, and then the measured data of a sensor is acquired on line and used as an input sample of the least-squares support-vector machine online-predicting model to realize that the output value of the sensor at the next moment is predicted in real time as the predicting model is trained on line. Whether sensor faults occur or not is detected by comparing residual errors generated by the predicting value and the actual output value of the sensor. When the faults occur, the unary linear regression for a residual-error sequence is carried out by a least-squares method to realize the identification of the deviation and drift faults of the sensor, and furthermore, measures can be more effectively taken to carry out real-time compensation for the output of the sensor. Through the sensor-fault diagnosing method, the online fault diagnosis of the sensor can be rapidly and accurately realized, and the sensor-fault diagnosing method is particularly applicable to diagnosing the deviation faults and the drift faults of the sensor.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Automatic shoe sole edge line tracking method based on robot
InactiveCN104463851ASave human effortQuick scanImage enhancementImage analysisThree levelGeneration process
The invention provides an automatic shoe sole edge line tracking method based on a robot. The method includes the steps that firstly, a shoe with a shoe sole bound is scanned, after point cloud data are acquired, point cloud feature points are acquired through a weighted PCA three-level-set total least square method, the feature points are divided into blocks and projected to a two-dimensional region, a longest feature line in a two-dimensional image is acquired through a two-dimensional line segment splicing method, the feature line is back projected to three-dimensional space, a closed three-dimensional curve of the edge of the shoe sole is thinned through a space linear projection method, a new curve is generated through a scanned current vamp and the three-dimensional closed curve generated previously in the generation process, the curve is tracked through the industrial robot, and then automatic grinding, liquid medicine coating and glue spraying operation and the like can be achieved. The method can be widely applied to an automatic shoe-making system, and the production efficiency and product quality are improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
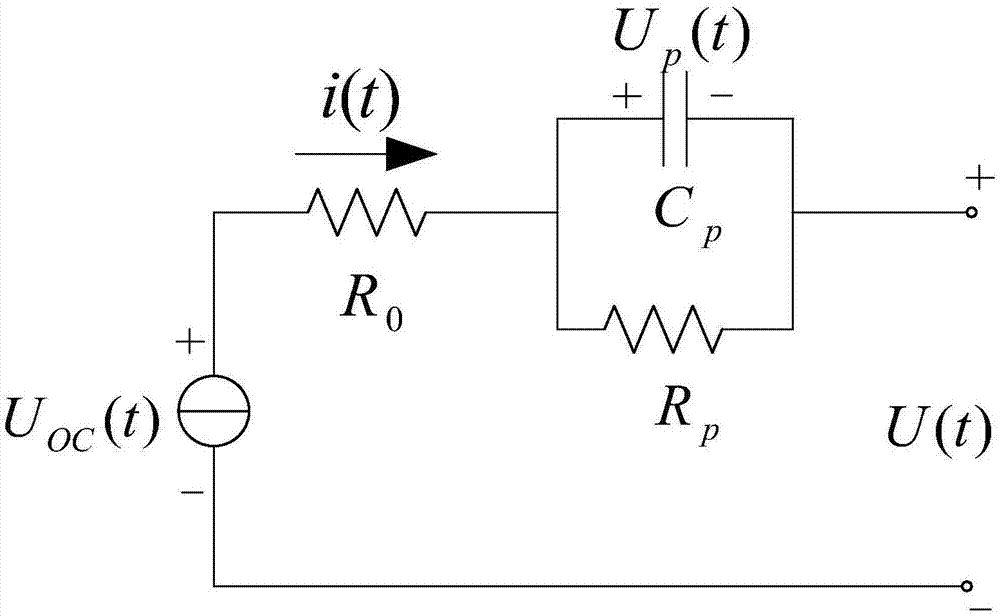
Power battery SOC (state of charge) estimation system and method based on ARMAX (autoregressive-moving-average exogenous) model
InactiveCN107576919AHigh precisionEliminate SaturationElectrical testingMoving averageForgetting factor
The invention discloses a power battery SOC (state of charge) estimation system and method based on ARMAX (autoregressive-moving-average exogenous) model. The method comprises the steps of representing polarization reaction of a battery base on RC (resistor-capacitor) structure, discretizing a Thevenin battery model, and introducing the ARMAX model; identifying parameters of the Thevenin battery model; calculating the parameters of the Thevenin battery model based on a least squares estimation method; establishing a following linear relationship between open-circuit voltage and SOC of the battery, and acquiring an estimated value of the SOC. The ARMAX model is introduced based on the RC equivalent circuit model; a recursive least squares method with forgetting factors is used to identify parameters of the model; the estimated value of SOC is found according to an OCU (Uoc)-SOC relation table, and accordingly, the problems of difficulty in establishing a battery mathematic model and precisely predicting SOC are solved; influences of model errors upon parameters are fully considered, and SOC estimation accuracy is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF PETROCHEMICAL TECH
Road conditions video camera marking method under traffic monitoring surroundings
InactiveCN101118648AImprove robustnessMeet the requirements of high-precision camera calibrationTelevision system detailsImage analysisMonitoring systemModel parameters
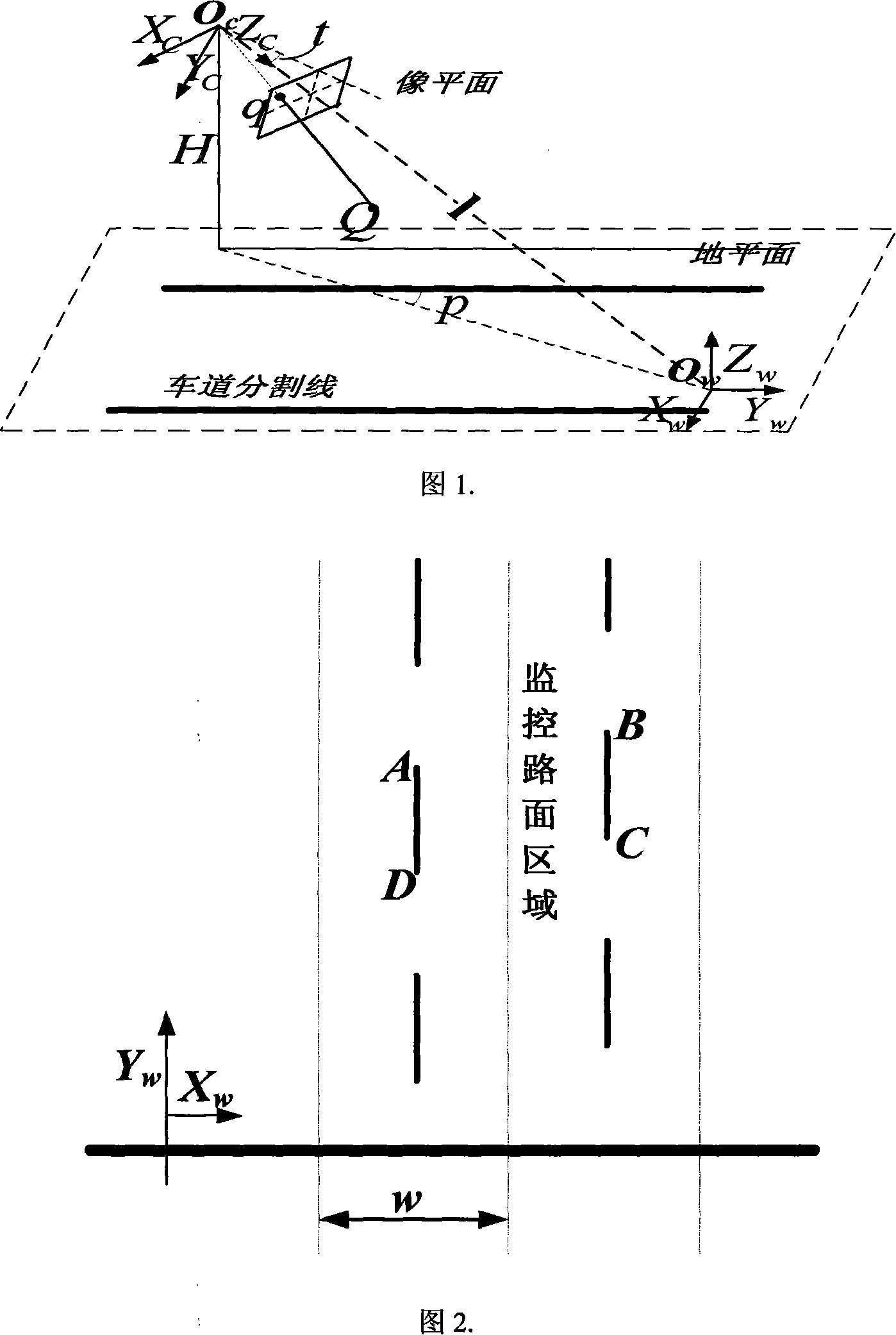
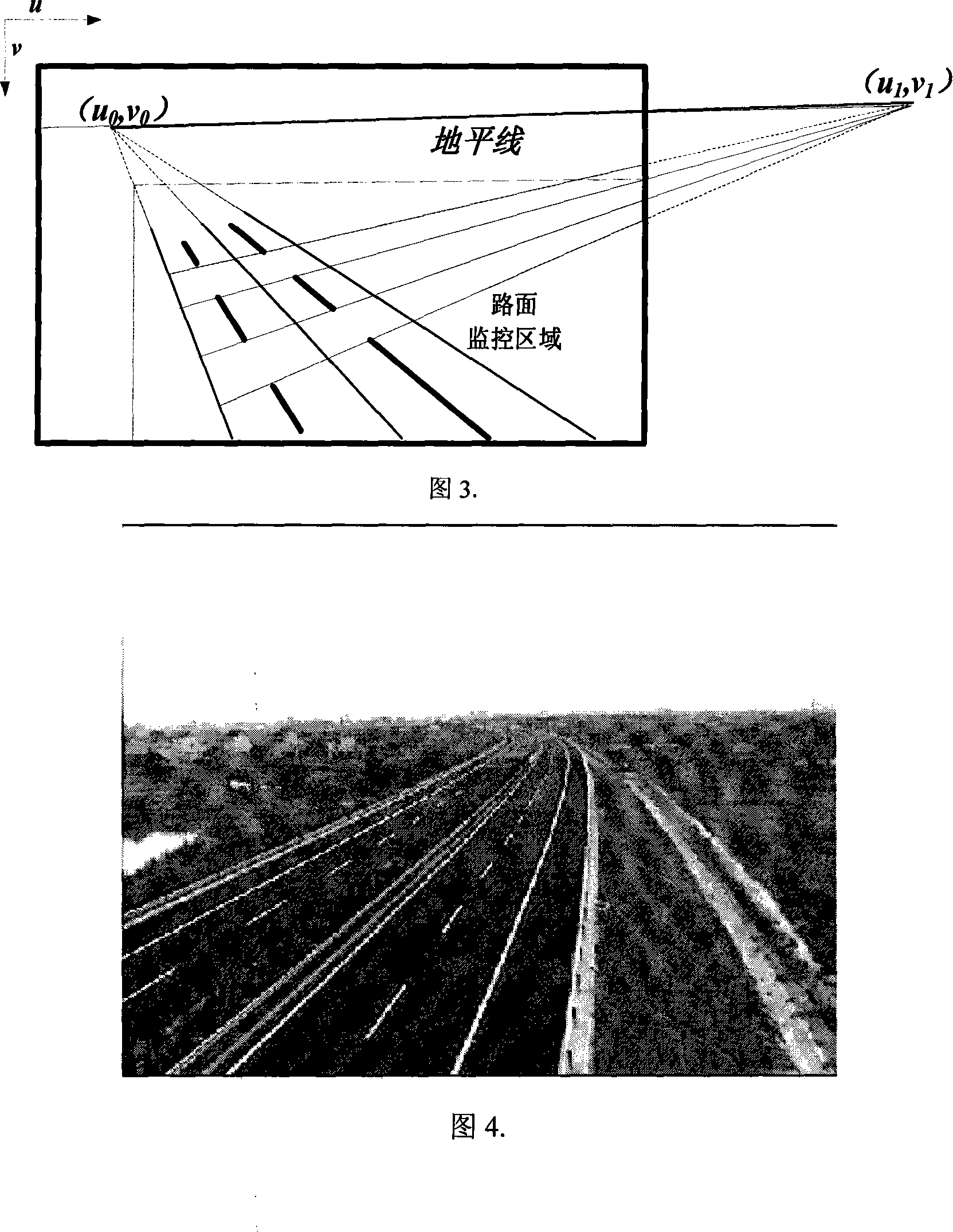
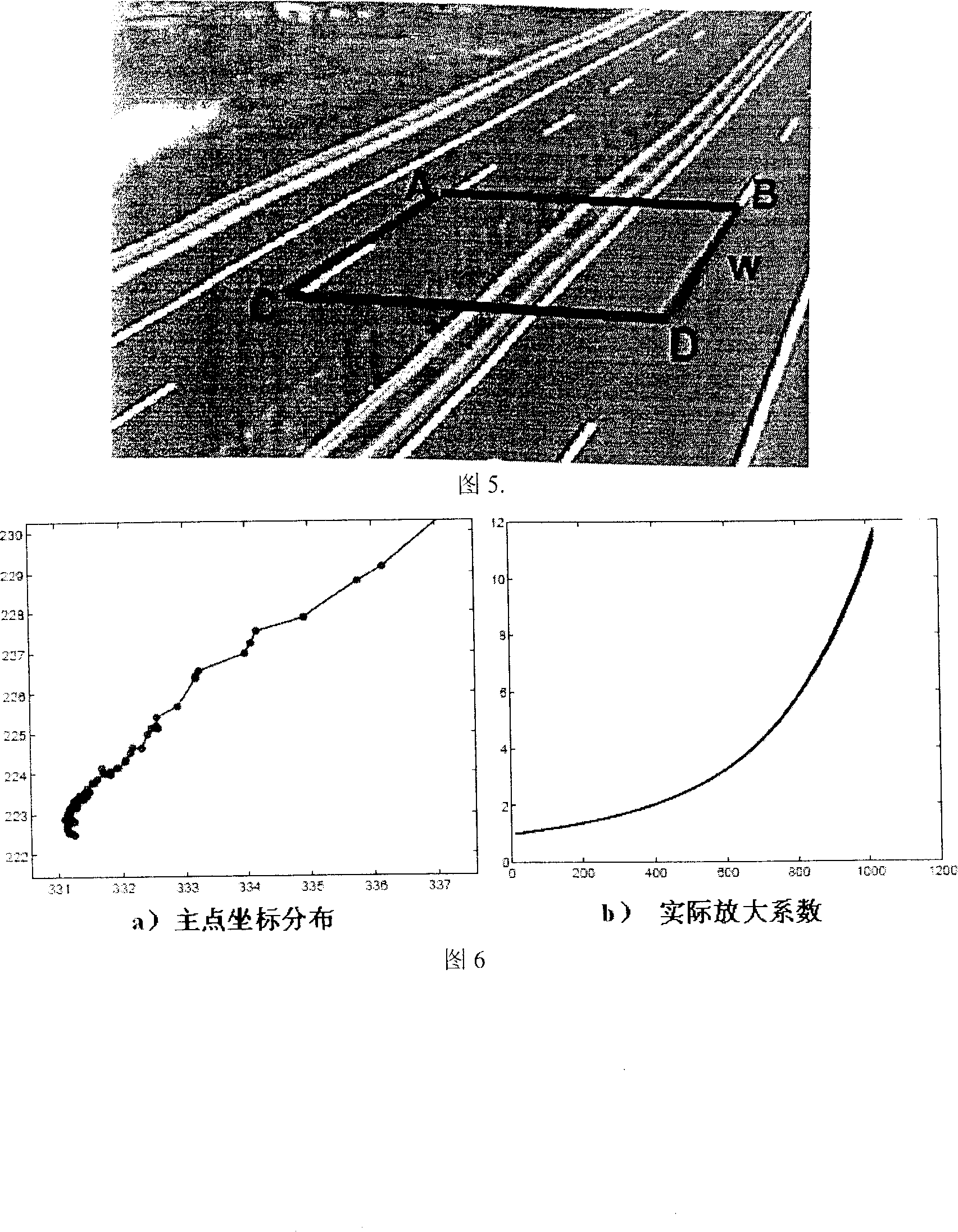
A road condition video camera demarcating method under the traffic monitoring condition includes the following demarcating steps: (1) visual model describing and relevant coordinate system creating: according to the requirement of the monitoring system performance, a classical Tsai transmission projection model is used for reference, and according to the feature of the road condition imaging, a new visual model is presented after conducting corresponding amendment on the classical Tsai transmission projection model, and three kinds of coordinates are established. (2) demarcating the main point of a video camera and the extension factor: the image monitoring light stream is used as the demarcating basic element; by the extension movement of the video camera, a reference frame forecast image and the difference value of the light stream field in a real time frame sampling image are used as the restriction, a constraint equation is established by adopting the least square method, the main point coordinate of the video camera and the actual magnification coefficient of the video camera can be distinguished by the powell direction family method. (3) Demarcated object selecting and parameter linearity evaluating. (4) Accuracy making on the internal and external parameters of the video camera: according to all the angle points of the monitored image and the corresponding world coordinate point, the Levenberg-Marguardt optimization algorithm is adopted to make accuracy on the video camera model parameter, and then the video camera demarcating is finished.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Round array phase interferometer two-dimensional (2D) direction-finding method based on virtual base line
