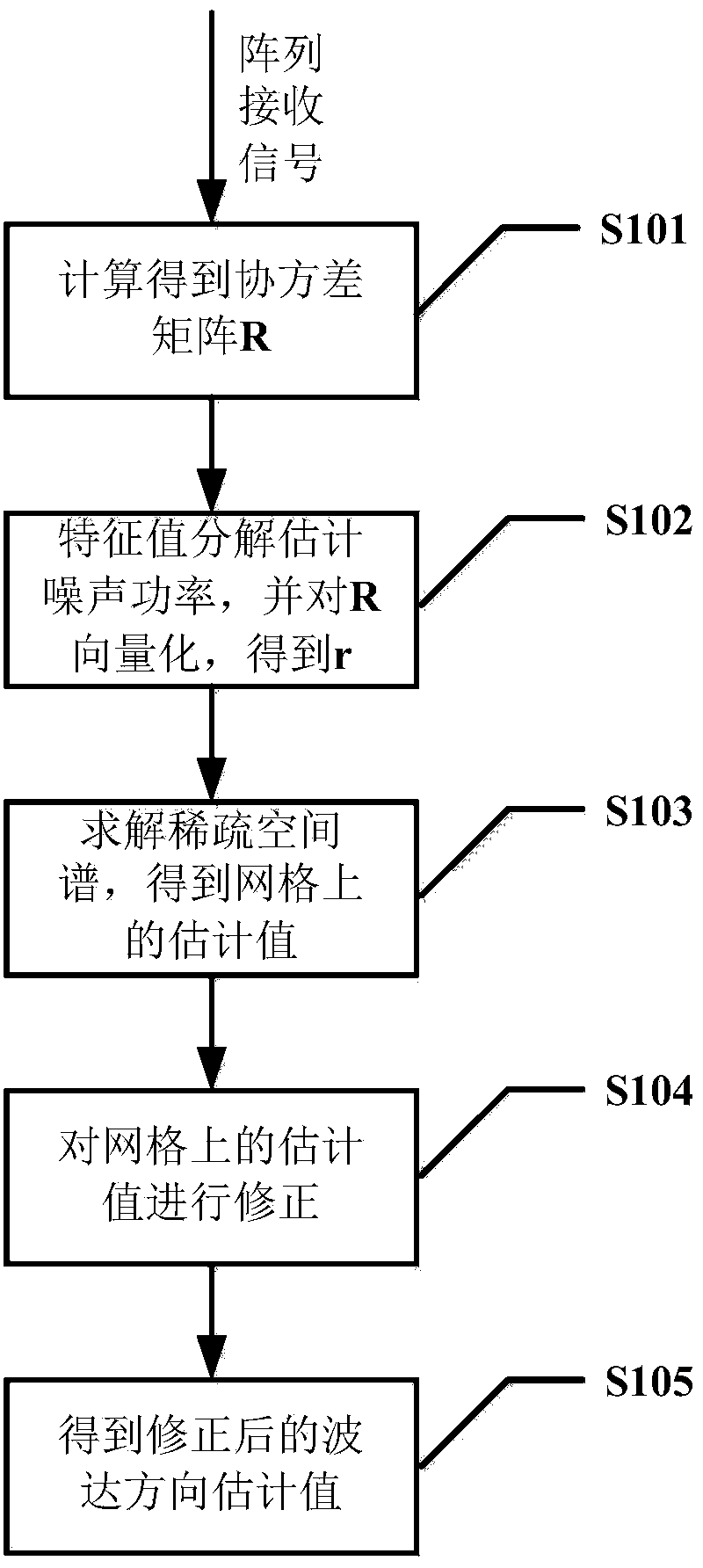
Far-field narrow-band DOA estimation method based on covariance matrix sparse representation
A technology of covariance matrix and sparse representation, which is applied to direction finders, direction finders using radio waves, measuring devices, etc., which can solve the problems of estimation performance deterioration and height correlation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] The simulation condition of embodiment 1 and embodiment 2 is the model of mesh matching, so estimated value That is, the final direction of arrival estimated value, without correction. The simulation conditions of Embodiment 3 and Embodiment 4 are mesh mismatch models. In the embodiment, root mean square error (RMSE) is used to evaluate the performance of each algorithm, which is defined as: RMSE = 1 Mon Σ m = 1 Mon 1 K Σ k = 1 K ( θ ^ k , m - ...
