Microactuator arrangement for deflecting electromagnetic radiation
A technology of micro-actuator and electromagnetic radiation, which is applied in installation, instrumentation, optics, etc., to achieve the effects of space saving, compactness, cheap manufacturing, and large deflection angle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
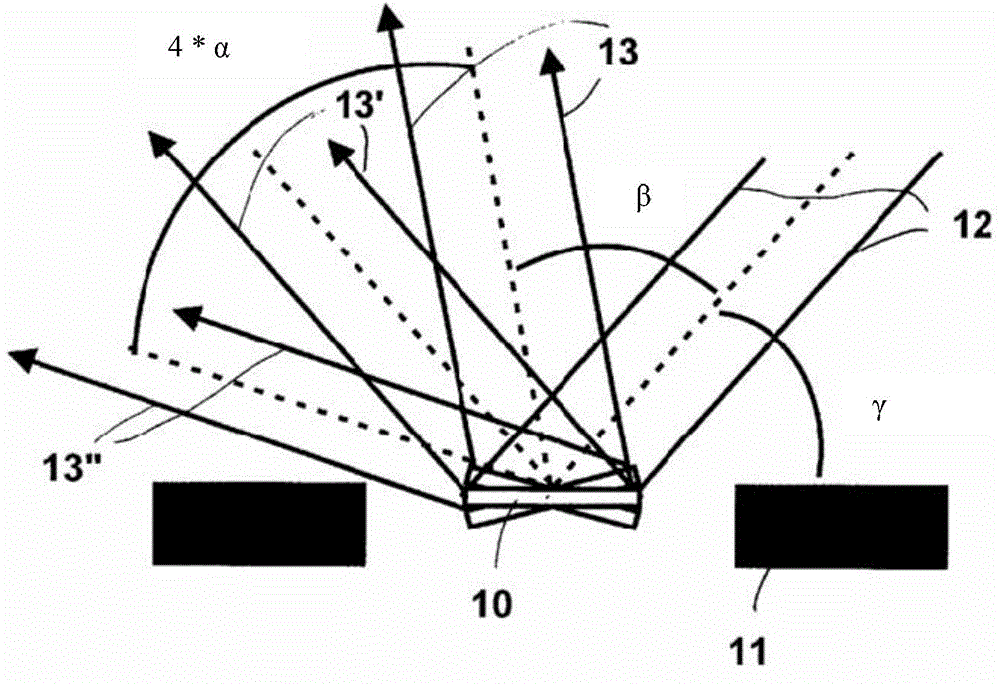
[0047] figure 1 Schematic representation of a microactuator designed as a scanner with a mirror plate 10 in different pivot positions, a chip frame 11 surrounding the mirror, and the indicated incident beam bundle 12 and mirror plate in different positions Several deflected beam bundles 13, 13', 13''. The beam entry angle or incident angle of the beam bundle 12, i.e. the angle between the mirror surface in the idling position and the incident or outgoing beam is denoted as "γ", and the smallest angle between the incident beam 12 and the scanning outgoing beam is designated as "β ”, where the angle realizes the spatial separation of the incident beam and the scanning angle region given by the oscillating mirror, and the angle “α” is the amplitude of the mechanical oscillation of the mirror 10. As mentioned in the introductory part of this specification, this figure is used to illustrate the expected scanning angles of MEMS scanners.
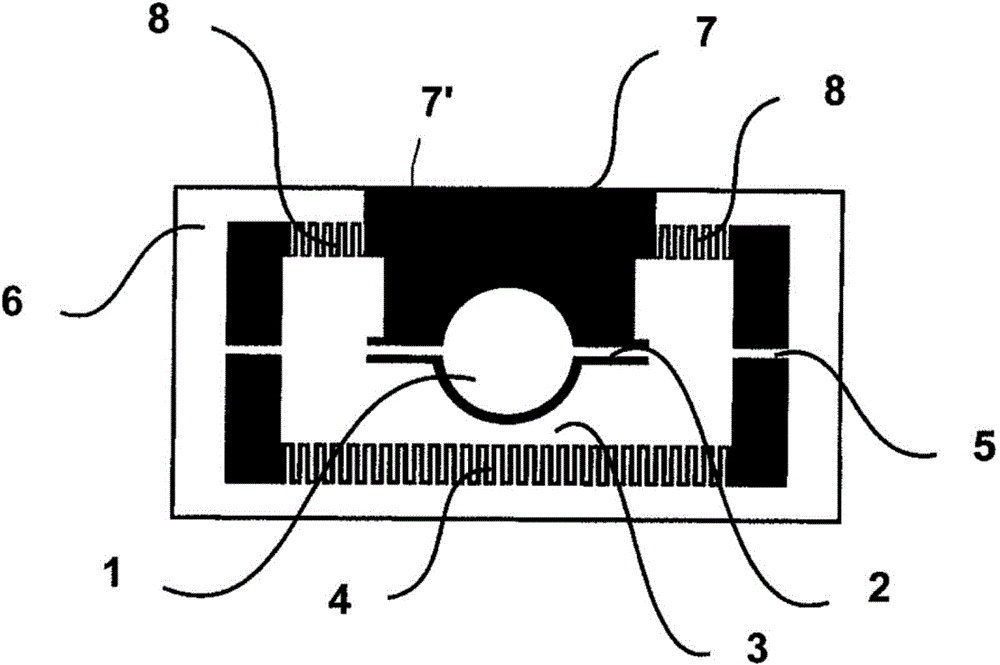
[0048] The microactuator device accordin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com