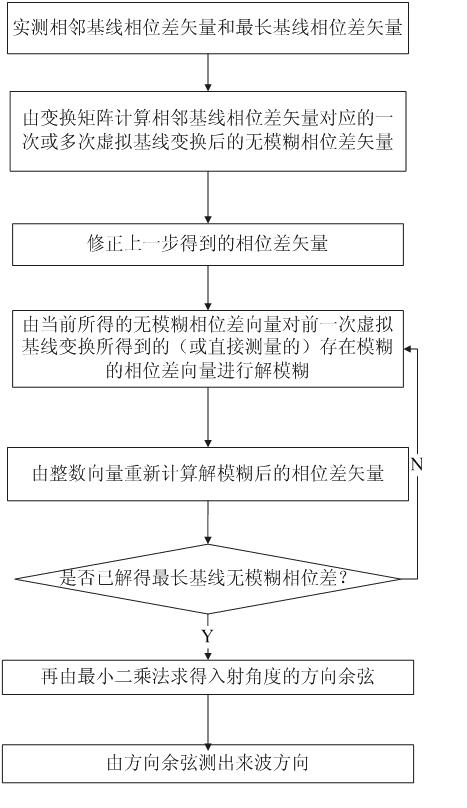
The invention belongs to the technical field of communication radar, in particular relates to a broadband phase interferometer two-dimensional (2D) direction-finding method in radio monitoring. The invention provides a least square phase interferometer 2D direction-finding method based on a virtual base line defuzzification. The method comprises the following steps: firstly performing the virtualbase line conversion on a phase difference vector that is really measured on a short base line and has phase ambiguity once or several times so as to obtain a non-ambiguity virtual phase difference vector corresponding to the short base line; then orderly performing the defuzzification on the virtual phase difference vector, an adjacent base line phase difference vector and the longest base line phase difference vector, which all have ambiguity, according to the virtual phase difference vector, and finally estimating an incident direction by using the least square method according to the non-ambiguity longest base line difference vector. The defuzzification based on the virtual base line conversion provided by the invention can be used for obtaining a high-accuracy and non-ambiguity 2D direction-finding result in existence of angle-measuring ambiguity, and is an efficient 2D angle-measuring algorithm.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
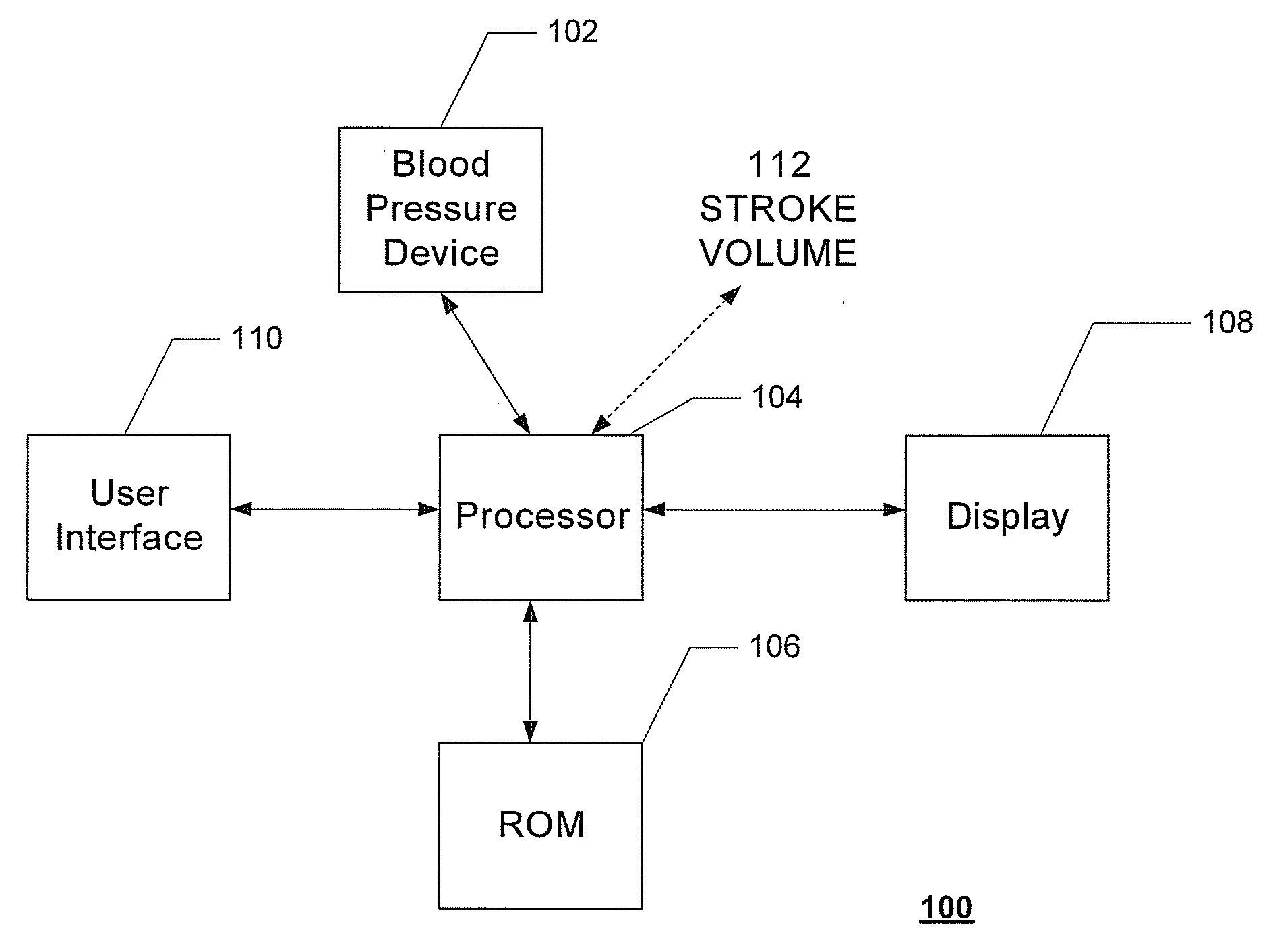
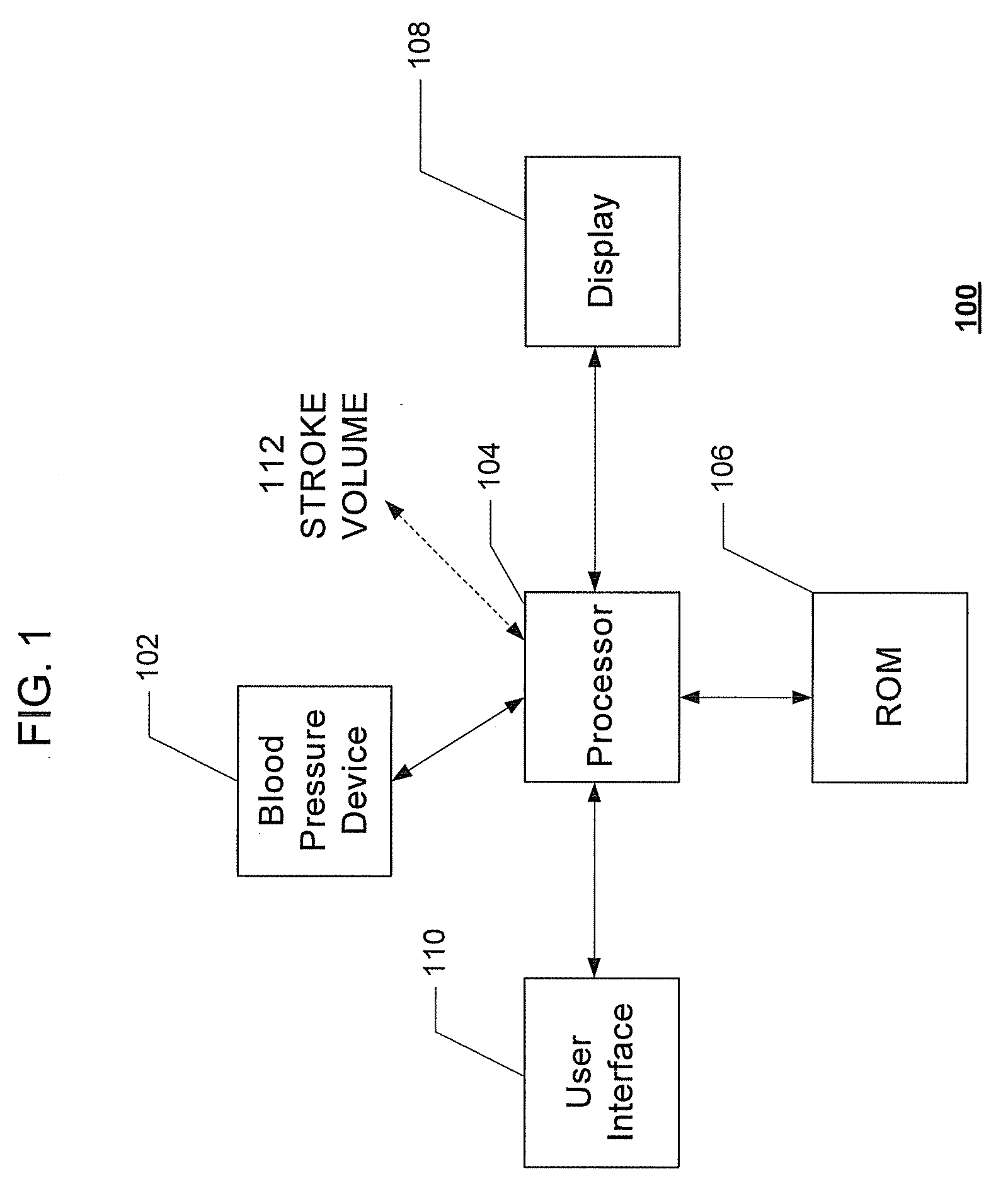
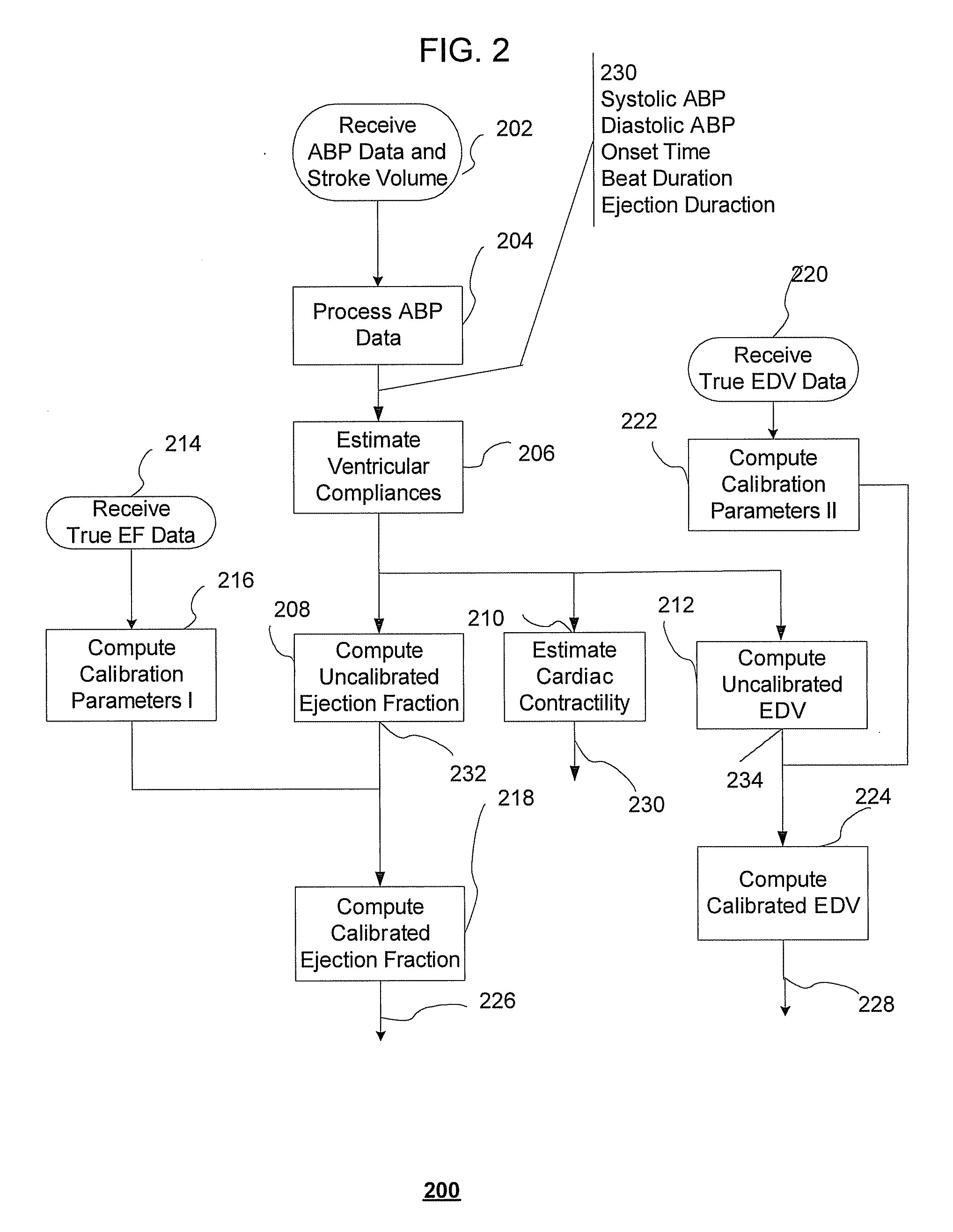
Systems and methods for model-based estimation of cardiac ejection fraction, cardiac contractility, and ventricular end-diastolic volume
The methods and systems for estimating cardiac ejection fraction, cardiac contractility, and ventricular end-diastolic volume on a beat-by-beat basis include observing arterial blood pressure waveforms to determine ventricular compliances for a pressure-volume loop in the ventricle. Uncalibrated or calibrated cardiac ejection fraction may be calculated from estimates of stroke volume and the ventricular compliances. Cardiac contractility may be calculated from estimates of a ventricular compliance. Uncalibrated or calibrated ventricular end-diastolic volume may also be calculated from estimates of stroke volume and the ventricular compliances. A set of calibration parameters for calibrating cardiac ejection fraction or ventricular end-diastolic volume may be estimated in a least-squares manner.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
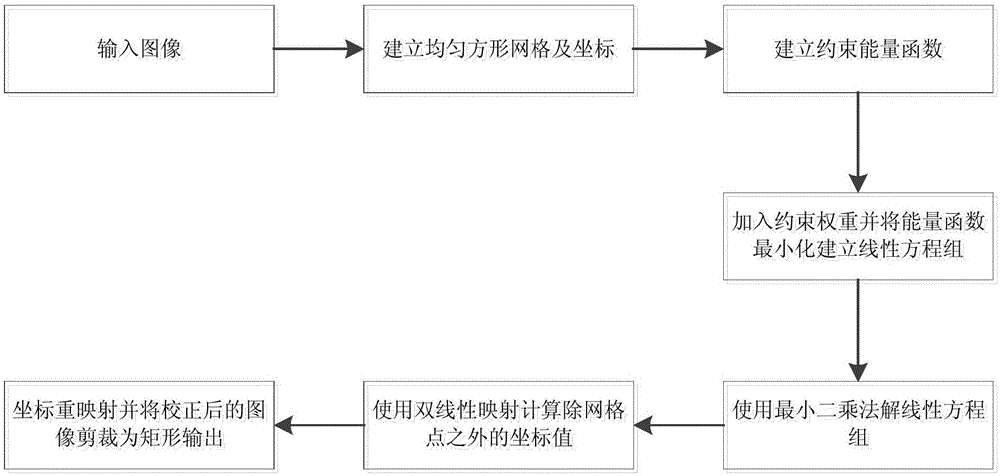
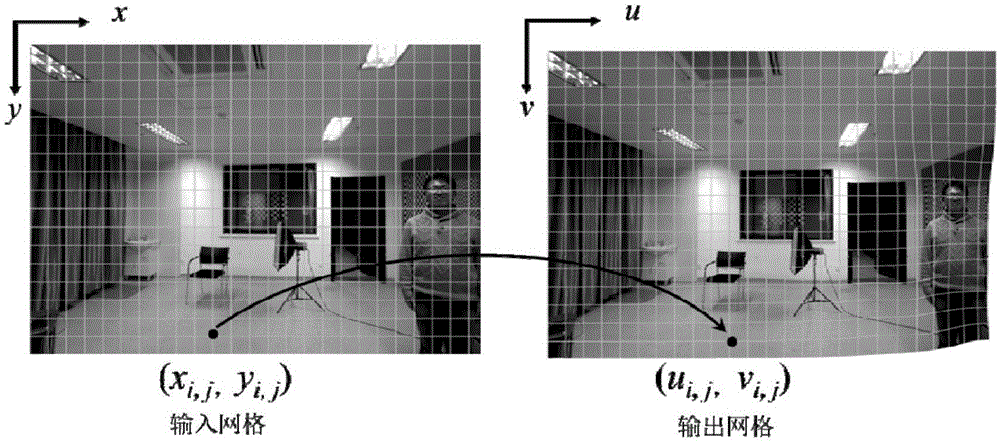
Image stretching distortion adaptive correction method
InactiveCN105046657ANot subject to bendingUncut imaginationImage enhancementImage analysisFace detectionAlgorithm
The invention provides an image stretching distortion adaptive correction method comprising: dividing an image into uniform square grids and establishing an input-output coordinate; determining a person area and a background area by using a face detection algorithm, establishing homographic constraint for each grid in order to correct the stretching distortion appearing in the person area, establishing homographic compatible constraint for adjacent grids in order to guarantee the continuity of the grids; determining a linear area by using a linear detection algorithm and establishing linear maintaining constraint for the linear area in order to protect a corrected line against bending; guaranteeing the uniform continuity of the whole image by means of global coordinate smoothness and uniformity constraint; using an energy function to express the constraint, adding weights and adding the energy equations, computing a coordinate value with the minimum energy by using a least square method so as to obtain a corrected image coordinate value; performing rendering by using bilinear mapping to obtain a final corrected image.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
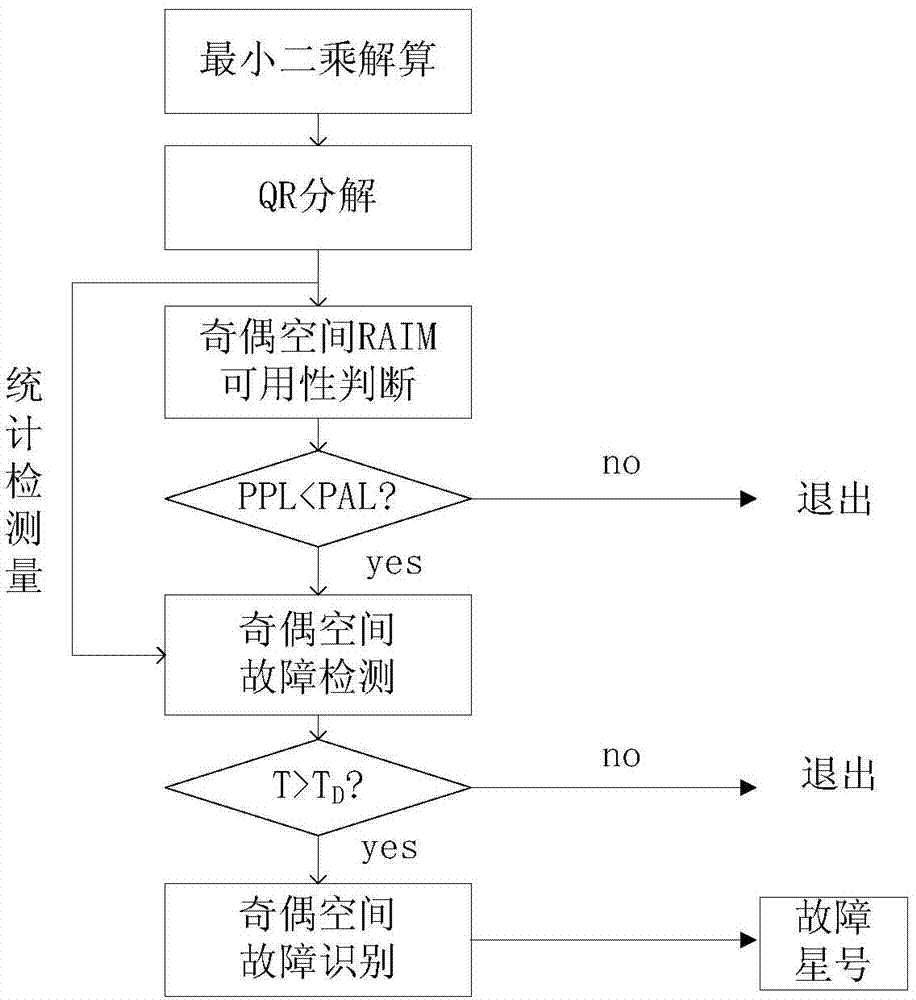
Self-integrity monitoring method suitable for satellite-borne navigation receiver
ActiveCN103592656AReduce computationAvoid complex operationsSatellite radio beaconingQR decompositionUsability
