Center shaft structure of delta robot
A technology of robot and shaft structure, which is applied in the direction of manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., which can solve the problems of reduced operating precision, reduced efficiency, and large inertia, and achieve the effects of high-speed stable rotation, high precision and efficiency, and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
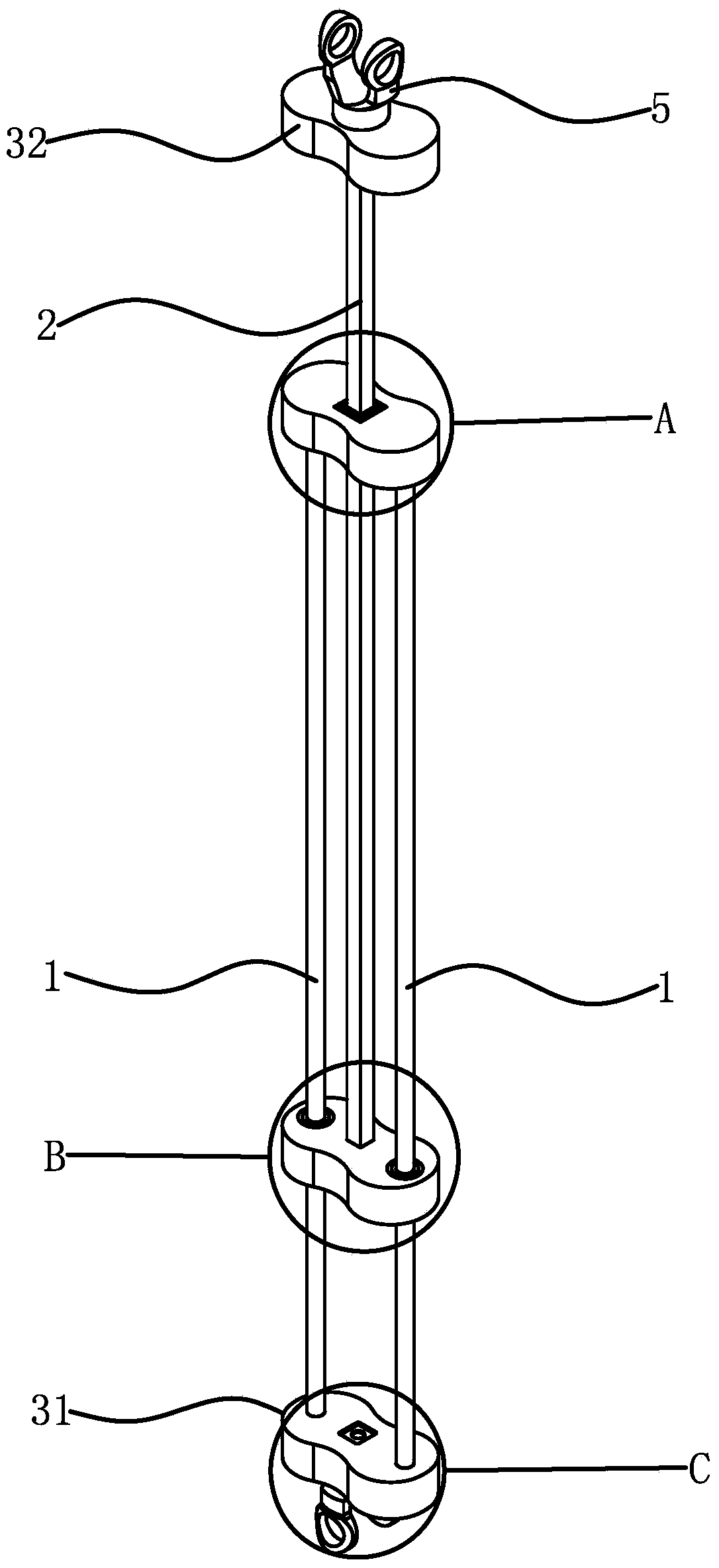
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, a central axis structure of a delta robot includes two robot driving arms 1 and a robot control arm 2, the two robot driving arms 1 are parallel to each other, and one end of the robot driving arm 1 is fixed by a fixed sleeve 31 Together, the other end is fixedly connected with a slider 11, the robot control arm 2 is parallel to the robot driving arm 1, and one end of the robot control arm 2 passes through the slider 11, and the robot control arm 2 and the slider 11 circle The direction is fixed, and it can slide axially relative to the slider one 11. The robot driving arm 1 and the robot control arm 2 are both made of carbon fiber material. The central axis of the delta robot needs to have the basic functions of expansion and rotation, and the structure of the central axis slides and connects the robot driving arm 1 and the robot control arm 2 through the slider 11. The robot driving arm 1 and the driving platform of the delta robot The robo...