Embodiment 2
[0059] In the case of grid matching, the root mean square error of the estimated value of the present invention changes with the number of snapshots:
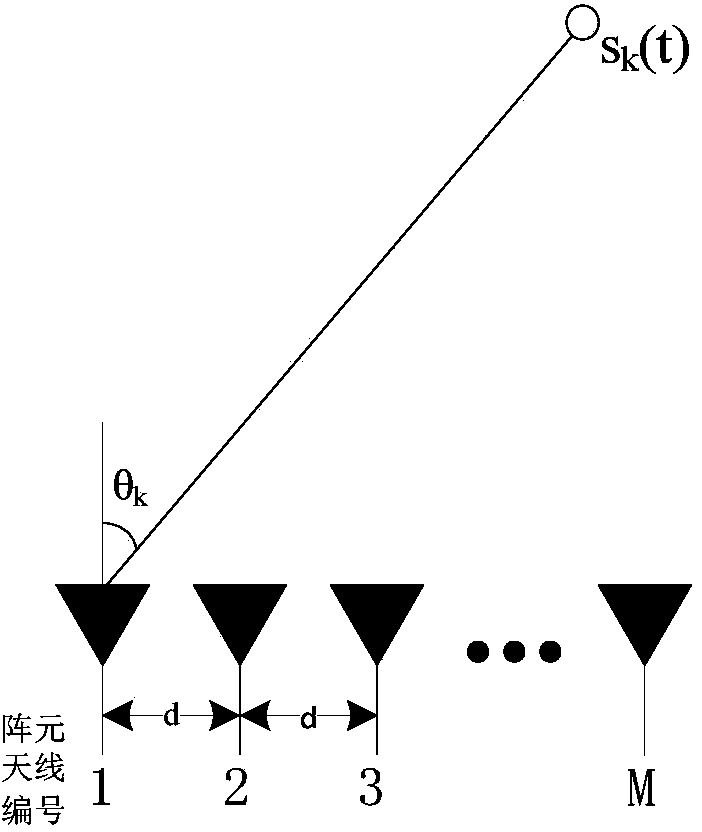
[0060] The receiving array that embodiment 1 adopts is as attached figure 2The half-wavelength uniform linear array consisting of 8 array elements is shown. The reference array element is the array element antenna numbered 1. Four signal sources with the same power are incident on the array according to the incident direction [-35°, -10°, 15°, 40°]. In order to make the corners of the incident direction on the grid, the discretization grid is set to {-90°,-89°,...,89°} with an interval of 1°. The reference signal-to-noise ratio SNR is fixed at 10dB. The number of snapshots ranges from 100 to 600, with an interval of 100, and 1000 Monte Carlo experiments are performed for each snapshot.
[0061] DOA estimation method in embodiment 2 comprises the following steps:
[0062] Obtain the covariance matrix R according to the arr...
