Method for invalidating sensor measurements after a picking action in a robot system
A sensor and measurement value technology, applied in the field of invalidating the sensor measurement value after picking up the action in the robot system, can solve the problems of time-consuming, energy consumption of the second reading, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0059] Reference will now be made in detail to embodiments of the invention, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings.
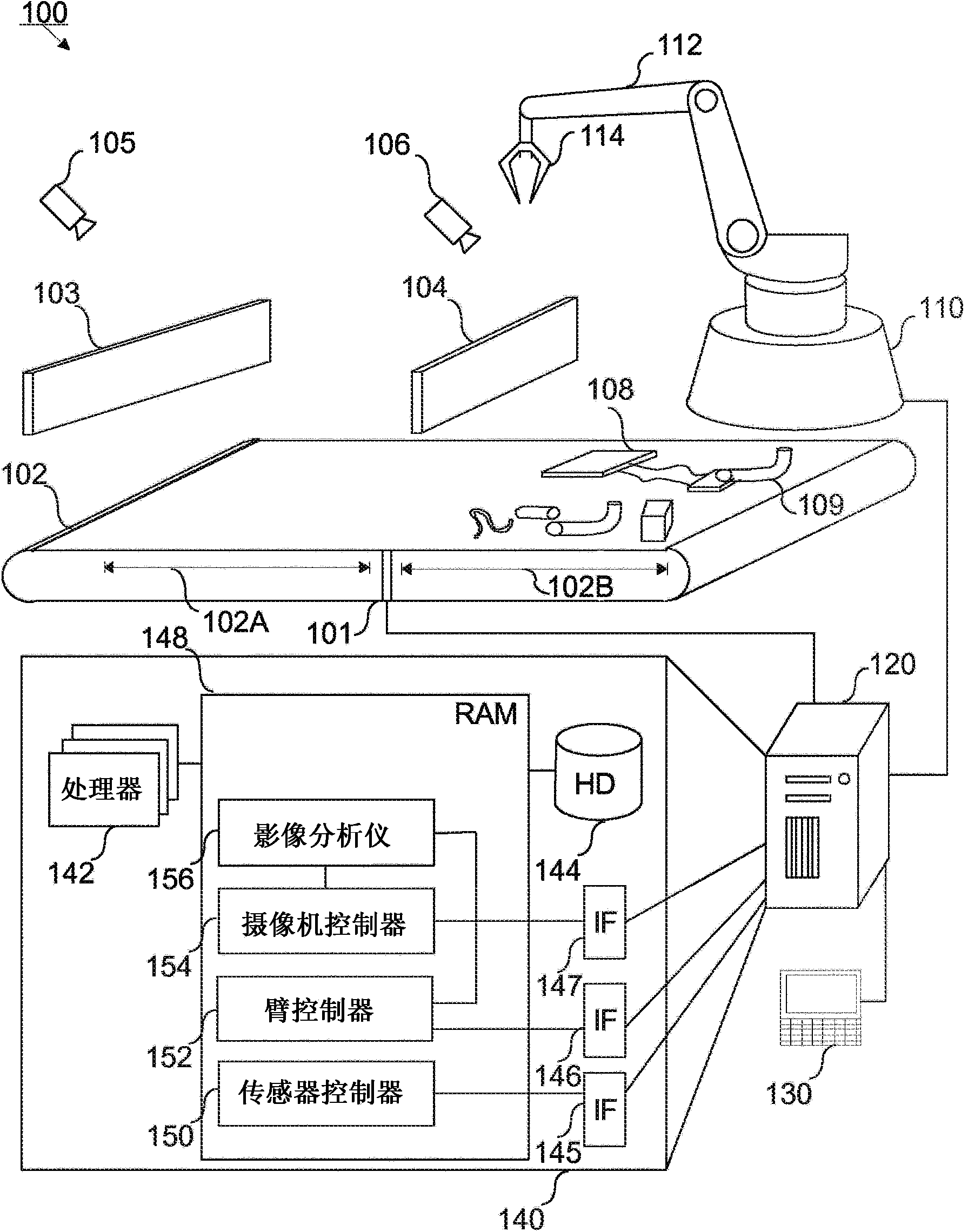
[0060] figure 1 is a block diagram illustrating a robotic system employing two line sensor arrays in one embodiment of the invention.
[0061] figure 1In this example, the robot system 100 includes a robot 110 , such as an industrial robot, which includes a robot arm 112 . Attached to the robotic arm 116 is a gripper 114, which may also be a gripper or jaw. The robotic arm 116 is capable of moving the gripper 112 within the operating area 102B of the conveyor belt 102 . The robotic arm 112 may include a number of motors, such as servo motors that enable controlled rotation, pitch, and pinch of the robotic arm. The various movements of the robotic arm 112 and gripper 114 are effected by actuators. For example, the actuator may be an electric actuator, a pneumatic actuator, or a hydraulic actuator, or any combination of these actuato...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com