Embodiment 2
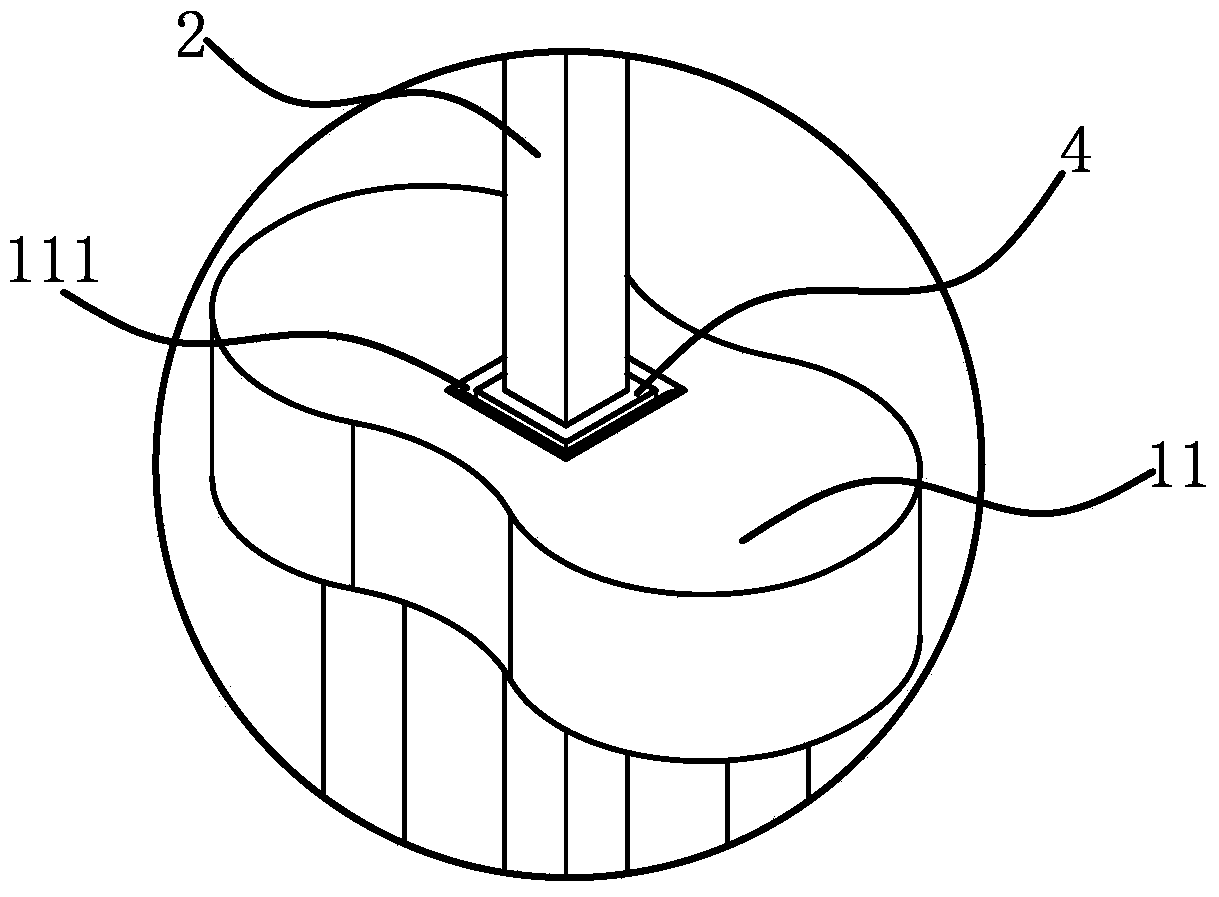
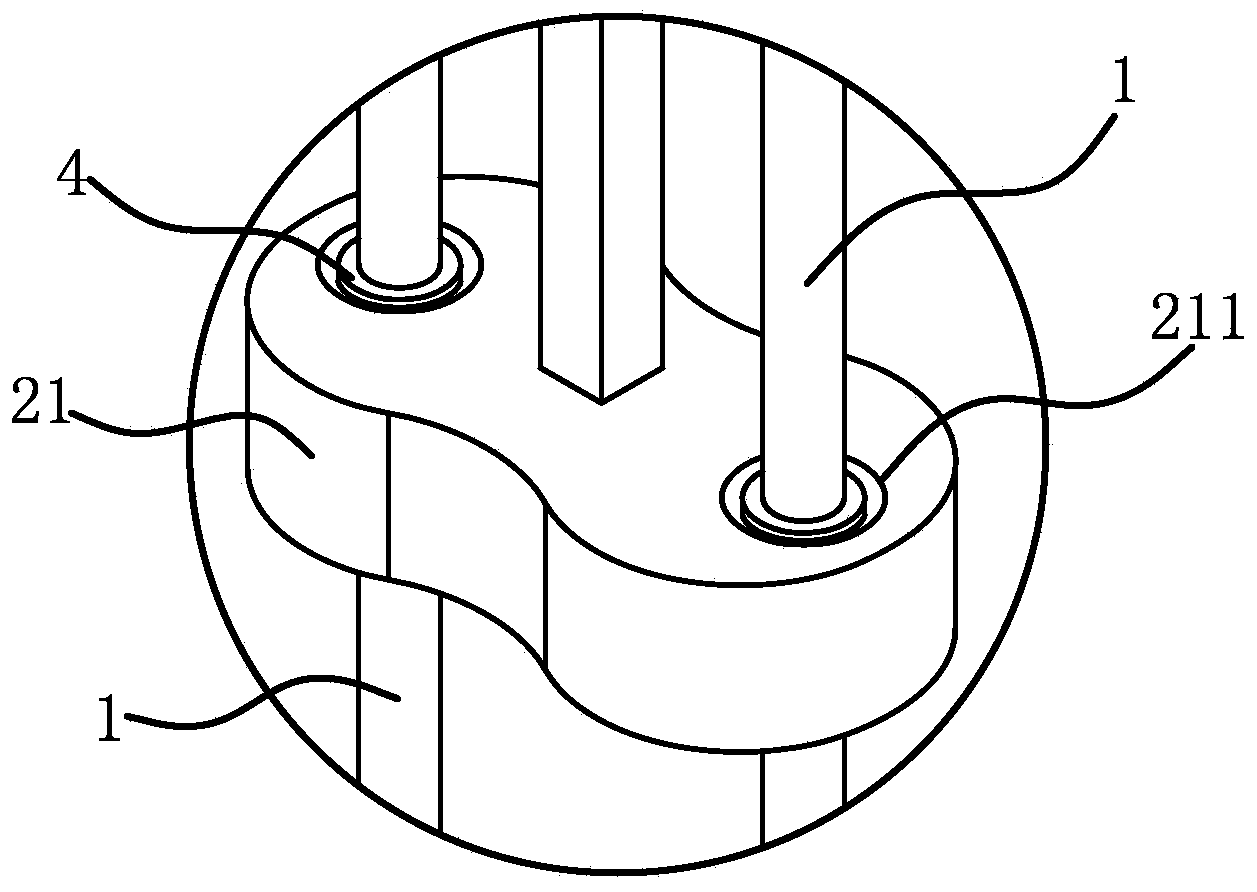
[0037] The structure of the polishing machine is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that Figure 5 , Image 6 As shown, the number of the robot driving arm 1 and the robot control arm 2 is two, and one end of the two robot control arms 2 is fixedly connected through the fixing sleeve 2 32, and the other end is fixedly connected with the slider 2 21, and the slider 1 11 There are two guide holes 211, and two guide holes 111 are opened on the slider 21. The two robot driving arms 1 respectively slide and penetrate in the two guide holes 211, and the two robot control arms 2 respectively slide and penetrate in the two guide holes. In the first guide hole 111, two robot driving arms 1 pass through two guide holes 211, which ensures the circumferential fixation between the slider two 21 and the two robot driving arms 1. Similarly, the two robot control arms 2 pass through Through the two guide holes 111, the circumferential fixation between the slider 11...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The structure of the polishing machine is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that Figure 7 , Figure 8 , Figure 9 As shown, the number of the robot driving arm 1 and the robot control arm 2 is three, and one end of the two robot control arms 2 is fixedly connected by the fixing sleeve 2 32, and the other end is fixedly connected with the slider 2 21, and the slider 1 11 is provided with There are three guide holes 211, and three guide holes 111 are opened on the slider 21, and the three robot driving arms 1 respectively slide through the three guide holes 211, and the three robot control arms 2 respectively slide through the three In the guide hole 111, obviously, more robot driving arms 1 and robot control arms 2 can make the overall strength higher, and in order to reduce the use of carbon fiber materials and reduce weight, under the premise of the same load capacity, the robot The driving arm 1 and the robot control arm 2 can be process...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com