A self-integrity monitoring method suitable for a satellite-borne navigation receiver can reflect statistics detection amount of monitoring data quality by utilizing a pseudo-range information structure of the satellite-borne navigation receiver and detect faulted satellites according to the index requirements of a system and a distribution structure detection threshold obeyed by statistics amount. The self-integrity monitoring method suitable constructs the statistics detection amount of an odd-even space through QR decomposition of a primary observation array and based on the least square method, and carries out usability judgment, fault detection and fault identification in the odd-even space. The self-integrity monitoring method has higher response speed, saves more resources and is more suitable for satellite-borne application.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
Adaptive genetic algorithm-based single-frequency GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) integer ambiguity acquisition method
InactiveCN102736094AReduce correlationAvoid complex calculationsSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceInteger ambiguity
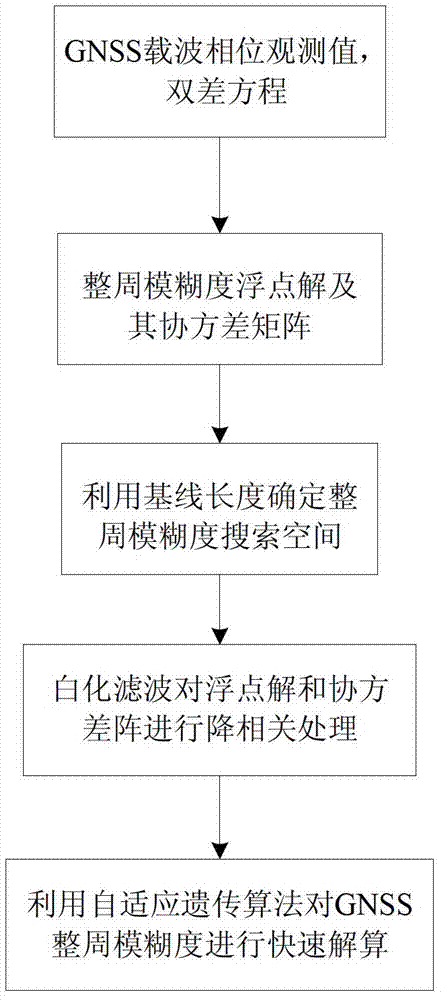
The invention discloses an adaptive genetic algorithm-based single-frequency GNSS integer ambiguity acquisition method. The method includes the following steps: step 1: acquiring the observed data of a GNSS carrier phase, and establishing a double-difference observation equation for the GNSS carrier phase; step 2: according to the double-difference observation equation obtained in step 1, utilizing the least square method to acquire the float solution and corresponding covariance matrix of GNSS integer ambiguity; step 3: utilizing known base length as a constraint condition to determine the search space of integer ambiguity; step 4: utilizing the whitening filter method to decorrelate the float solution and covariance matrix of integer ambiguity obtained in step 2; step 5: according to anobjective function, determining a fitness function, determining each operating parameter in the adaptive genetic algorithm, finally, introducing the adaptive genetic algorithm into fast solution on integer ambiguity, and searching the optimal solution of integer ambiguity.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Broadband signal arriving direction estimation method based on iteration spectral reconfiguration
InactiveCN103091661AOvercoming the defect of requiring angle pre-estimationOvercoming the defect of angle pre-estimationRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsFourier transform on finite groupsCovariance matrix
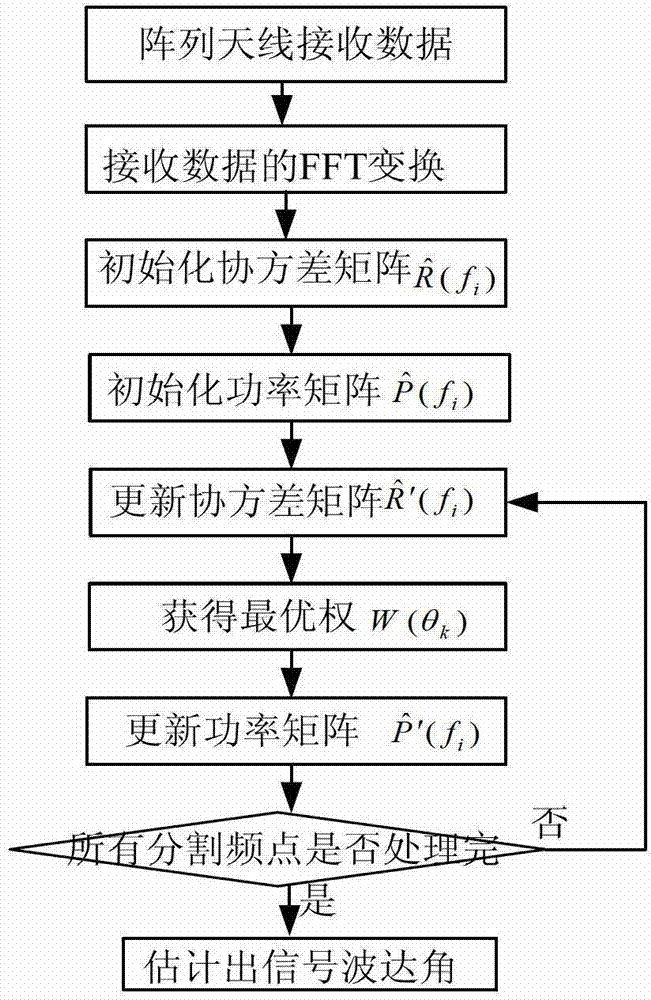
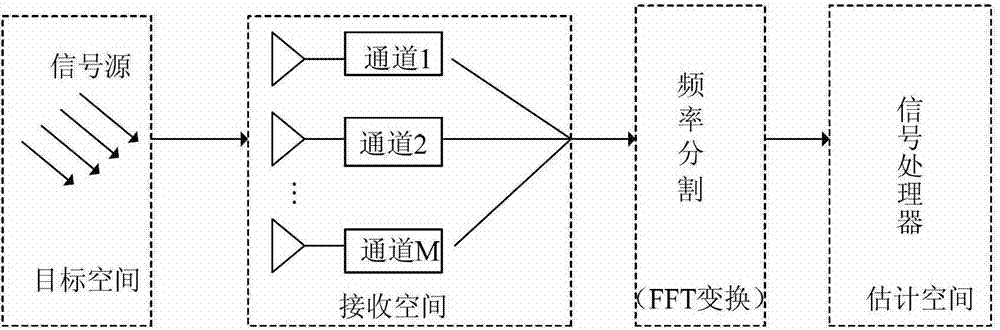
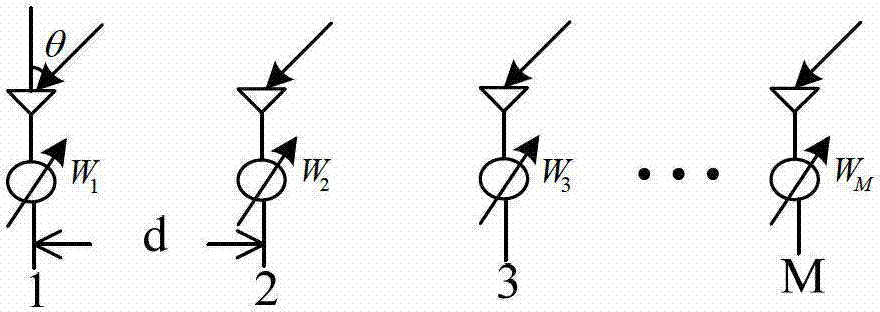
The invention discloses a broadband signal arriving direction estimation method based on iteration spectral reconfiguration. The realizing process comprises the steps of transforming array antenna receiving data into a frequency domain through windowing Fourier transform, conducting multi-sub-band frequency domain segmentation to the data in the frequency domain, initializing each covariance matrix of each sub-band, obtaining an initialized power matrix of a frequency point according to a covariance matrix of one frequency point in the sub-bands, updating the covariance matrix of a signal at the position of the frequency point according to the initialized power matrix, obtaining corresponding optimum weight of a search angle space by the adoption of the least-squares method, updating the power of each corresponding angle according to the optimum weight on each search angle to obtain the initialized power matrix of a next frequency point and conducting iteration process, and estimating the signal arriving direction through a power spectral peak of the search angle space. The broadband signal arriving direction estimation method based on the iteration spectral reconfiguration can estimate the signal arriving direction of an incidence signal source under the conditions of weak signals and short data, is high in precision, and has the advantage of decorrelation.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Far-field narrow-band DOA estimation method based on covariance matrix sparse representation
InactiveCN103983944AIncrease the amount of calculationImprove estimation accuracyRadio wave finder detailsAlgorithmSpace power
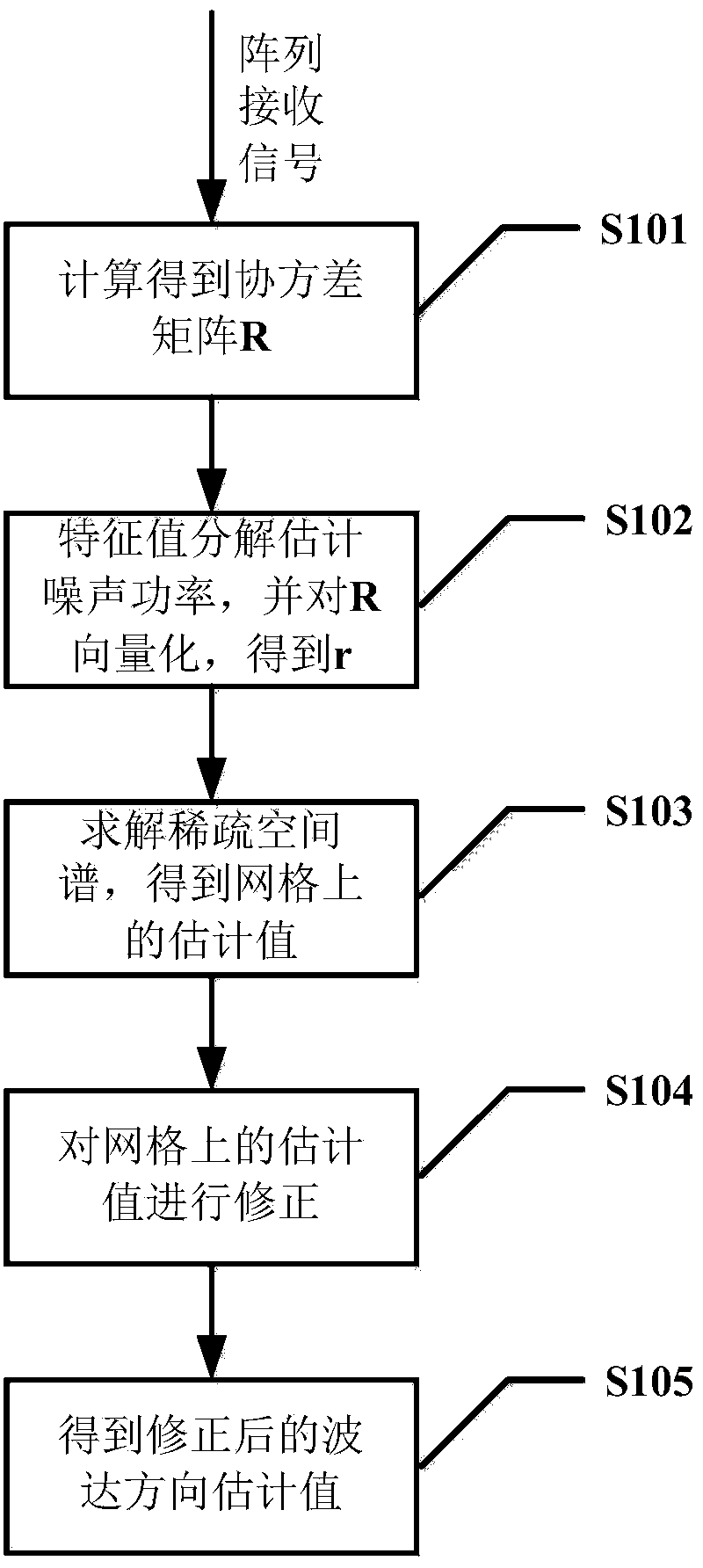
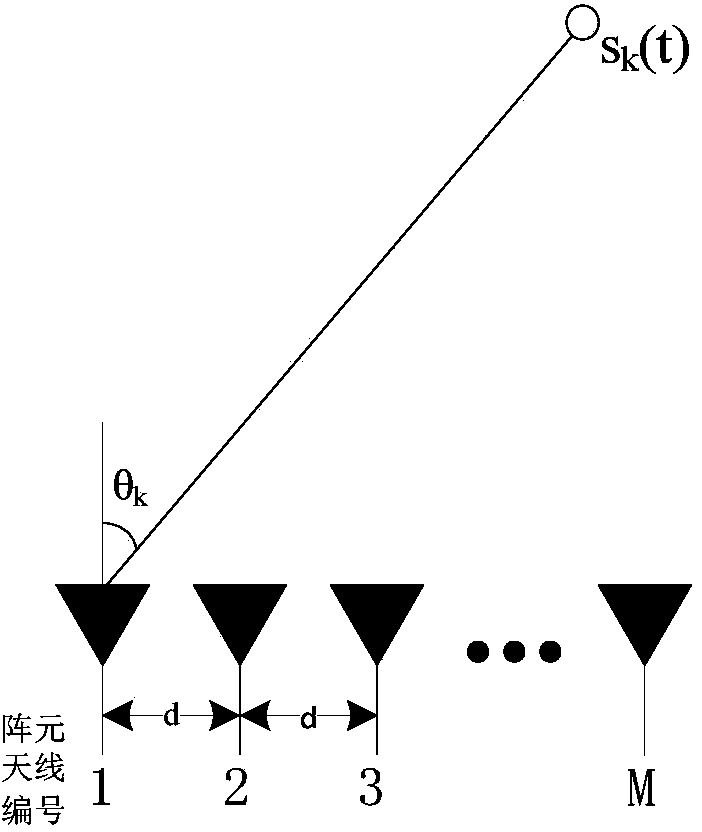
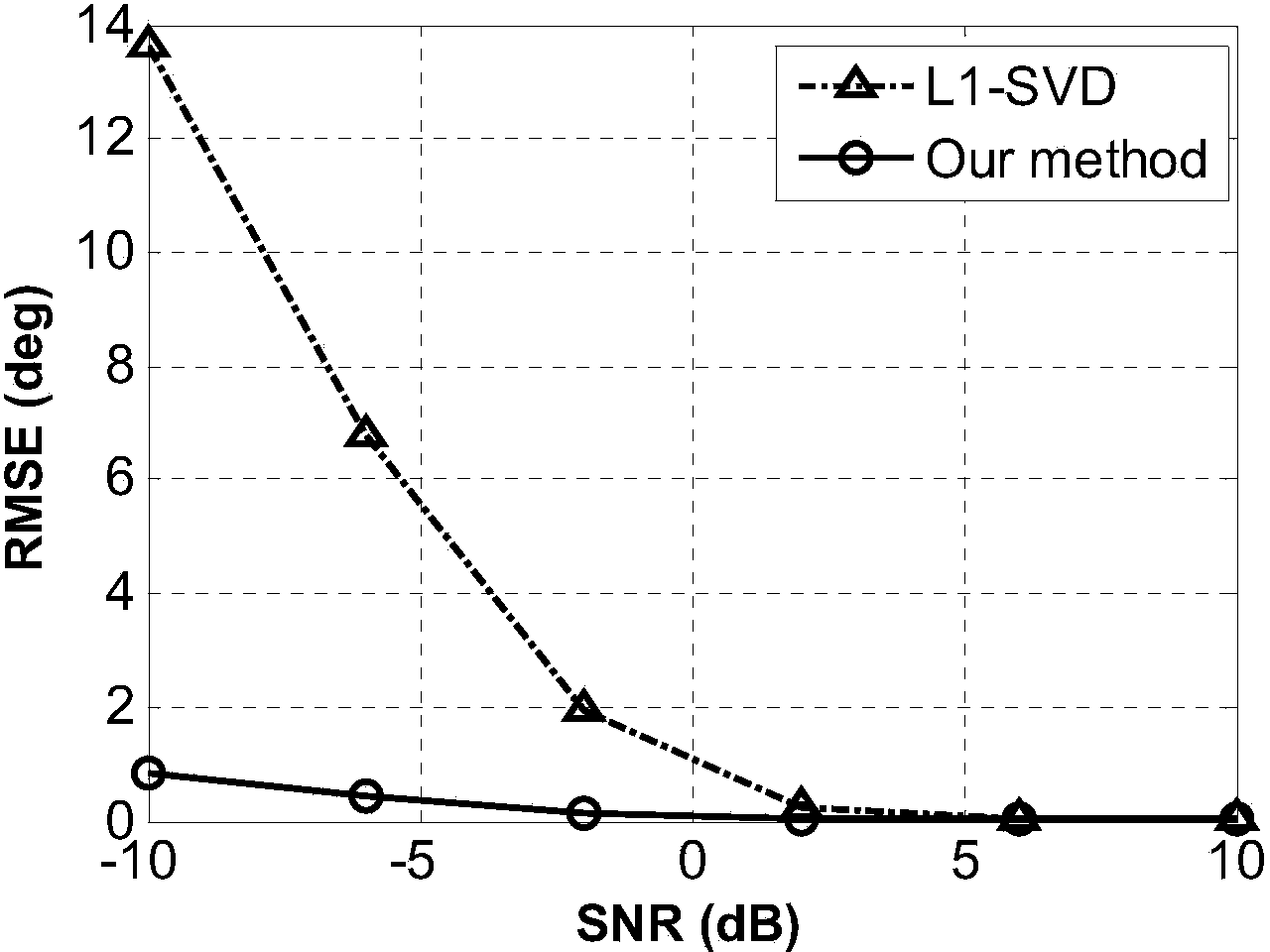
The invention provides a far-field narrow-band DOA estimation method based on covariance matrix sparse representation. Based on the sparsity on a space domain in the wave arrival direction, a covariance matrix is changed into a sparse representation model, under a module with a matched gridding, a sparse space power spectrum is solved through an optimization minimization method, and the point, corresponding to a support set of the power spectrum, on the gridding is the wave arrival direction angle obtained through estimation. For the condition that the actual wave arrival direction angle is not on the gridding, namely under a model with the mismatched gridding, a first-order Taylor expansion method is adopted to approach the guide vector of the actual wave arrival direction angle, and then the point, obtained through estimation, on the gridding is corrected through a least-square method to achieve higher estimation accuracy. The far-field narrow-band DOA estimation method based on covariance matrix sparse representation can achieve high-accuracy DOA estimation performance on the rough gridding.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
