Model modification method with damp considered based on basic stimulation response data
A technology of stimulus response and model correction, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as increasing test costs, reducing product design efficiency, and reducing the accuracy of dynamic response predictions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
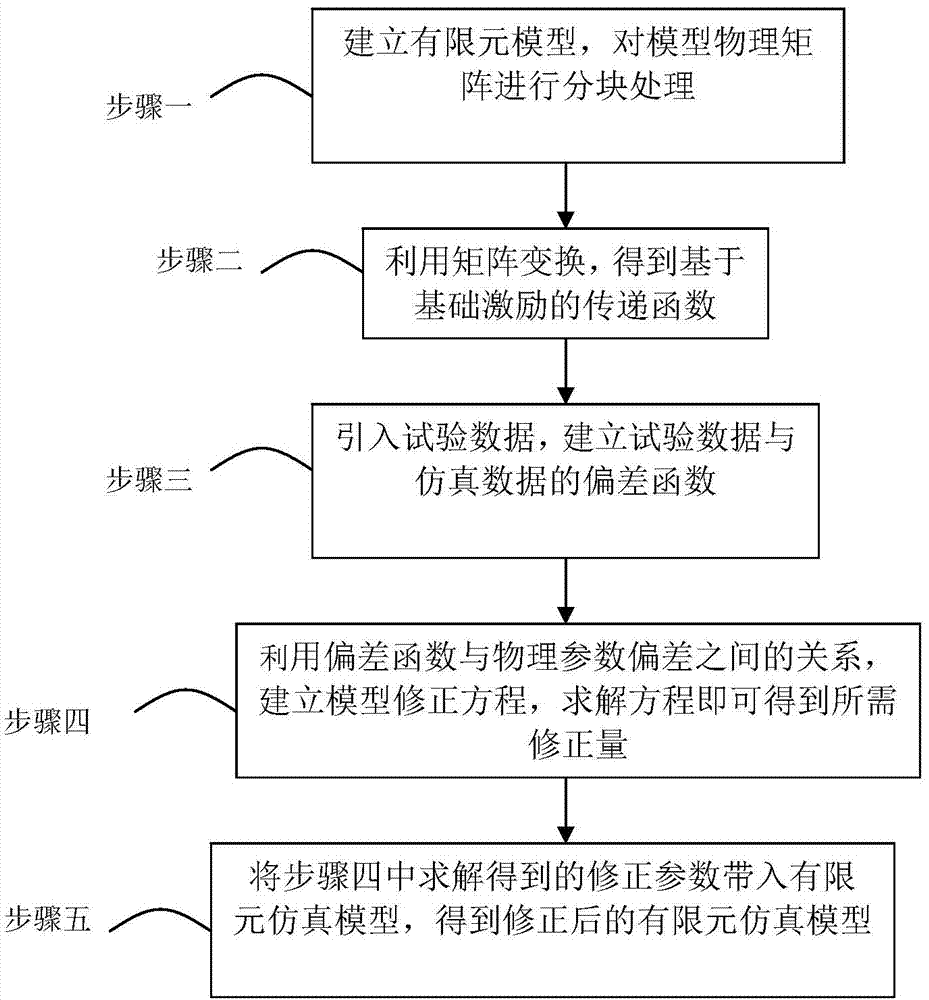
[0033] Specific implementation mode 1: The damping-based model correction method based on the basic excitation response data of this implementation mode is implemented in the following steps:
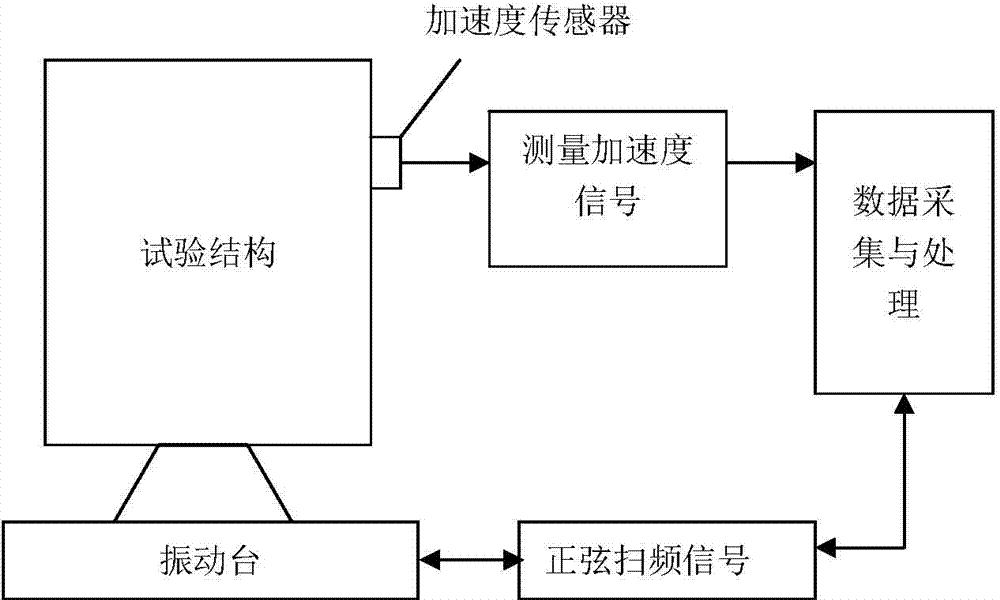
[0034] 1. First, use the finite element software to establish the finite element simulation model of the system. After the finite element simulation model is established, the stiffness K, structural damping G, viscous damping C and mass matrix M in the physical matrix are exported to obtain a system considering damping Kinetic equations:
[0035] ([K]+i[G]+iω[C]-ω 2 [M]){u}={f}
[0036] Among them, the stiffness K, structural damping G, viscous damping C, and mass matrix M are partitioned according to the connection with the shaking table in the finite element simulation model, and the sub-matrix is obtained:
[0037] [ K ] = [ ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0053] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 in that: the finite element software in the step 1 is MSC.Nastran.
[0054] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0055] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is:
[0056] In the first step, for the viscous damping C, the Rayleigh damping assumption is used to fit the viscous damping coefficient:
[0057] The damping matrix is Rayleigh damping, and Rayleigh damping assumes that the damping is linearly related to the mass matrix and stiffness matrix;
[0058] C=αM+βK
[0059] where α, β are viscous damping coefficients, same as modal damping ξ i (Can be determined by modal test or identified by telemetry signal)
[0060] The relationship is as follows
[0061] ξ i = 1 2 ω i ( α + β ω i 2 )
[0062] The constants α, β were det...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com