A method for obtaining organic fertilizer and biological protein at the same time by biologically treating unsuitable fresh tobacco leaves with the larvae of P.
A technology of palm fly and bio-organic fertilizer, which is applied in application, animal feed, animal feed, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing capacity, reducing the cost of crushing, and promoting the effect of biological treatment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
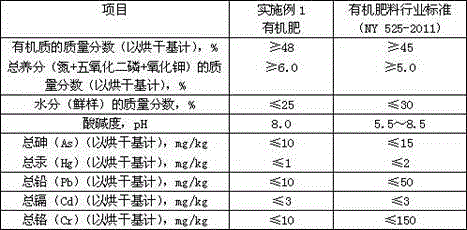
Embodiment 1
[0057] S1. Use a grass cutter to chop unsuitable fresh tobacco leaves into fragments with a particle size of 2 to 3 cm, add appropriate amount of auxiliary materials, stir evenly, and prepare compost; the formula of compost mentioned in S1 is shown in Table 1:
[0058] Table 1
[0059] raw material name
Mass percentage (%)
Not suitable for fresh tobacco leaves (fragments)
65
20
5
5
5
[0060] S2. Pour the culture material into the container, the culture material is 6cm thick, and insert an appropriate amount of the newly hatched larvae of the sarcophagus on the surface of the culture material, and the insertion density is: 0.2g of the newly hatched larvae of the palm fly / kg of the culture material;
[0061] S3. The newly-hatched larvae of Sarcophagus spp. began to decompose and transform the compost on the 1st day, and ensure that the moisture content of the compost was about...
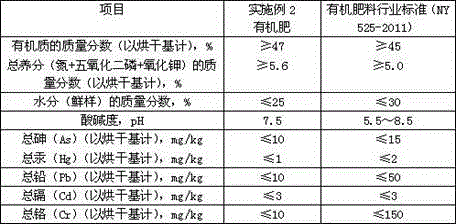
Embodiment 2
[0067] S1. Use a grass cutter to chop unsuitable fresh tobacco leaves into fragments with a particle size of 2 to 3 cm, add appropriate amount of auxiliary materials, stir evenly, and prepare compost; the formula of compost described in S1 is shown in Table 3:
[0068] table 3
[0069] raw material name
Mass percentage (%)
Not suitable for fresh tobacco leaves (fragments)
75
10
bran powder
5
5
5
[0070] S2. The compost is poured into the container, the compost is 8cm thick, and an appropriate amount of newly hatched larvae of S. sarcophagus is inserted on the surface of the compost, and the insertion density is: 1.0g of newly hatched larvae of S. sativa / kg compost;
[0071] S3. The newly-hatched larvae of Sarcophagus spp. began to decompose and transform the compost on the 1st day, and ensure that the moisture content of the compost was about 60%. On the 4th day, put a larger container...
Embodiment 3
[0077] S1. Use a grass cutter to chop unsuitable fresh tobacco leaves into fragments with a particle size of 2 to 3 cm, add appropriate amount of auxiliary materials, stir evenly, and prepare compost; the formula of compost described in S1 is shown in Table 5:
[0078] table 5
[0079] raw material name
Mass percentage (%)
Not suitable for fresh tobacco leaves (fragments)
85
bran
0
bran powder
5
5
5
[0080] S2. Pour the compost into the container, the compost is 10cm thick, and insert an appropriate amount of newly hatched larvae of Sarcophagus spp. on the surface of the compost, and the insertion density is: 2.0g of the newly hatched larvae of S.
[0081] S3. The newly-hatched larvae of Sarcophagus spp. began to decompose and transform the compost on the 1st day, and ensure that the moisture content of the compost was about 60%. On the 4th day, a larger container was placed outside the cul...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com