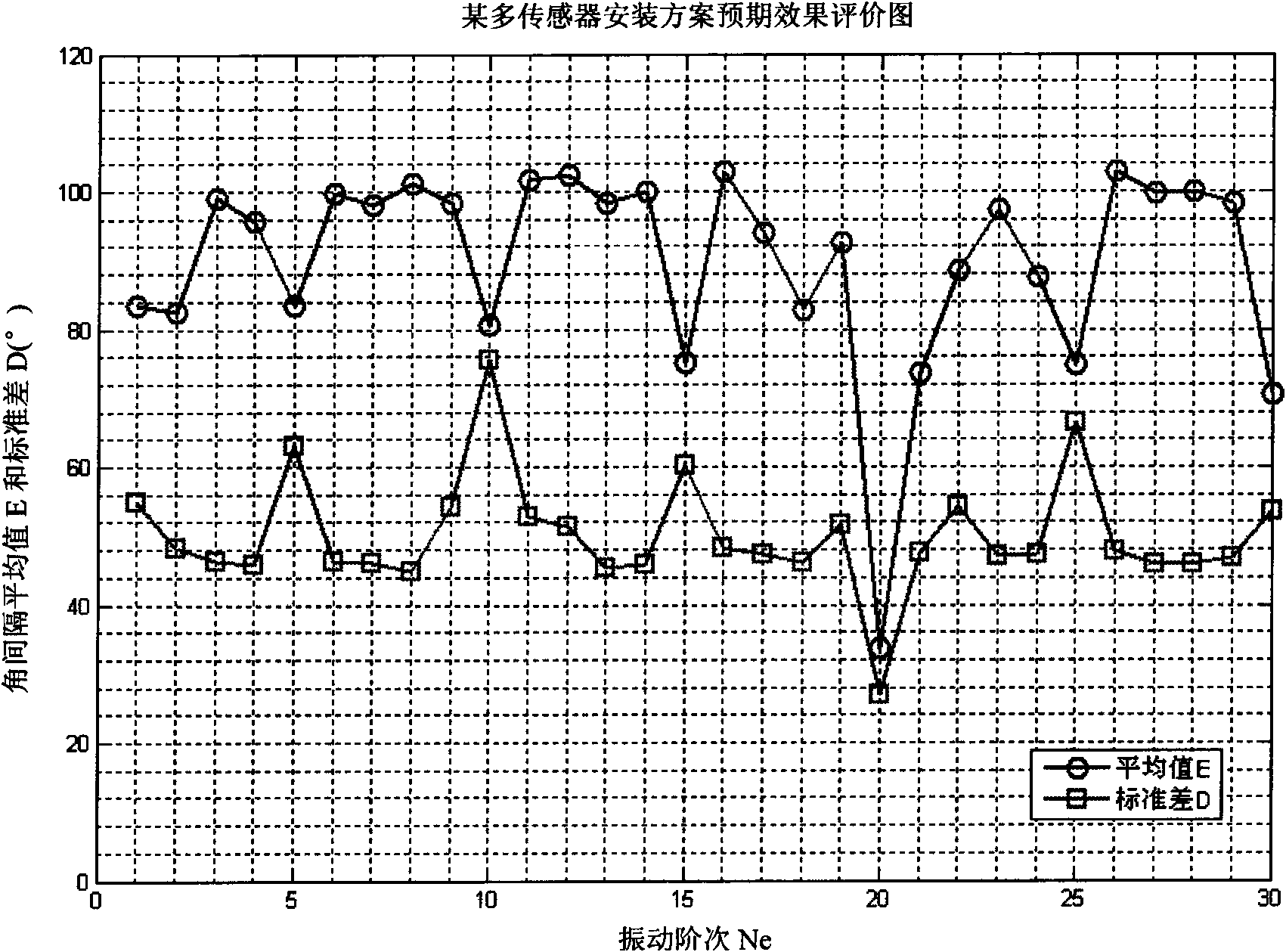
Method for detecting synchronous vibration parameters of high-speed rotary blade under constant speed
ActiveCN101629846AEasy to measureMeet the needs of real-time online monitoringVibration measurement in solidsResonant frequencyDouble ValueMultiple sensor
The invention relates to a method for detecting vibration of a blade of a rotary machine, in particular to a method for detecting synchronous vibration parameters of a high-speed rotary blade under a constant speed. In order to eliminate limitation of taking uniform variable speed running as a precondition and meet the demand of real-time online monitoring, the invention adopts the technical scheme that based on a bladetip timing vibration detection principle, the synchronous vibration displacement yi of a certain blade, detected by a bladetip timing sensor, is indicated as following: yi=Asin(Nealphai+Phi0)+C(i=0,1,2...). A frequency doubling traversal range containing actual synchronous vibration frequency doubling Ne of the blade is selected, and then an actual installing included angle alphai of the bladetip timing sensor and the selected frequency doubling Nej are substituted into the formula so as to work out the vibration displacement of different frequency doubling corresponding to a multiple-sensor theory measured by a least square method; the square and the radix of an error between the calculated vibration displacement and the vibration displacement of actual measurement are worked out, and the frequency doubling of the minimum value of the square and the radix of the error is taken as the frequency doubling value of the actual vibration of the blade in a frequency doubling traversal process. The invention is mainly applied to the method for detecting the vibration of the blade of the rotary machine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHONGXIN POWER MEASUREMENT & CONTROL TECH
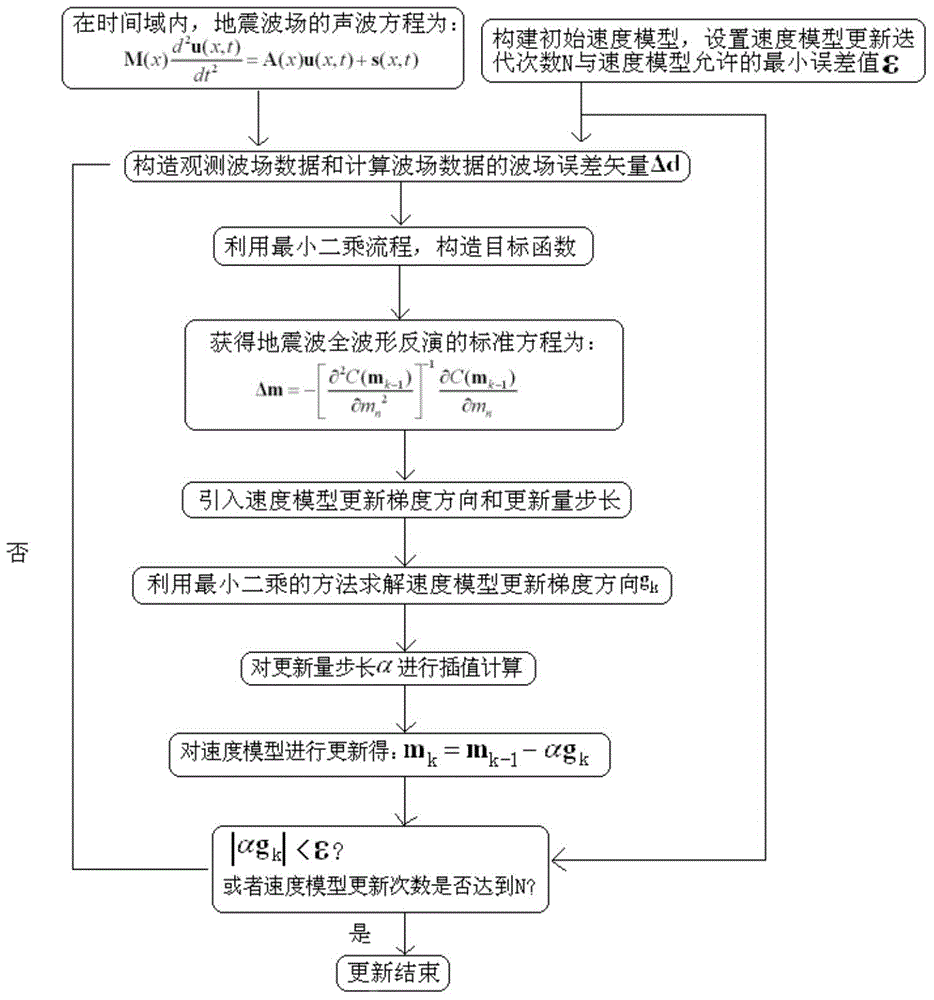
Seismic wave full waveform inversion method based on least square gradient update speed model
ActiveCN105005076AImprove update gradient accuracyQuick updateSeismic signal processingWave fieldFull waveform
The present invention relates to a seismic wave full waveform inversion method based on a least square gradient update speed model, comprising the following steps: 1) obtaining a sound wave equation of a seismic wave field in time domain; 2) constructing an initial speed model, setting a speed model update iteration number N and an allowed minimum error value epsilon; 3) constructing observation wave field data and calculating a wave field error vector of the wave field data; 4) constructing an object function; 5) calculating the object function to obtain a standard equation of seismic wave full waveform inversion; 6) introducing a speed model update gradient direction g<k> and an update amount step length alpha; 7) solving the speed model update gradient direction g<k> by using a least square method; 8) performing interpolation calculation for the update amount step length alpha; and 9) updating the speed model, wherein m<k>=m<k-1>+alpha*g<k>; when |alpha*g<k>| < epsilon or the update number of the speed model reaches the speed model update iteration number N, ending the update of the speed model; otherwise, entering into the step 3). The seismic wave full waveform inversion method of the present invention can quickly achieve update of the speed model, and can be widely applied in seismic wave full waveform inversion.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
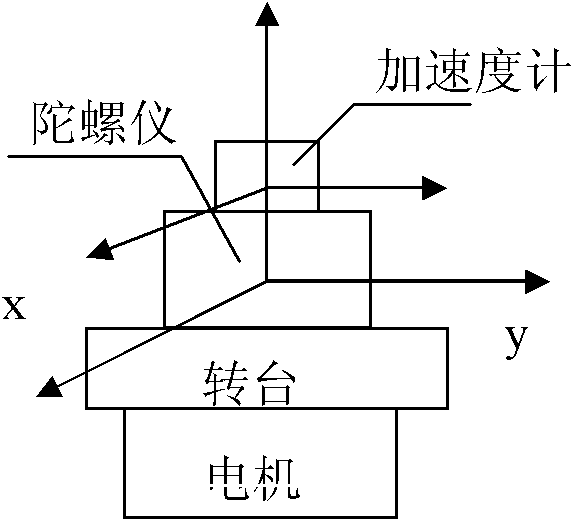
Dynamically rotary modulated north-seeking method for gyroscope
InactiveCN102840856AReduce system errorNorth Seeking ExpressSagnac effect gyrometersRotary gyroscopesGyroscopeAccelerometer
The invention belongs to the field of an inert measuring technique or geophysical experiment and instrument, in particular to a dynamically rotary modulated north-seeking method for a gyroscope. The dynamically rotary modulated north-seeking method for the gyroscope provided by the invention aims to realize fast and precise north-seeking measurement under the condition that a carrier has a large attitude angle without leveling or knowing the latitude of a measuring point, so that the speed of geodesic operation is improved. A rotary table which rotates uniformly at an angular speed Omega is used. The rotary table is provided with the gyroscope and two accelerometers. The method comprises the steps of: first, solving an angle of pitch and a roll angle by the two accelerometers; then, solving the geographic latitude L and a course angle by the gyroscope; and after calculating an initial value, improving the precision by using a real time recursive least square method. The dynamically rotary modulated north-seeking method for the gyroscope provided by the invention has the advantages that fast and precise north-seeking measurement can be realized under the condition without leveling or knowing the latitude of the measuring point, so that the speed of geodesic operation is improved.
