Three-dimensional hall sensor for detecting a spatial magnetic field
A Hall sensor, space magnetic field technology, applied in the size/direction of the magnetic field, the geometrical arrangement of the magnetic sensor elements, the measurement of magnetic variables, etc., can solve the problem of lack of symmetry, and achieve the effect of simplifying the connection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
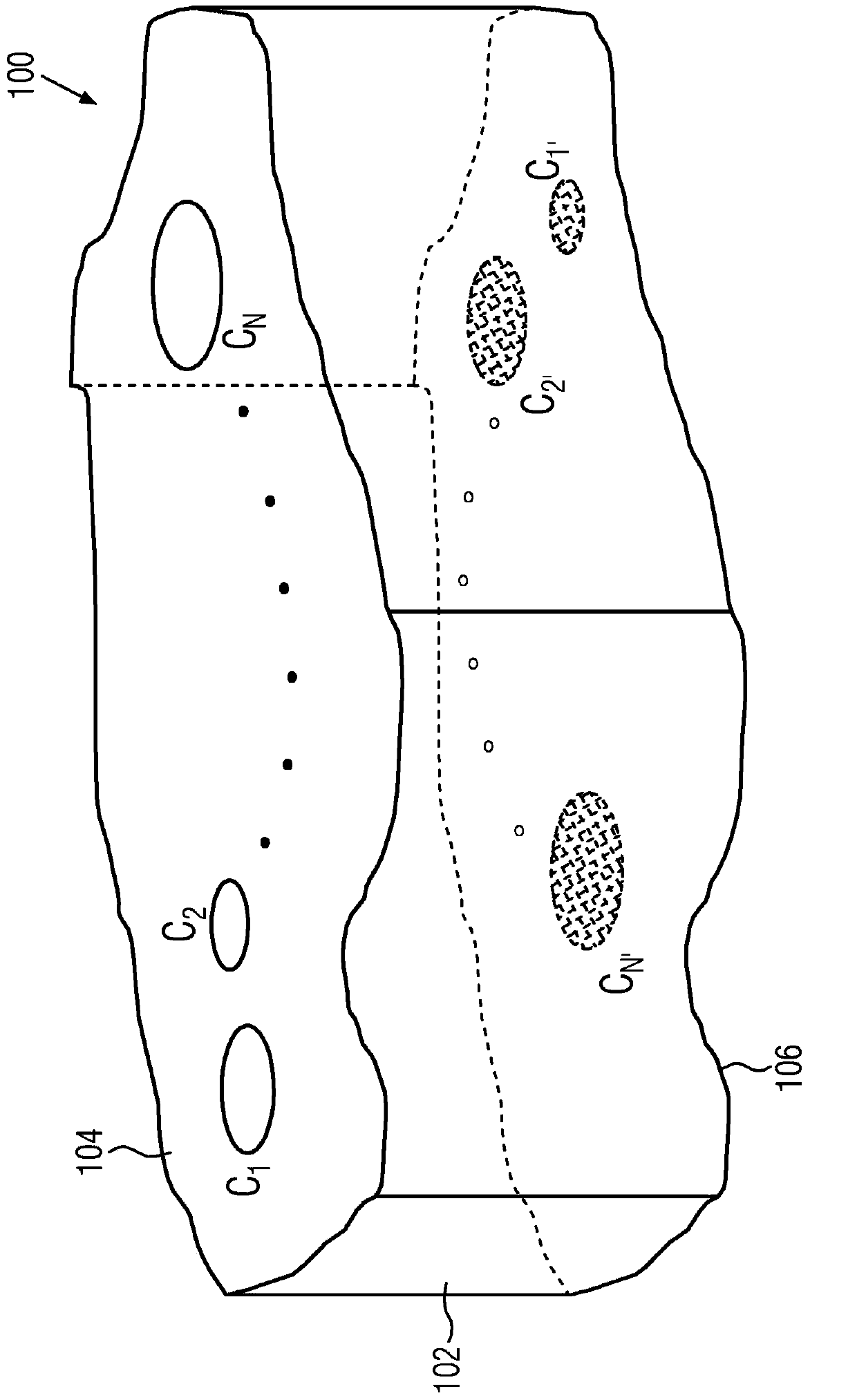
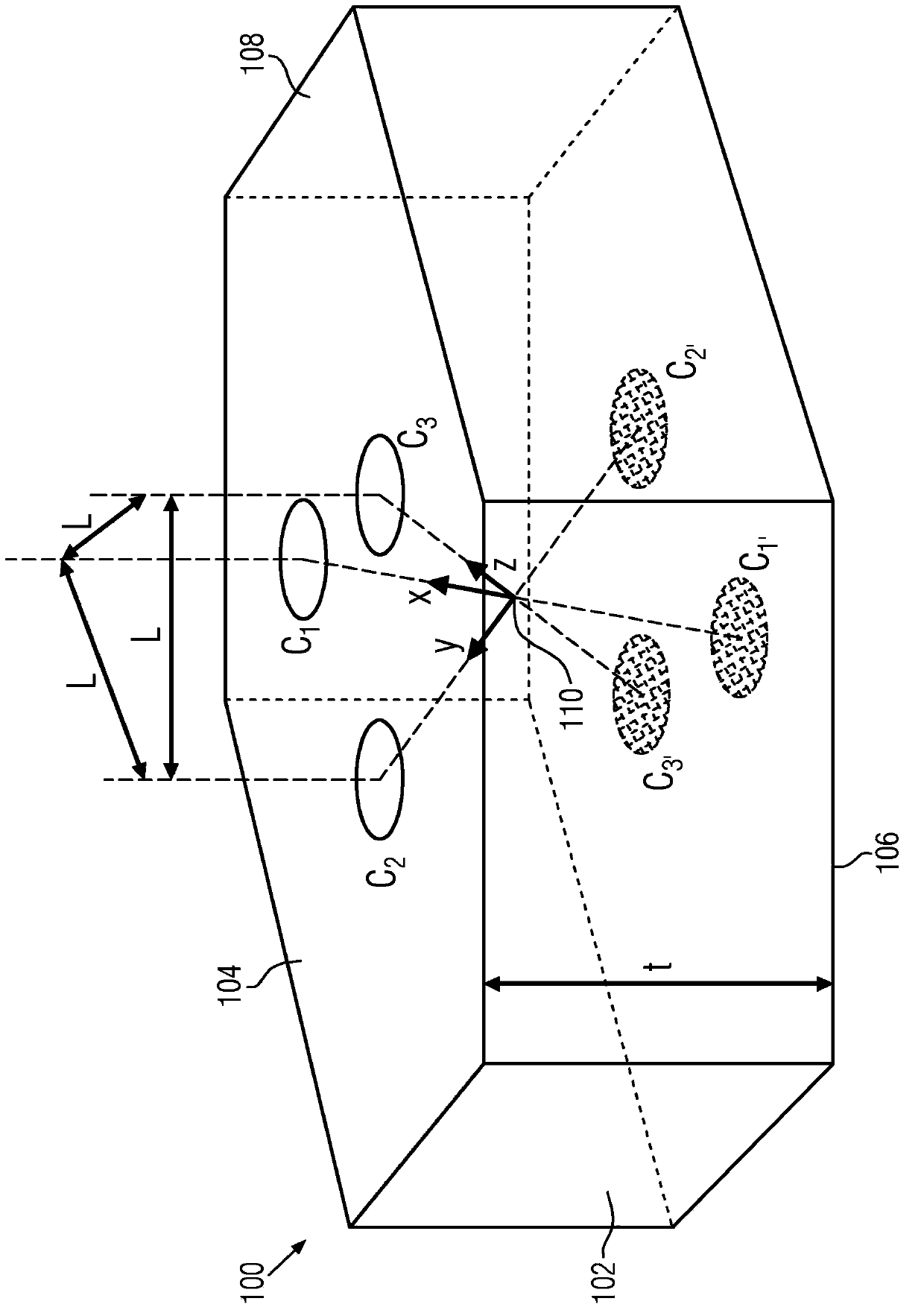
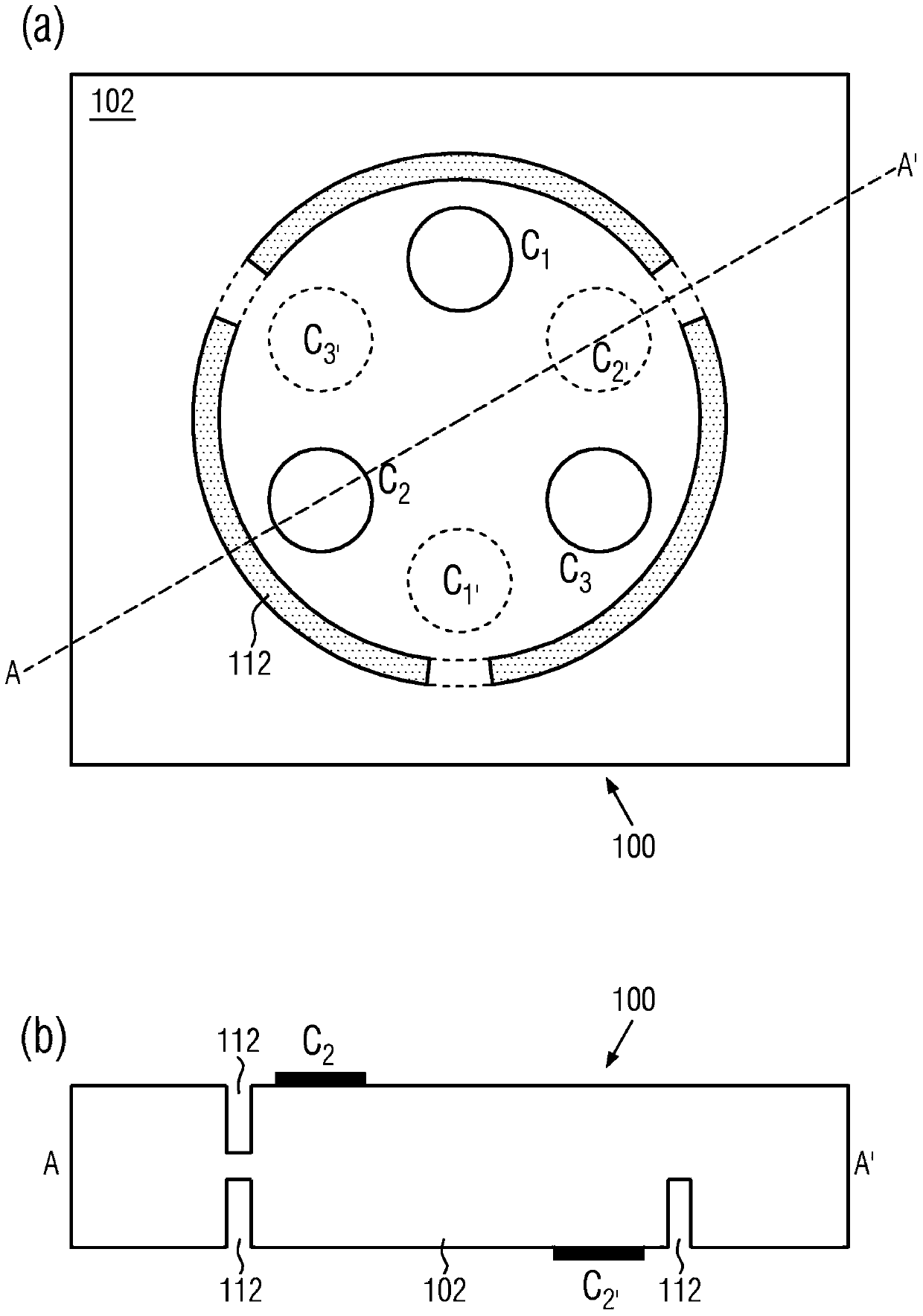
[0049] figure 1 The principle structure of the new magnetic field sensor in its most general design is shown. The magnetic field sensor 100 comprises a conductive substrate 102 which is delimited in the spatial direction by two ideally but not necessarily planar surfaces 104 , 106 , which are ideally but not necessarily oriented parallel to one another. The bounding surfaces 104 , 106 are subsequently referred to as upper or lower bounding surfaces. The conductive structure can be defined in two different spatial directions. At least three interfaces C i (i=1, 2...N, N≥3) and C i’ (i'=1, 2...N', N'≥3 and not necessarily equal to N) are integrated in the upper or lower interface 104, 106, respectively, via which the structure 100 can be electrically manipulated and the magnetic field-dependent Measure the signal.
[0050] During the operation of the magnetic field sensor 100, at the interface C of one of the bounding surfaces 104 i With the second interface C of the oppo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com