Ni-based heat-resistant alloy
A high-quality heat-resistant alloy technology, which is applied in the field of high-strength Ni-based heat-resistant alloys, can solve the problems of insufficient creep rupture strength of Fe-based alloys, and achieve the effect of dramatic improvement and ductility improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
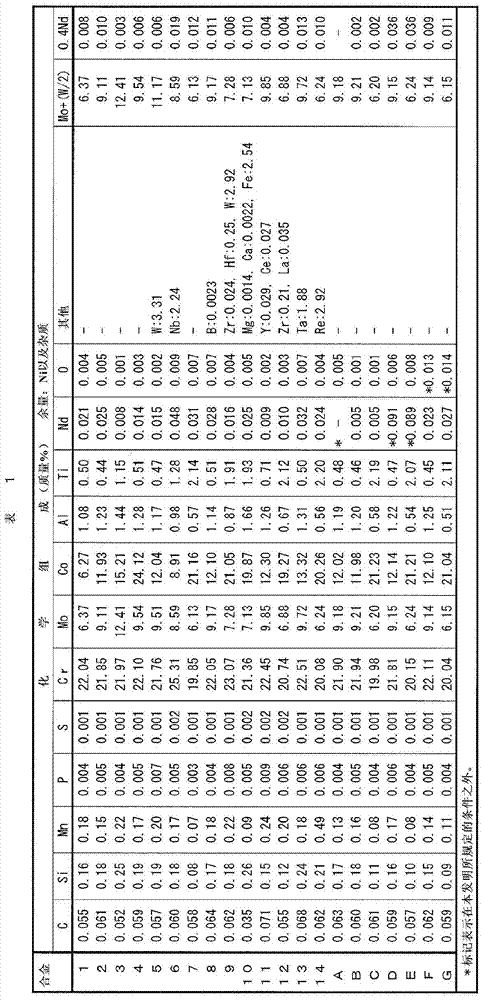
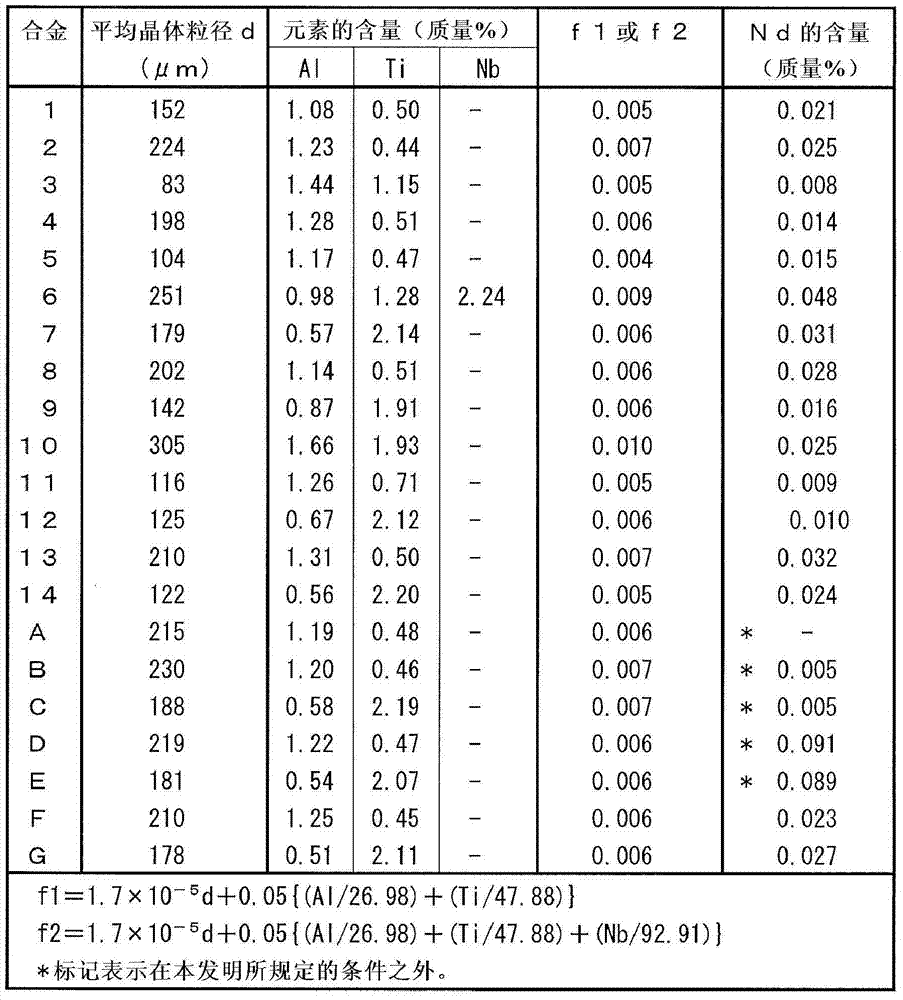
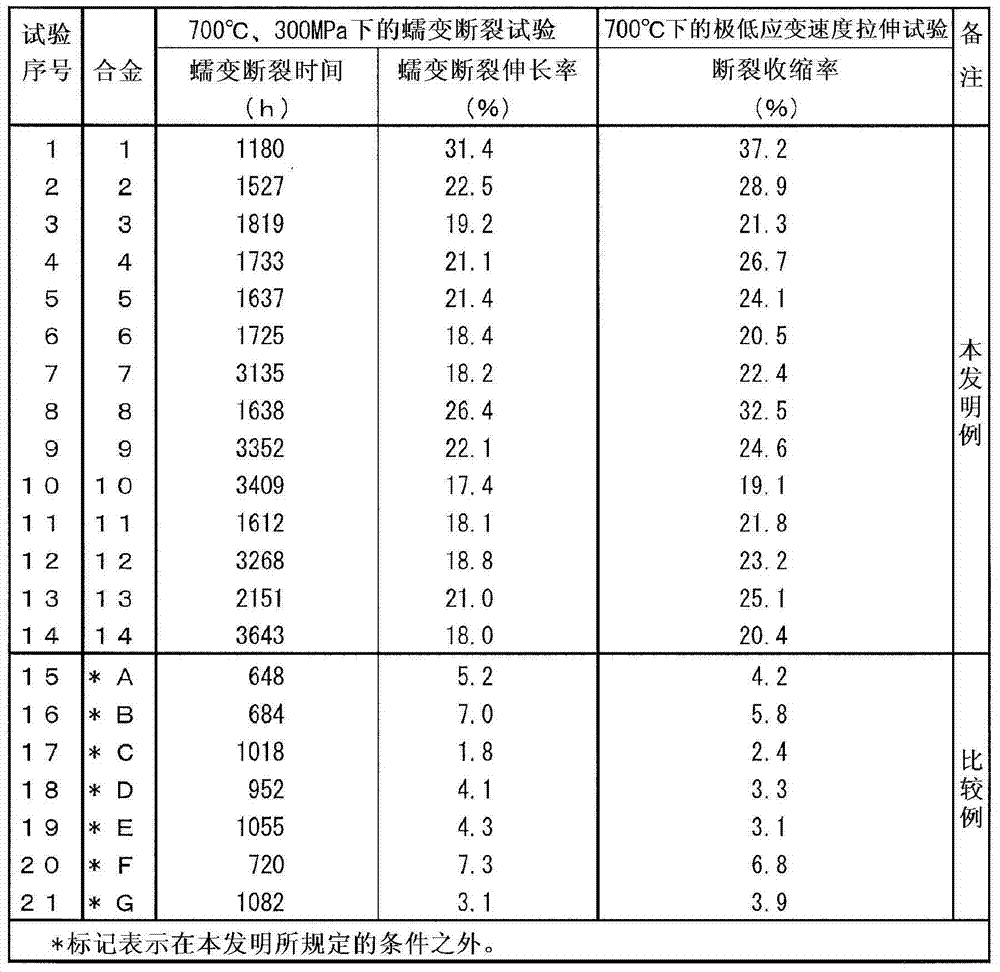
[0140] Ni-based alloys 1 to 14 and A to G having the chemical compositions shown in Table 1 were melted using a high-frequency vacuum melting furnace to obtain 30 kg ingots.
[0141] [Table 1]
[0142]
[0143] After heating the ingot obtained in this way to 1160 degreeC, hot forging was performed so that the final temperature might become 1000 degreeC, and it produced the plate material of thickness 15mm.
[0144] Next, using the plate material having a thickness of 15 mm, it was subjected to softening heat treatment at 1100° C., then cold-rolled to 10 mm, further kept at 1180° C. for 30 minutes, and then water-cooled.
[0145]Using a part of each plate with a thickness of 10 mm after being kept at the above-mentioned 1180°C for 30 minutes, mirror-polish the cut and resin-embedded test piece with the rolling longitudinal direction as the observation plane, and then use mixed acid or Kalin's reagent (Kalling reagent) corrosion, for optical microscope observation. Five fie...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com