Owner:西安测绘研究所
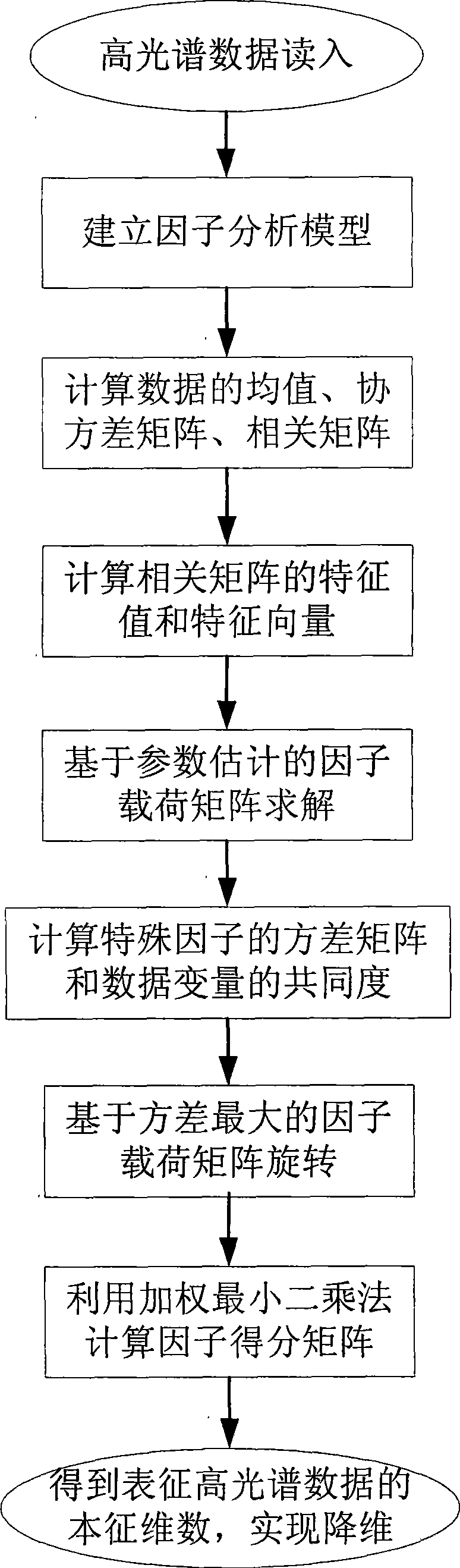
High-spectrum data dimensionality reduction method based on factor analysis model
InactiveCN101487892AMaintain propertiesEliminate dependenciesWave based measurement systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmCovariance
The invention provides a method for reducing dimensions of high spectroscopic data based on a factorial analysis model, comprising the following steps: (1) reading in the high spectroscopic data; (2) establishing the factorial analysis model for dimension reduction of the high spectroscopic data; (3) calculating average of data, covariance matrix and correlation matrix; (4) calculating proper value and standard eigen vector of the correlation matrix of the data; (5) carrying out solving on factor loading matrix by a parametric estimation method; (6) calculating covariance of special factors and communality of data variables in the factorial analysis model; (7) calculating the biggest factor loading spin matrix based on variance; (8) calculating factor scores by a least square method based on variance; and (9) obtaining eigen dimensionality characterizing high spectroscopic data, thereby realizing dimension reduction of the high spectroscopic data. The method is an automatic method for dimension reduction of the high spectroscopic data, which can effectively remove relativity of wave bands of the high spectroscopic data and improve separability of different categories of ground objects.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
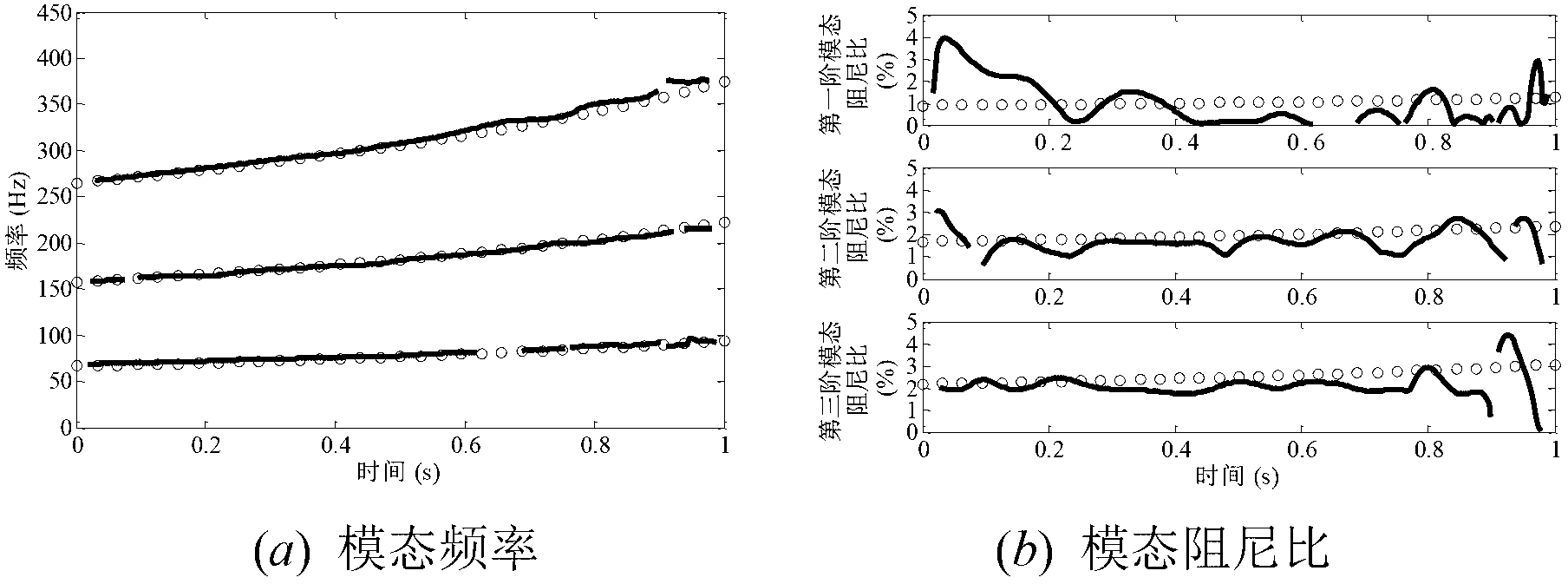
Time frequency domain time varying structure modal parameter identification method based on time varying common demominator model
ActiveCN102982196AReduce engagementEasy to useSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainStructural dynamics
The invention relates to a time frequency domain time varying structure modal parameter identification method based on a time varying common demominator model and belongs to the technical field of structural dynamics. Firstly, structural dynamics response signals measured and obtained by aircraft or spacecraft structures with the time varying characteristics under the work situations are analyzed in a time frequency mode to obtain a time relative power spectral function of non-parametric evaluation corresponding to time varying structures. Then, the time varying common demominator model is used as a parametric model of the time varying structural dynamics to evaluate to-be-evaluated parameters of the time varying common demominator model through a least squares methods of the time domain. Finally, the evaluated to-be-evaluated parameters of the time varying common demominator model is utilized to calculate the model frequency and the model damping ratio corresponding to the time varying common demominator model. The time frequency domain time varying structure modal parameter identification method based on the time varying common demominator model is suitable for model parameters recognition of time varying structure in the field of aircraft and spacecraft engineering application and has the advantages of being simple and convenient to use. Furthermore, users are low in participation degree.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
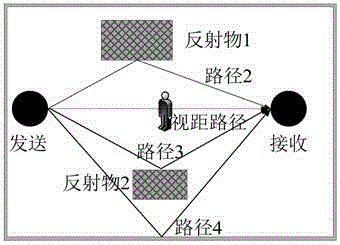
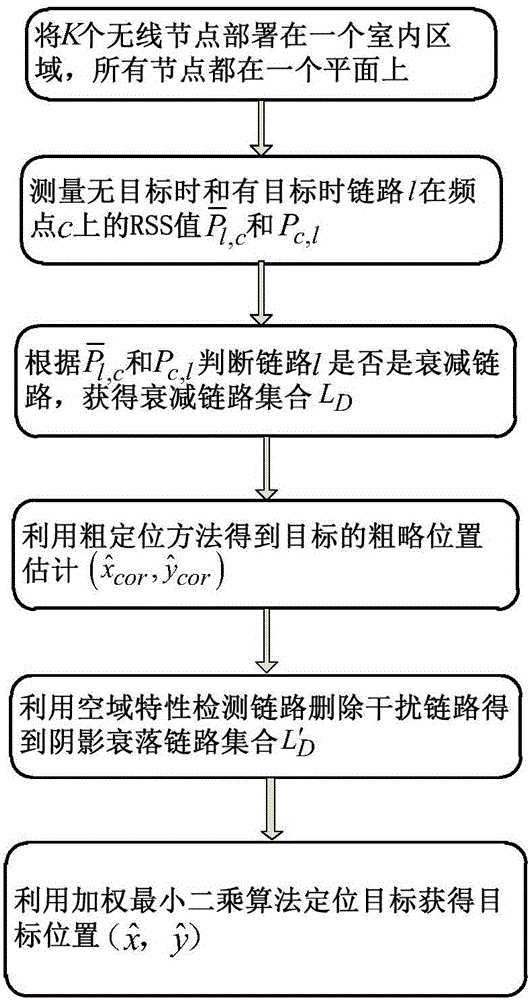
Robust passive passiveness target positioning method based on multiple frequency points
ActiveCN105116375AEasy to detectHigh positioning accuracyPosition fixationUltrasound attenuationEngineering
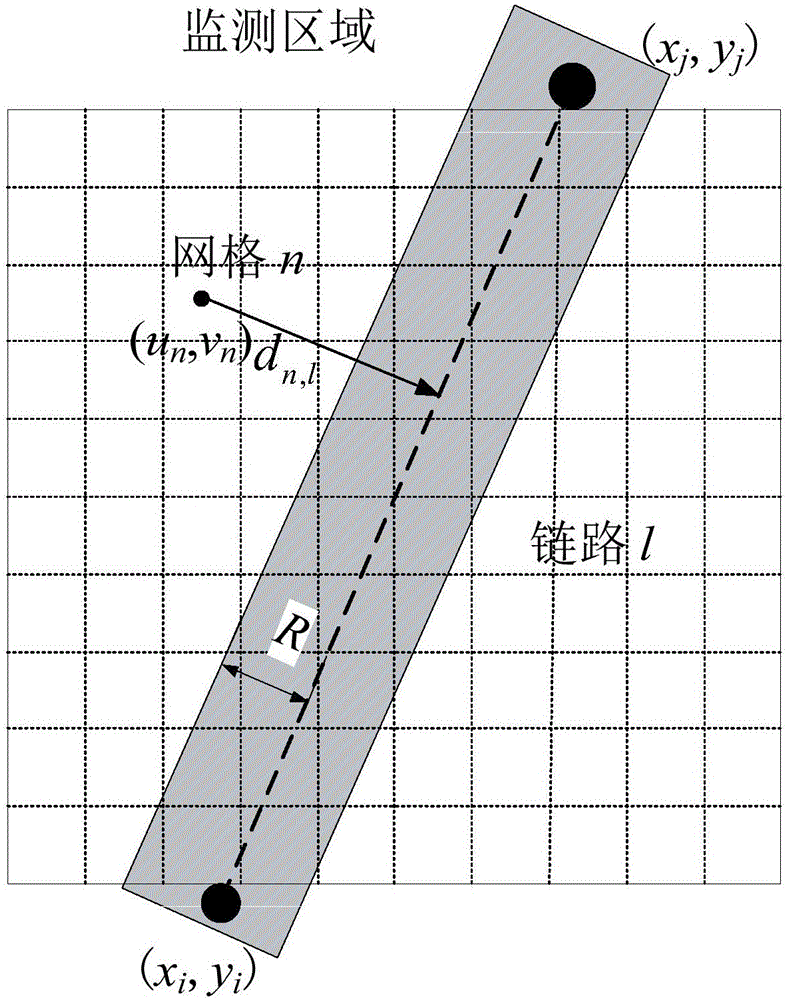
The invention discloses a robust passive passiveness target positioning method based on multiple frequency points, and belongs to the technical field of target detection and positioning in a wireless network. The method detects an attenuation link through measurement of a variable quantity of an RSS value of a link on the multiple frequency points, deletes an interference link through coarse positioning of a target to obtain a shadow attenuation link set, and then performs accurate positioning on the target by utilizing a weighted least square method. Compared with attenuation link detection under a single frequency point, attenuation link detection adopted in the method based on the multiple frequency points has better performance in indoor multi-path environment, can improve detection performance and positioning precision of the target in a monitoring region, and can reduce the false alarm probability of a system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Pseudo-range differential positioning method of long base line
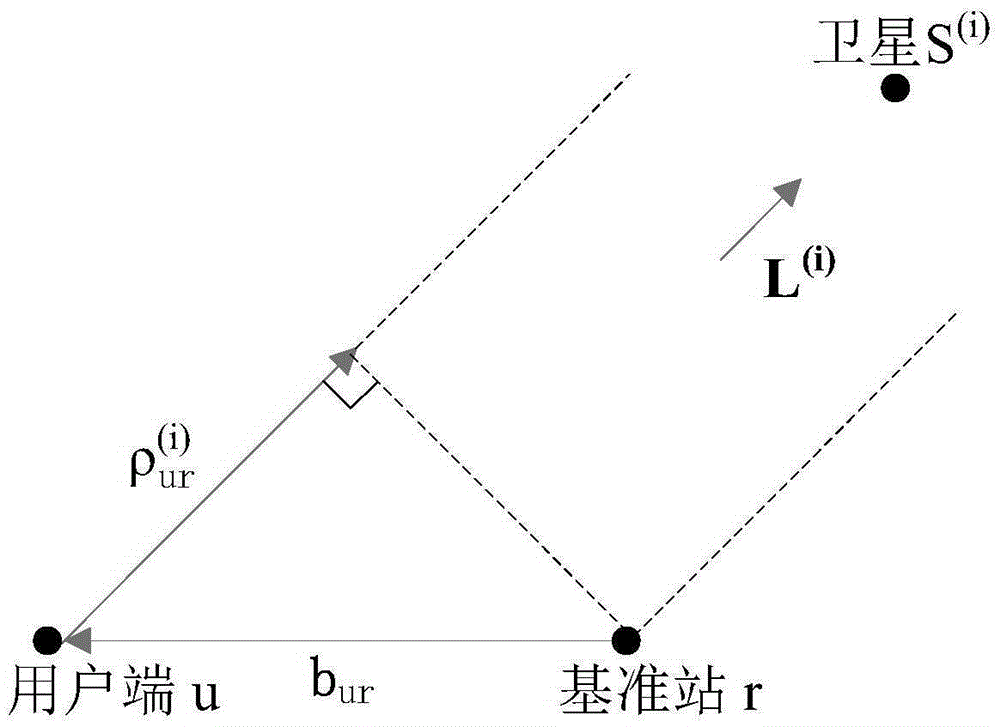
InactiveCN105242292ASolve the problem that the positioning error is also gradually increasingEliminate errorsSatellite radio beaconingEngineeringLeast squares
The invention provides a pseudo-range differential positioning method of a long base line. A plurality of satellites, a user terminal and a base station form a satellite navigation pseudo-range differential model. A pseudo-range single-different equation relative to one same satellite is constructed by using pseudo-range observation equations of the base station, the user terminal, and the satellites; with pseudo-range single-different equations of different satellites, a non-linear pseudo-range dual-difference equation group containing multiple satellites is constructed; and then a position of the user terminal is obtained by using the Newton's method and the method of least squares. According to the positioning method, errors of the pseudo-range differential positioning model under base lines with different lengths can be eliminated and thus the increase with increasing of the length of the base line is prevented, so that a small error range can be kept and thus a high-precision positioning requirement can be completely met.