Embodiment 3
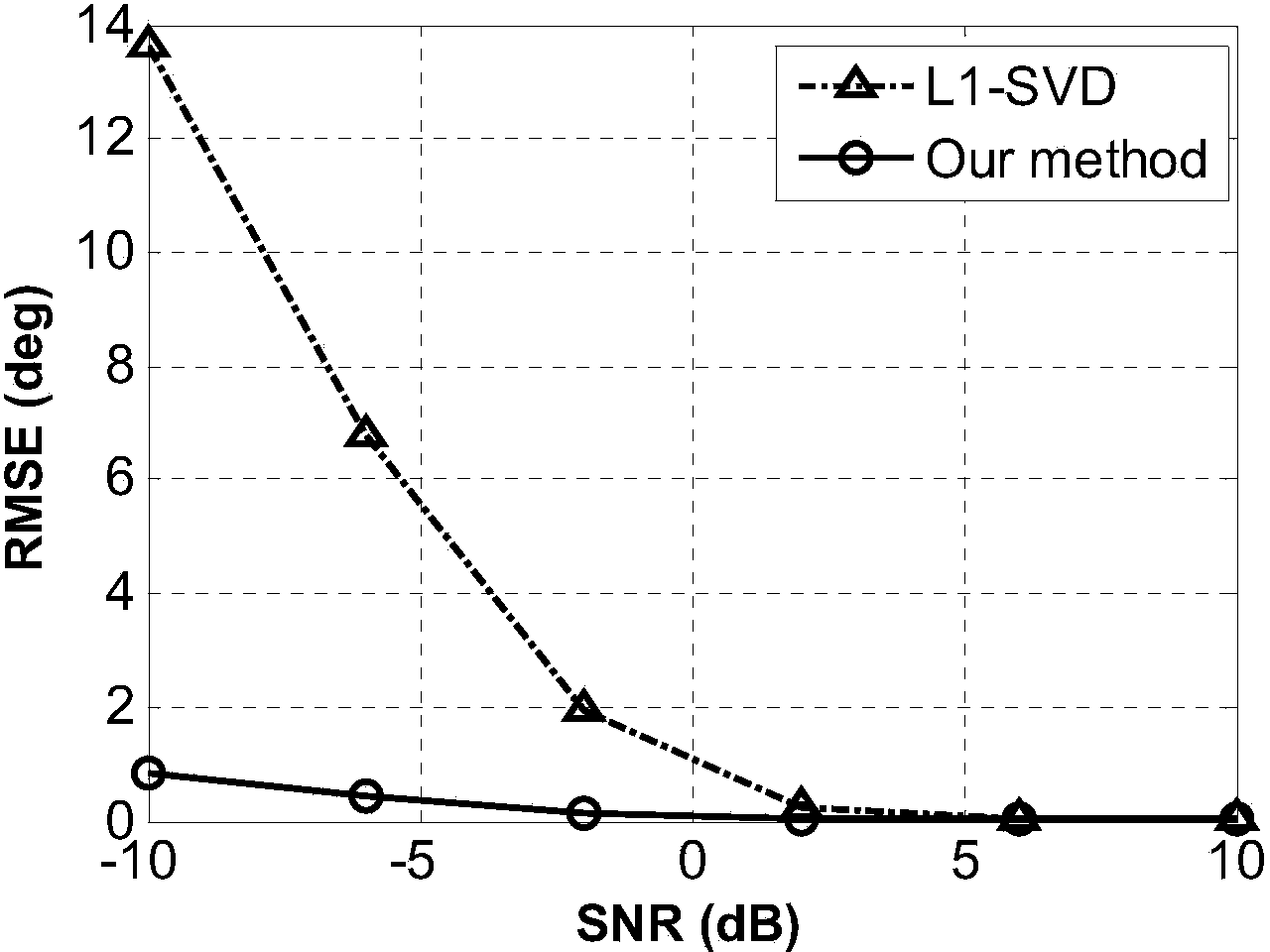
[0067] In the case of grid mismatch, the root mean square error of the estimated value of the present invention varies with the signal-to-noise ratio simulation:
[0068] The receiving array that embodiment 3 adopts is as attached figure 2 The half-wavelength uniform linear array consisting of 8 array elements is shown. The reference array element is the array element antenna numbered 1. Two signal sources with the same power are incident on the array according to the incident direction [-14.5°, 36.3°]. In order to prevent the incident direction angle from falling on the grid, the discretization grid is set to {-90°,-88°,...,88°} with an interval of 2°. The number of sampling snapshots is 200. The reference signal-to-noise ratio SNR was varied from -4dB to 20dB with an interval of 4dB, and 1000 Monte Carlo experiments were performed for each SNR.
[0069] DOA estimation method in embodiment 3 comprises the following steps:
[0070] Obtain the covariance matrix R accordin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com