Owner:NO 20 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
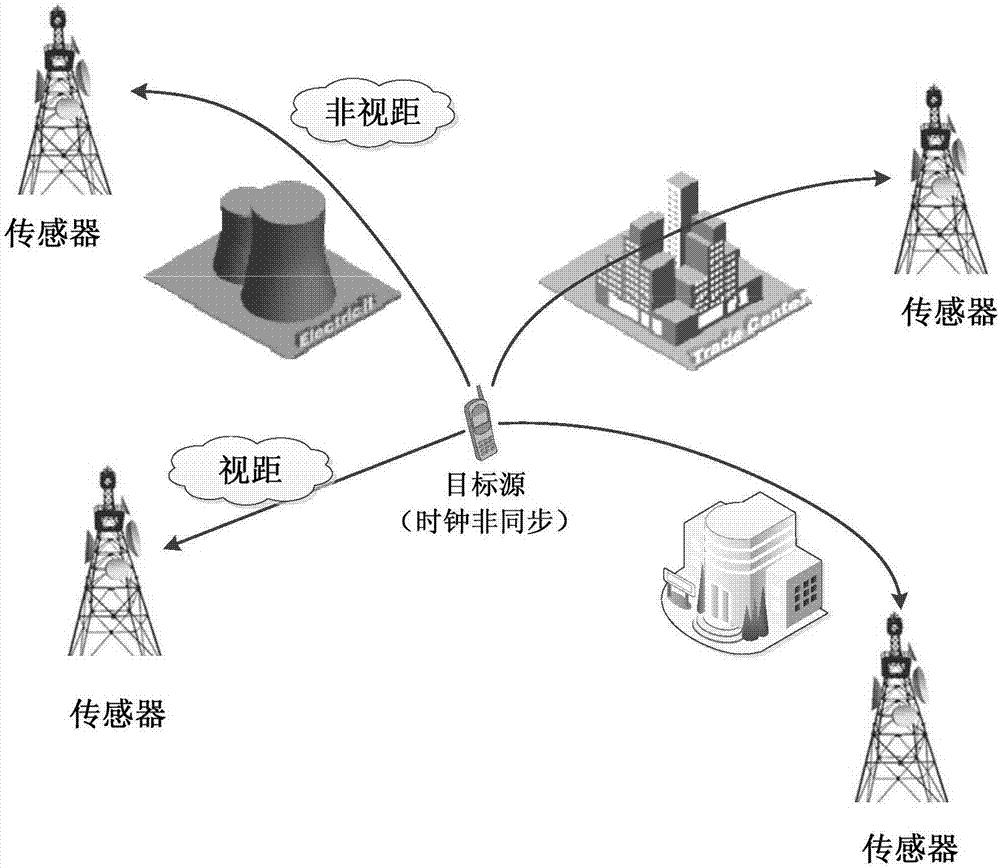
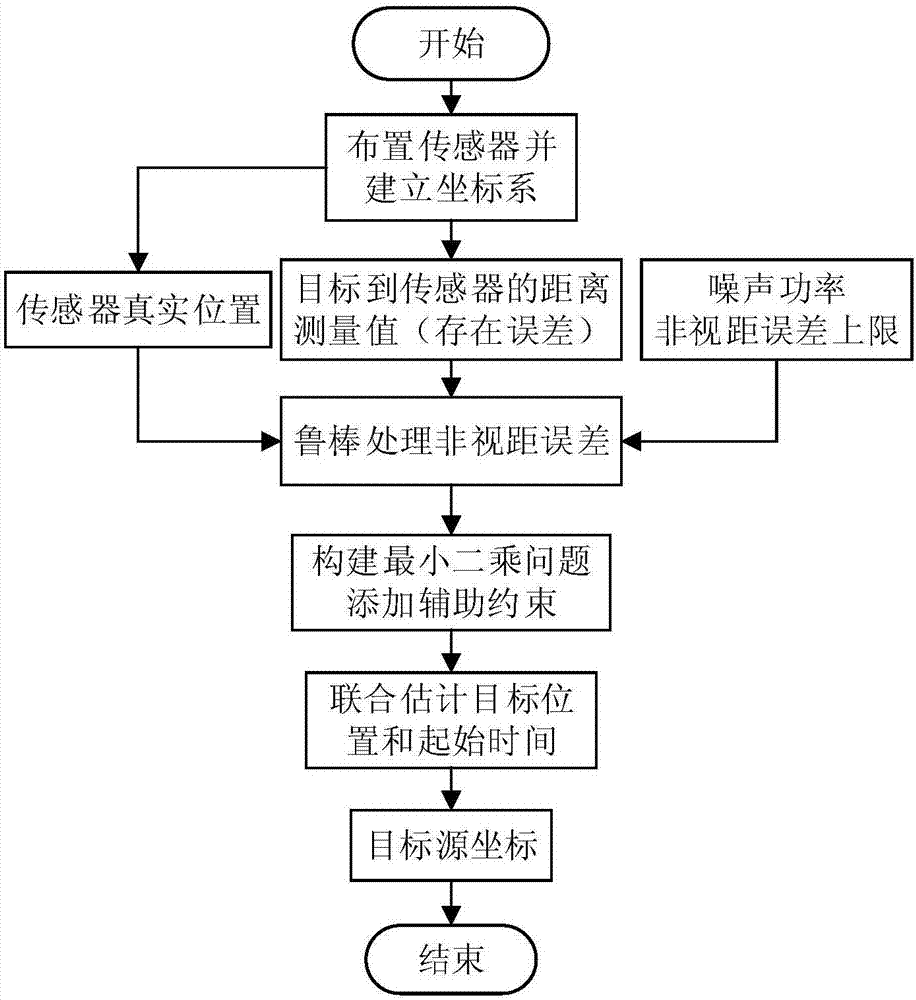
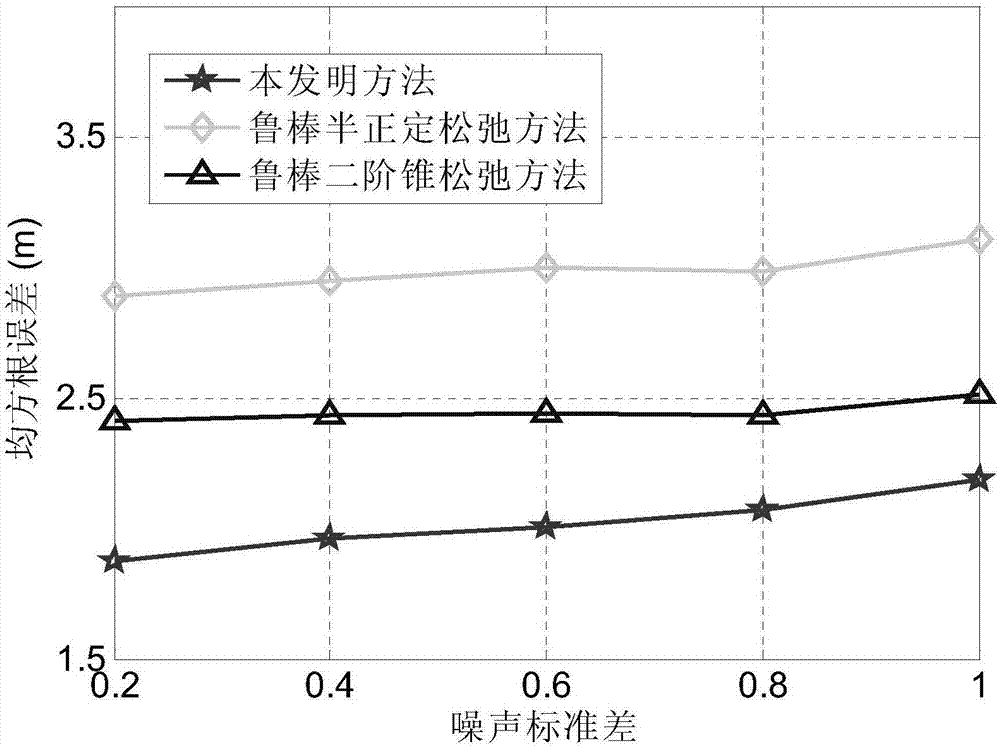
Positioning method based on arrival time of unknown starting time in non-line-of-sight environment
ActiveCN107271956APrecise positioningAdequate performance advantagePosition fixationStart timeInterior point method
The invention discloses a positioning method based on arrival time of unknown starting time in the non-line-of-sight environment. The method comprises steps of firstly establishing a model of a signal transmission distance between a target source and each sensor; obtaining a description of the measurement noise based on the model; according to the description of the measurement noise, using the robust weighted least squares method under the worst case to obtain the positioning problem in the environment of unknown signal transmission start time and non-line-of-sight errors, and converting the positioning problem into a non-convex positioning problem; by introducing auxiliary variables and using the second-order cone relaxation method, obtaining a second-order cone programming problem; and finally, using the interior point method to solve the second-order cone programming problem to get the final estimation value of the coordinate position of the target source in the reference coordinate system. The method has the advantages of being capable of simultaneously solving the problems of the unknown signal transmission start time and the non-line-of-sight errors so as to improve the positioning accuracy.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
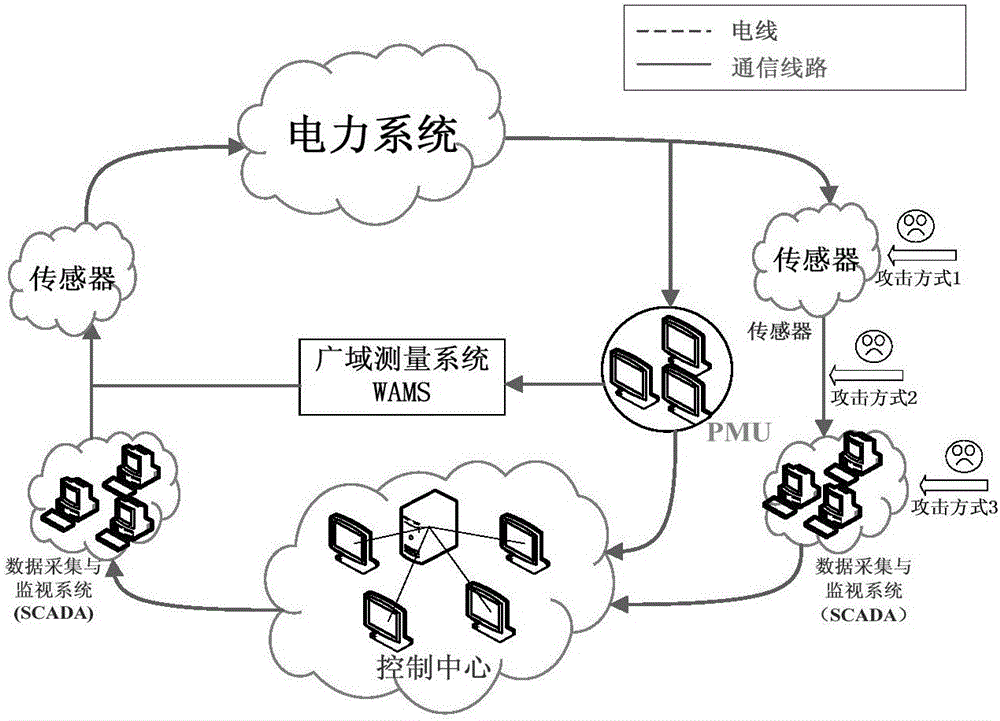
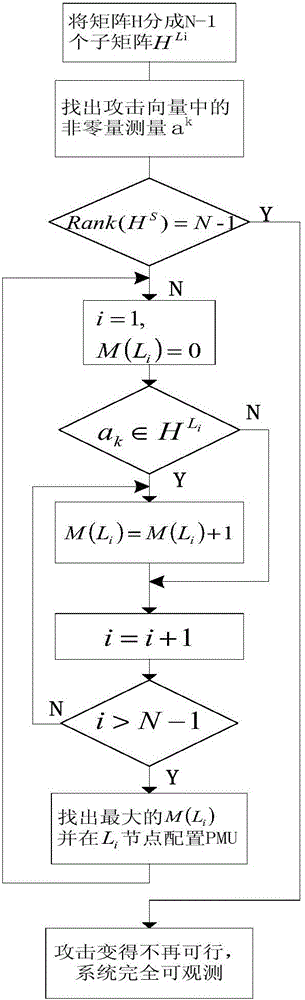
Method for defending data integrity attack in direct state estimation of power system
ActiveCN105791280AIntegrity attack implementationIntegrity Attack BlockingDigital data protectionPower oscillations reduction/preventionAttack modelData integrity
The invention discloses a method for defending a data integrity attack in direct state estimation of a power system. The method comprises the following steps: estimating a real-time state of a direct current system by using a weighted least square method; constructing a minimum cost data integrity attack model to simulate the behavior of an attacker; resolving the minimum cost data integrity attack by using an algorithm based on linear transformation to obtain an optimal attack vector at the moment; if the current optimal attack vector is obtained, realizing a PMU optimized configuration defense strategy based on a greedy algorithm, and after the configuration is completed, the occurrence of the data integrity attack is prevented from the source, and meanwhile, the complete observability of the system is guaranteed. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the data integrity attack in the direct state estimation of the power system can be accurately and quickly defended, and the accuracy and security of the state estimation of the power system are improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
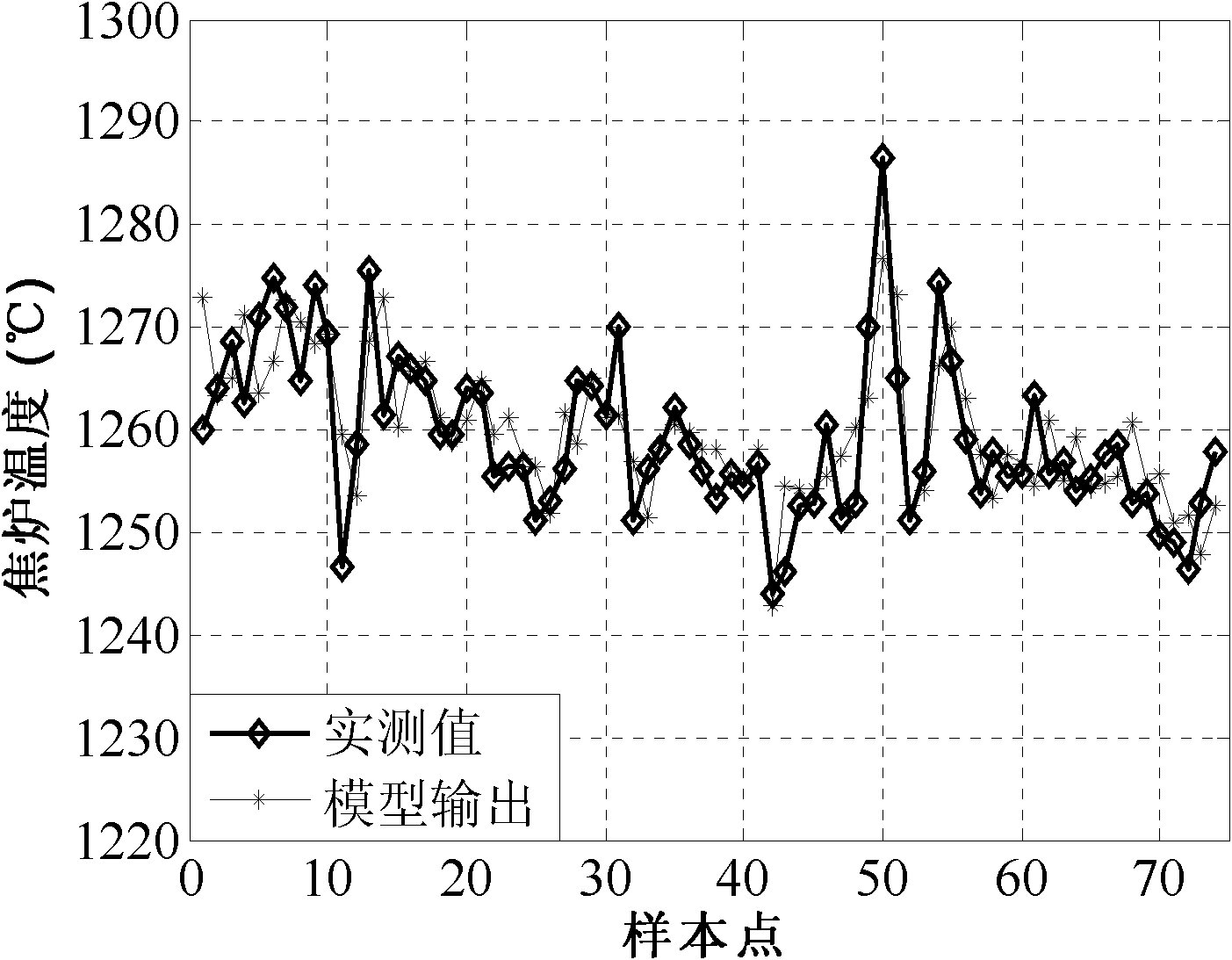
Coke furnace temperature predicting method based on dynamic working conditions in coke furnace heating and burning process
InactiveCN102176221AHigh precisionWith online self-adaptive abilityCombustible gas coke oven heatingSpecial data processing applicationsFurnace temperatureStructure learning
The invention discloses a coke furnace temperature predicting method based on dynamic working conditions in a coke furnace heating and burning process. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1, acquiring gas flow and coke furnace temperature data in various historical working conditions, and establishing a sample bank; 2, calculating the similarity of a current working point and a sample in the sample bank on the basis of an included angle of Euclidean distance and variation trend of the current working point and the sample in the sample bank; and 3, selecting a plurality of sample structural learning sets with maximum similarity; establishing a learning-set-based local linear model by adopting an iterative least square method; and calculating an output value corresponding to the current working point as a coke furnace temperature predicted value in the coke furnace heating and burning process. The coke furnace temperature predicting method based on dynamic working conditions in the coke furnace heating and burning process has high prediction accuracy, and has the online adaptive capability.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
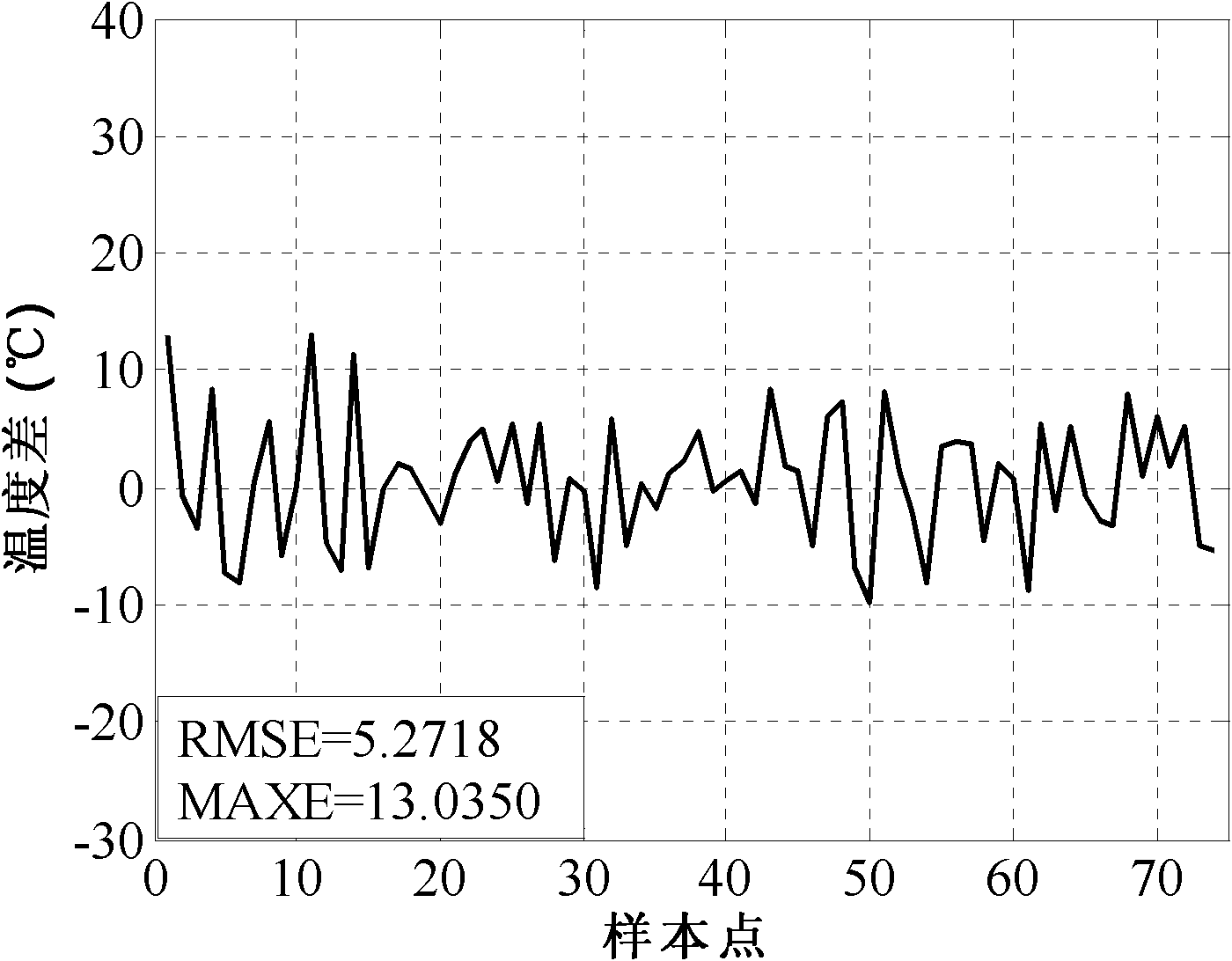
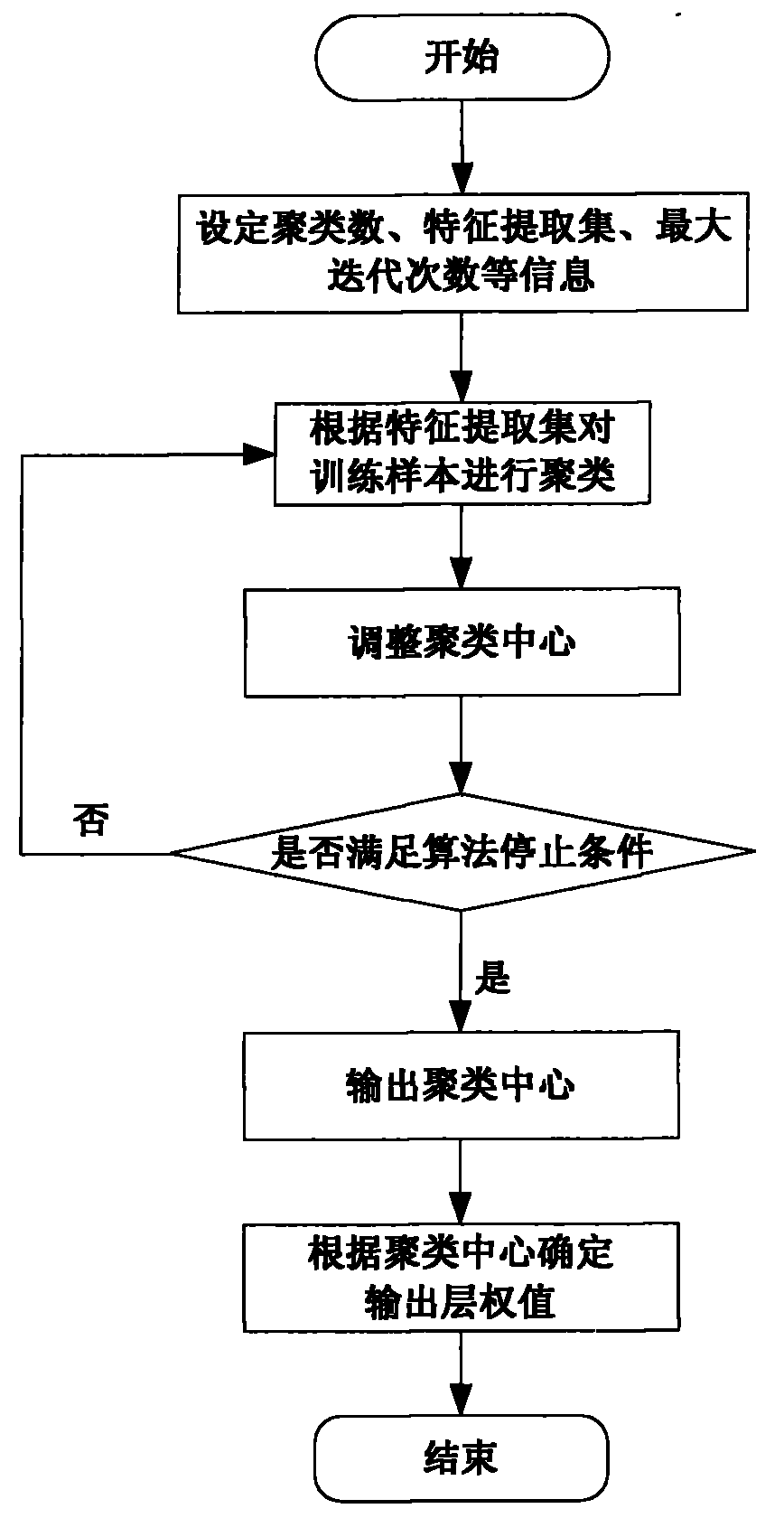
RBF neural network modeling method based on feature clustering
The invention relates to an RBF neural network modeling method based on feature clustering, which belongs to the field of automatic control, information technology and advanced manufacture. The invention particularly relates to an RBF neural network modeling method based on feature extraction function clustering, which can solve the modeling problem that data can be scattered. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: defining a feature extraction function based on existing mechanism knowledge, determining an RBF network center in a clustering algorithm based on the feature extraction function, and determining a weight value from the hidden layer to the output layer of the RBF network in a least square method. The invention also provides a clustering algorithm based on the feature extraction function, which is not used for directly clustering data, but is used for clustering data with scattering features through introduction of the feature extraction function based on the mechanism knowledge. The obtained clustering center is used as the RBF network center, and the weight value from the hidden layer to the output layer of the RBF network can be obtained with a linear interpolation method. The invention can effectively solve the modeling problem that the data has scattering features, and can achieve high modeling accuracy.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
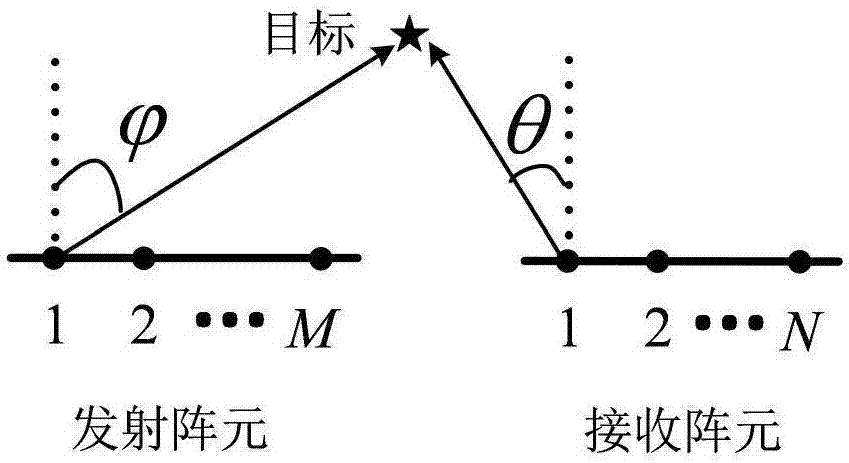
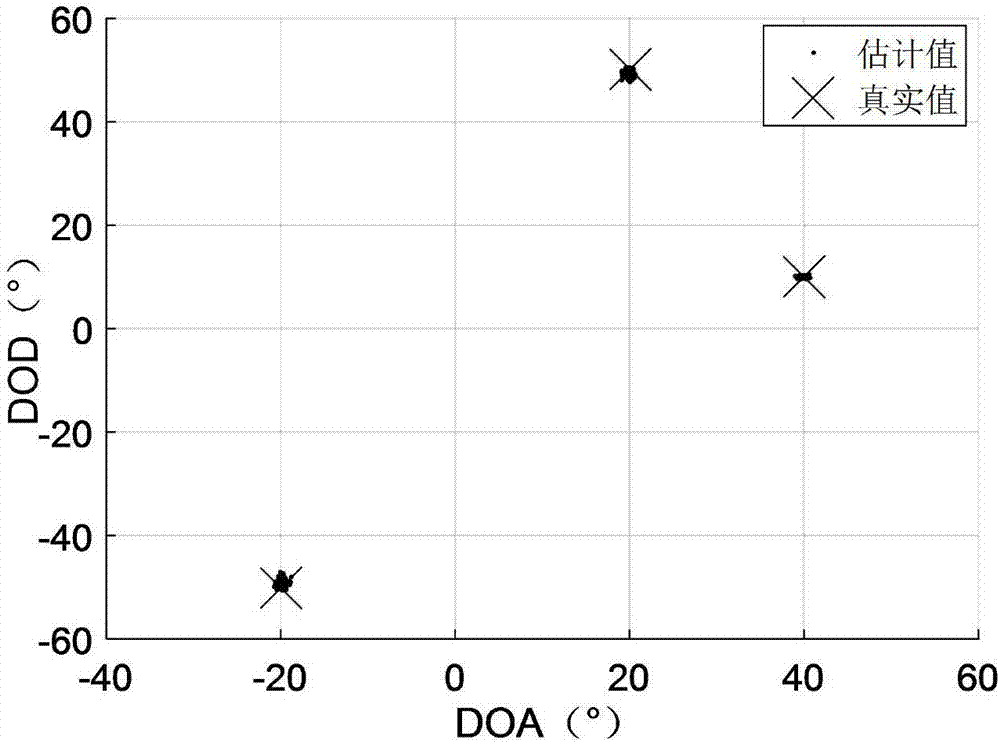
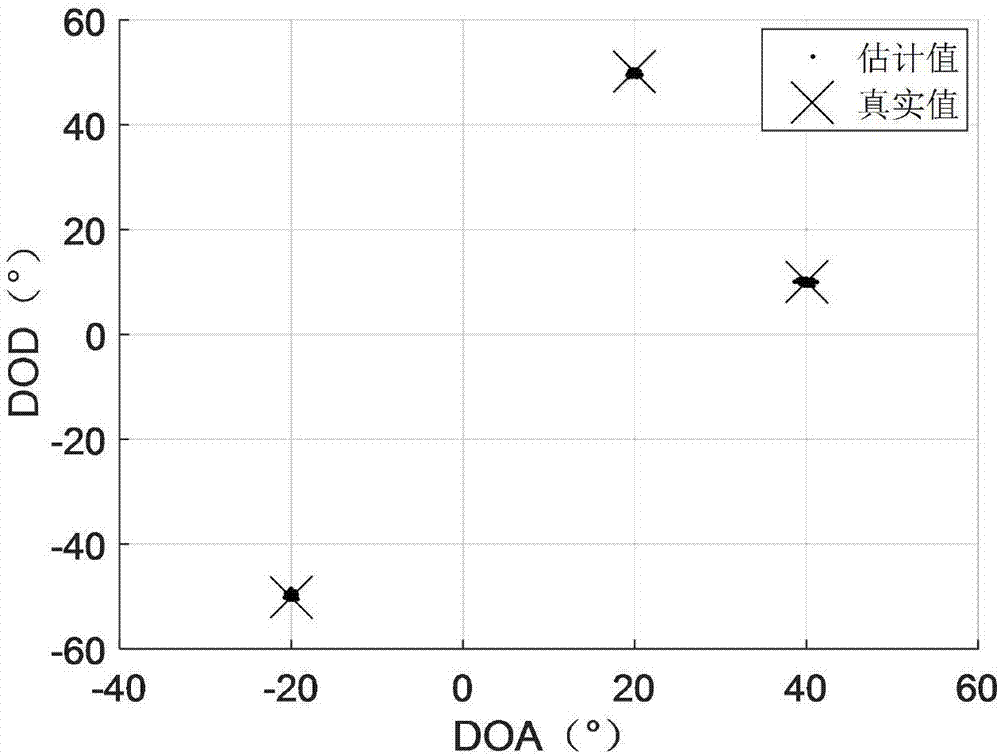
Mutual coupling condition-oriented bistatic MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) radar angle estimation method
ActiveCN107290730ARespond effectivelyReduce mutual coupling effectsRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsComplex mathematical operationsComputation complexityArray element
The present invention discloses a mutual coupling condition-oriented bistatic MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) radar angle estimation method. According to the method, radar data which have been subjected to matched filtering are expressed as a third-order tensor model by means of the multi-dimensional structure of array signals; since a uniform linear array mutual coupling matrix has a strip-shaped Toeplitz feature, the common scale conversion feature of a part of an array element directional matrix is utilized to eliminate the influence of mutual coupling; on the basis of a forward-backward smoothing technique and a unitary transformation technique, the augmented output trilinear model of decoupling-post data is constructed; and joint DOD (direction-of-departure) and DOA (direction-of-arrival) estimation is related with the trilinear model; and a target DOD and DOA are estimated through the least squares method. Compared with a traditional algorithm, the bistatic MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) radar angle estimation method under the mutual coupling condition can effectively deal with situations where mutual coupling exists between a transmitting array and a receiving array, can automatically match the estimated DOD and DOA, and can reduce computational complexity by using a feature that trilinear decomposition only involves real number operation.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
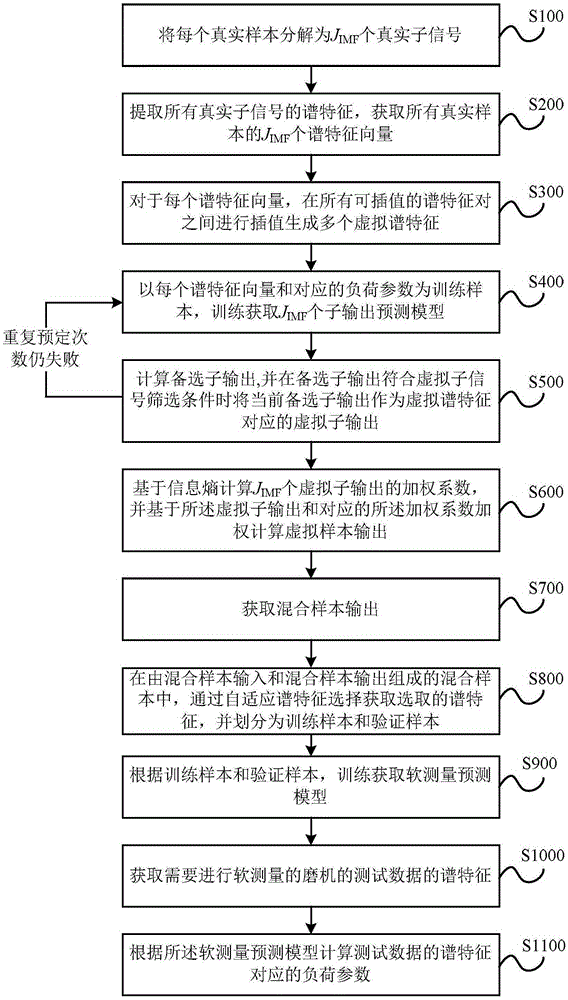
Mill load parameter soft measuring method based on virtual sample
The invention discloses a mill load parameter soft measuring method based on a virtual sample. The mill load parameter soft measuring method comprises the steps of acquiring a multi-dimension time domain sub-signal of mill cylinder vibration and vibration sound sample signal by means of ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) technology, and performing further processing for obtaining high-dimension spectral data with different time dimensions; then constructing a feasibility-based planning (FBP) model based on the high-dimension spectral data according to an improved selective integrated kernel partial least squares (IGASEN-KPLS) method, and generating a new virtual sample based on priori knowledge and an FBP model; then obtaining a mixed sampling model after mixing the new virtual sample with a true training sample, performing adaptive selection of a multiple-dimension spectral characteristic by means of a mutual information (MI) based characteristic selecting method, constructing a soft measuring model by means of the selected spectral characteristics and performing soft measurement.
Owner:中国人民解放军61599部队计算所 +1
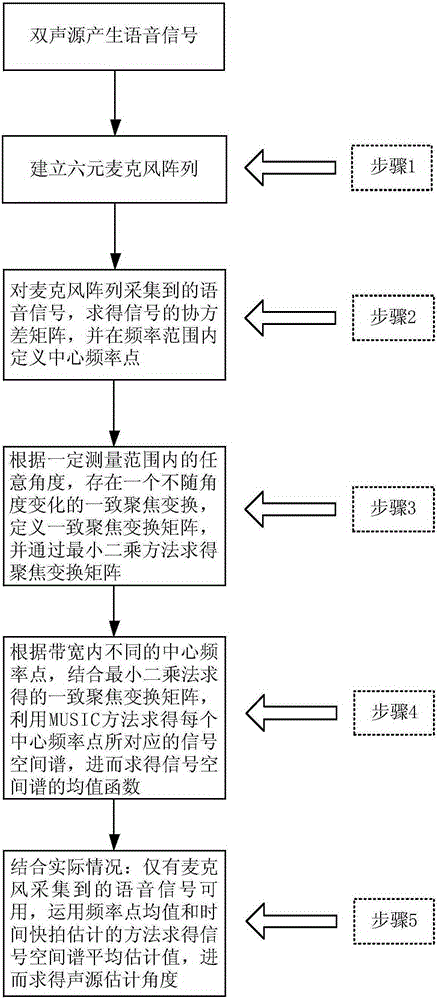
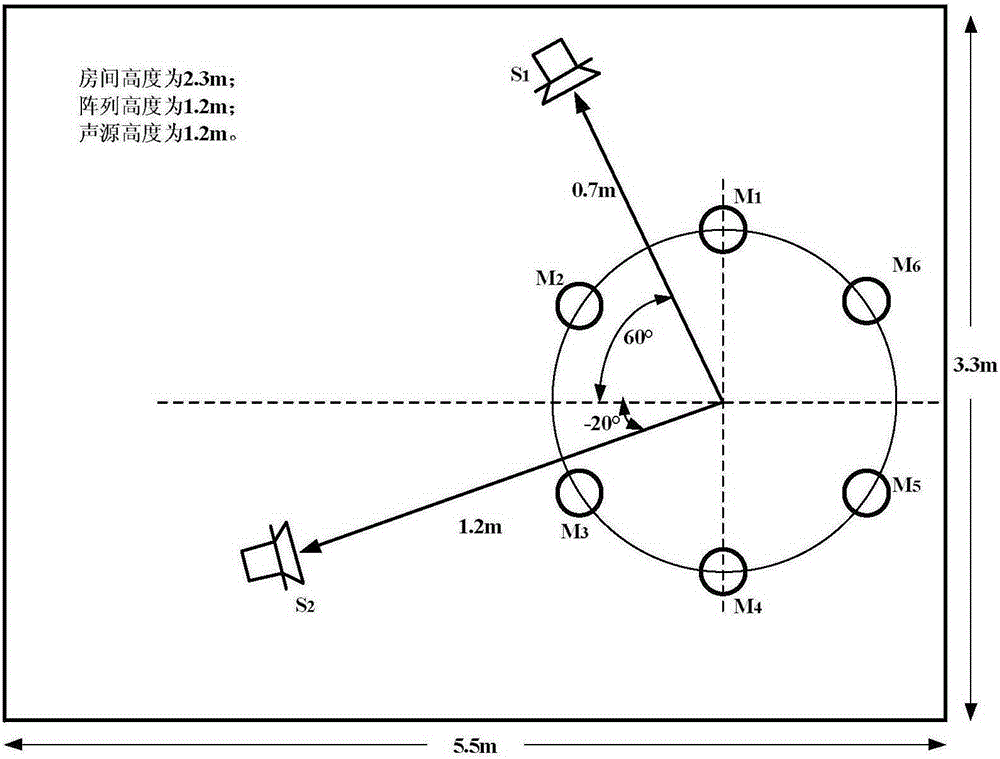
Double sound source localization method based on consistent focusing transform least square method
ActiveCN105301563AReduce distractionsHigh precisionPosition fixationSound sourcesSignal classification
The invention discloses a double sound source localization method based on a consistent focusing transform least square method. According to the method, a predesigned six-element circular microphone array is applied to acquire sound source signals, and the covariance matrix of the acquired signals is acquired; a focusing transform matrix is defined by utilizing the center frequency point of frequency range, and the focusing transform matrix is solved by the least square method; and a signal spatial spectrum corresponding to each center frequency point is acquired by utilizing the center frequency points of different bandwidths, a consistent focusing matrix and a multiple signal classification method, and then the average estimation value of the signal spatial spectrum is obtained by utilizing the average value of the frequency points and a time snapshot estimation method (MUSIC) so that a sound source azimuth angle estimation value is acquired. The method is high in sound source localization estimation accuracy so that an azimuth ambiguity problem can be effectively overcome.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Method for realizing sparse signal recovery on CPU (Central Processing Unit) based on OMP (Orthogonal Matching Pursuit) algorithm
InactiveCN102750262AReduce computational complexityFast convergenceComplex mathematical operationsComputation complexitySignal on
The invention discloses a method for realizing sparse signal recovery on a CPU (Central Processing Unit) based on an OMP (Orthogonal Matching Pursuit) algorithm. The method comprises the following steps of: generating an observation matrix on the CPU, and selecting a column with the greatest relevancy to the residual in the observation matrix to complement a basis matrix, wherein the residual is the difference between the observations generated by an actual observation signal and an estimation signal, and the basis matrix is a matrix formed by nonzero element index values in corresponding column vectors in the observation matrix; by use of a method of least squares, estimating the nonzero elements of an original signal on the basis matrix of the kth step; continuing to select the column with the greatest relevancy to the residual in the observation matrix on the CPU to complement the basis matrix, when the variance between the real observation and the estimation observation is lower than a specified threshold, ending the iterative operation. The method provided by the invention has the following advantages: in parallel realization of the OMP algorithm by the CPU, the advantages of low computational complexity and high convergence rate of the OMP algorithm are combined, and simultaneously, the characteristic of remarkable acceleration performance of the CPU algorithm to the vector computation is fully used, and the running speed of the sparse recovery algorithm is improved effectively.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for positioning dual-system combined satellite navigation receiver
InactiveCN101799552APositioning results are reliableGuaranteed reliabilitySatellite radio beaconingDeep space explorationSystem combination
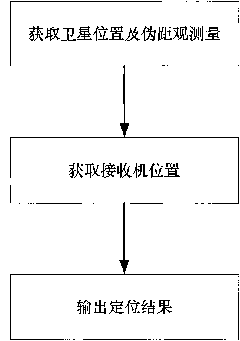
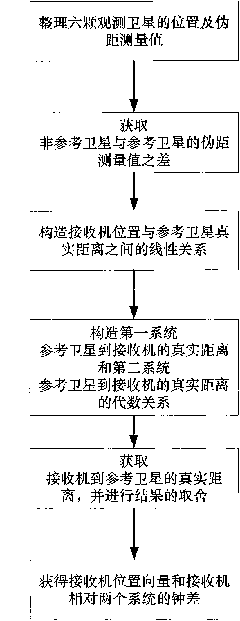
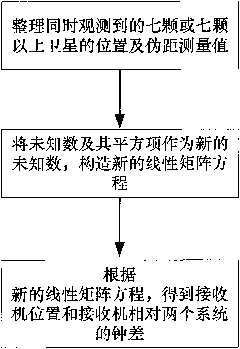
The invention discloses a method for positioning a dual-system combined satellite navigation receiver, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, acquiring positions of satellites and the pseudo-range observed quantity; secondly, according to different conditions for observing the satellites, adopting different steps to finish the positioning of the receiver so as to acquire the position of the receiver; and finally, outputting positioning results The method has two solutions according to the number of visible satellites: firstly, under the condition that two satellite systems have three visible satellites respectively, the position of the receiver can be acquired finally by using an algebraic processing method of a unary quadratic equation; and secondly, under the condition that the two satellite systems has seven or more visible satellites respectively, an observation equation set is converted into a linear equation set by using the redundancy of observation information, and a least square method is finally used to perform processing directly. The method needs no initial estimated value of a navigation position and also needs no iterated operation processing to ensure that the receiver can obtain a reliable positioning result during a deep space exploration and in other special environments.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
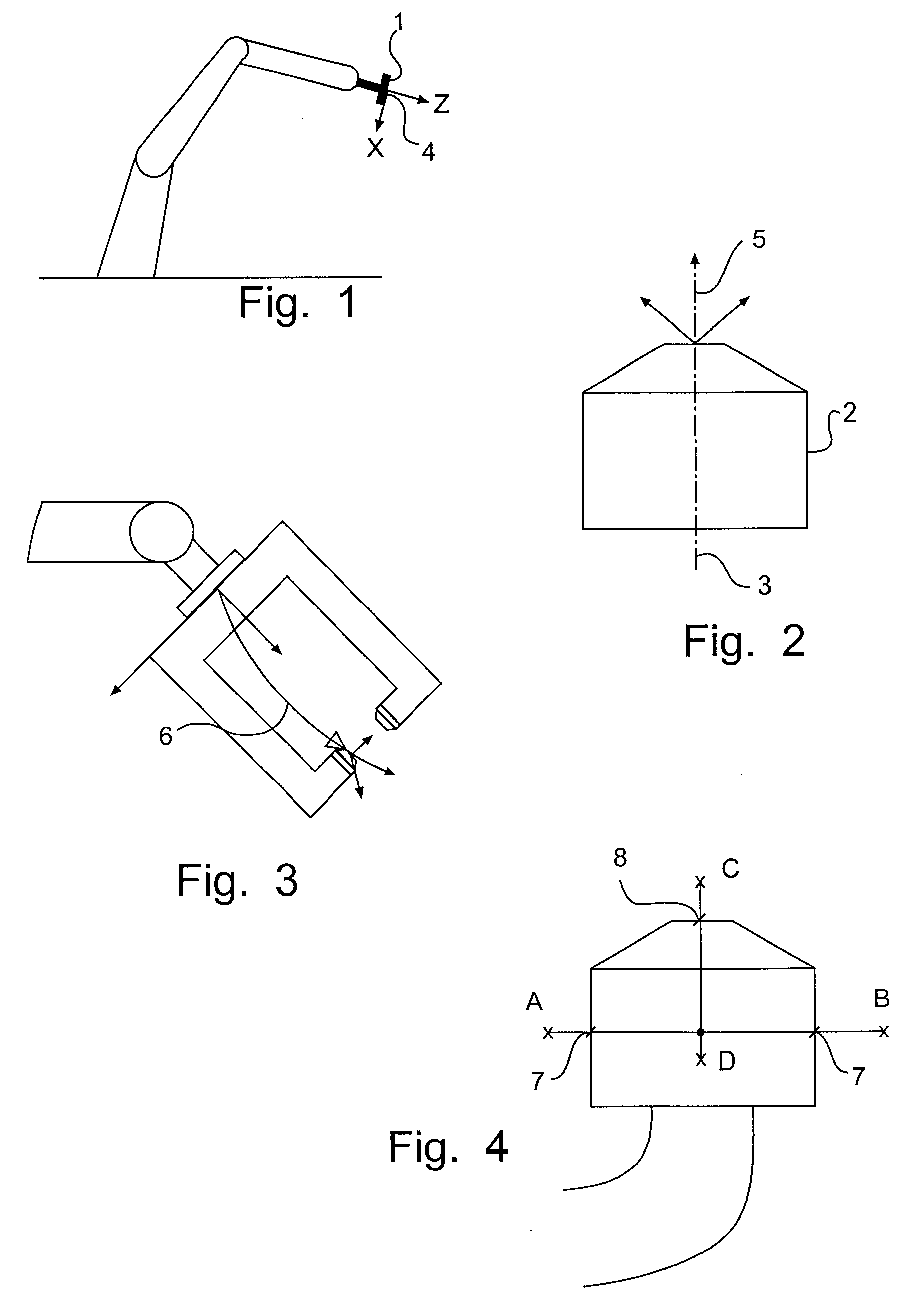
Method for cell alignment and identification and calibration of robot tool
InactiveUS6356808B1CalibrationQuick and inexpensiveProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsTangential contactEngineering
A method for cell alignment, identification and calibration of part of a robot tool, preferably a part of the robot tool, is positioned close to a detector, whereupon it is moved repeatedly past the limit of the area of detection of the detector. During the movement, the pose of the robot is registered each time the surface of said robot tool comes into tangential contact with the area of detection, and an over determined system of equations is formed, consisting of a correlation between the registered poses and unknown parameters regarding the detection area of the detector and the location of the robot part in space. An error vector is introduced into the system of equations, which is then solved while minimizing the error vector, preferably in the least square sense, in order to thus identify said unknown parameters and the error vector.
Owner:ROBOTKONSULT
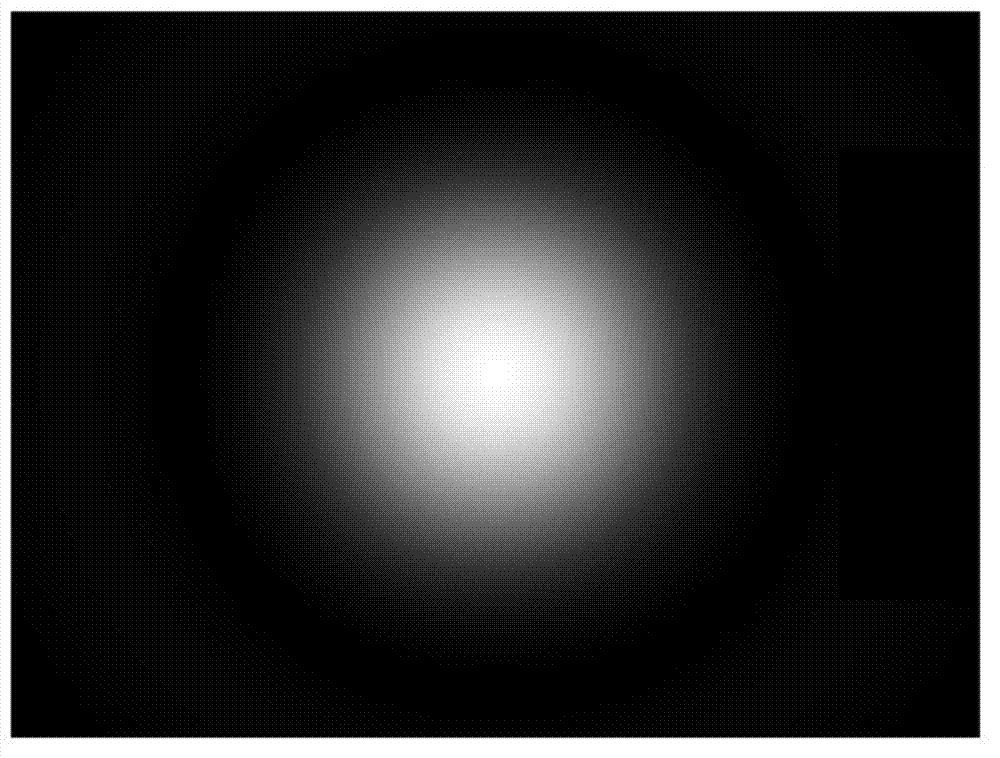
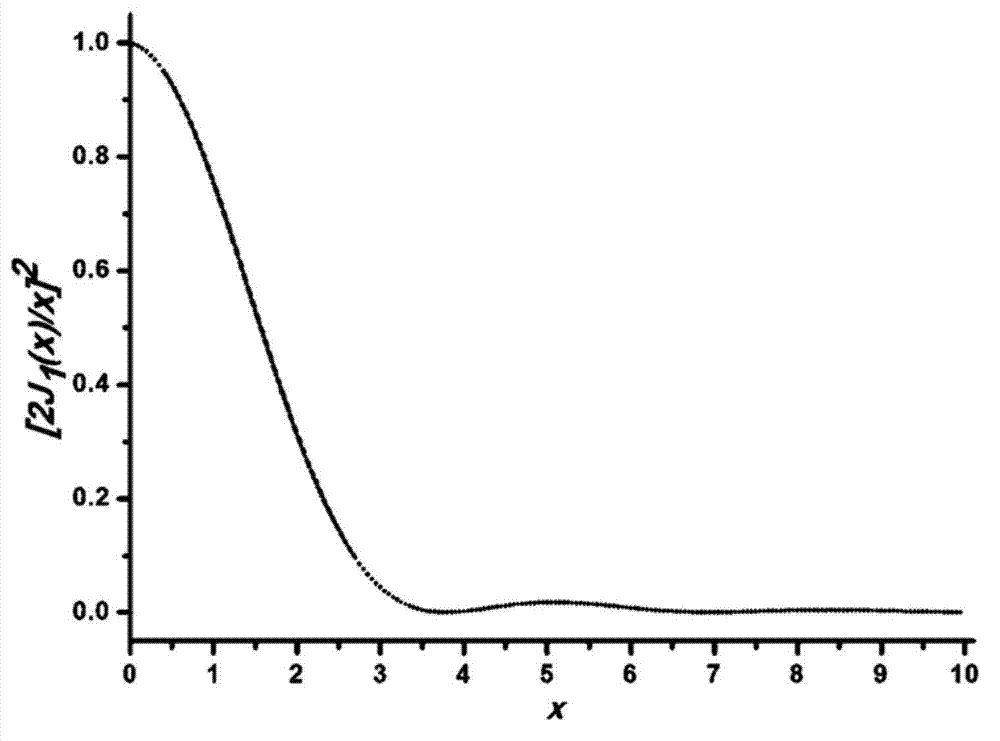
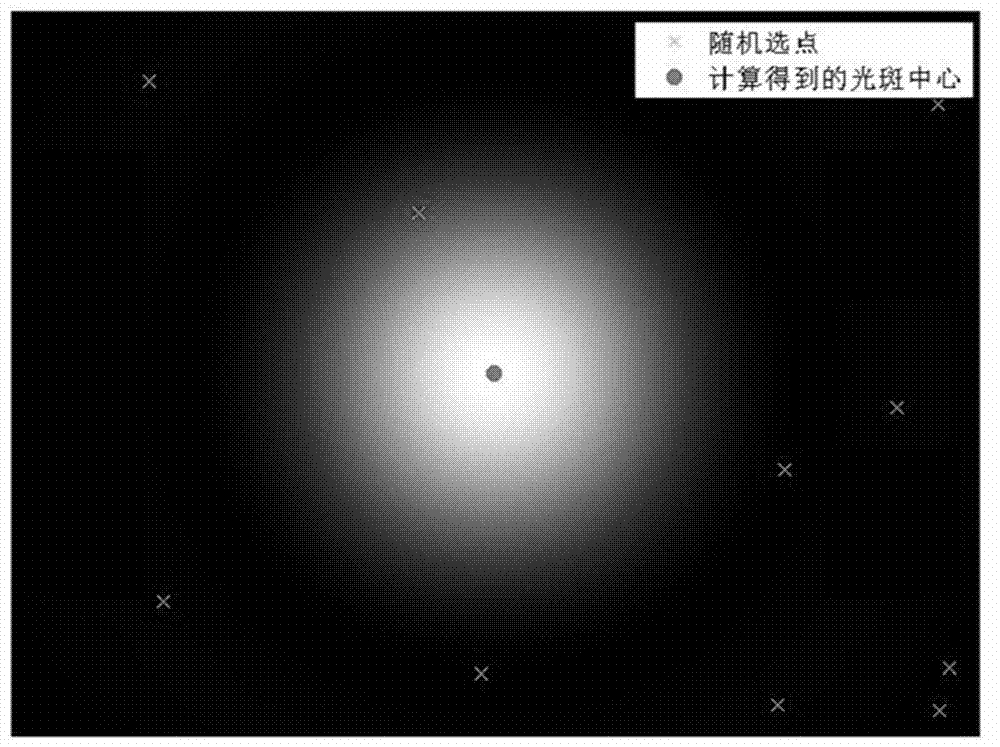
Light spot image center quick locating method
ActiveCN103093223AReduce resource usageEasy to implementCharacter and pattern recognitionLight spotGray level
The invention relates to a light spot image center quick locating method which is characterized by comprising the steps that (1) gray level distribution I (x, y) of a light spot image is acquired through measurement; (2) a point on the light spot image is selected randomly, gradient of the acquired point is computed; (3) a straight line which passes through the point and a light spot center is computed; (4) N points are selected randomly, N is larger than or equal to 2, the step (2) and the step (3) are repeated, linear equations of the acquired straight line passing through the light spot center are combined to an equation set; (5) the equation set is solved through a least square method, and the position (x0, y0) of the light spot center is acquired. According to the light spot image center quick locating method, a small number of points are selected randomly to quickly locate the light spot center, real-time performance is high, storage amount is small, hardware implementation is convenient, and center location can be achieved on the condition that light spot images are distributed unevenly.
Owner:安徽欧泰祺智慧水务科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com