A Speculative Hadoop Scheduling Method Based on Load Balancing
A scheduling method and load balancing technology, applied in multi-programming devices, resource allocation, etc., can solve the problems of slow task running and job running, and achieve the effect of improving performance and avoiding load imbalance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
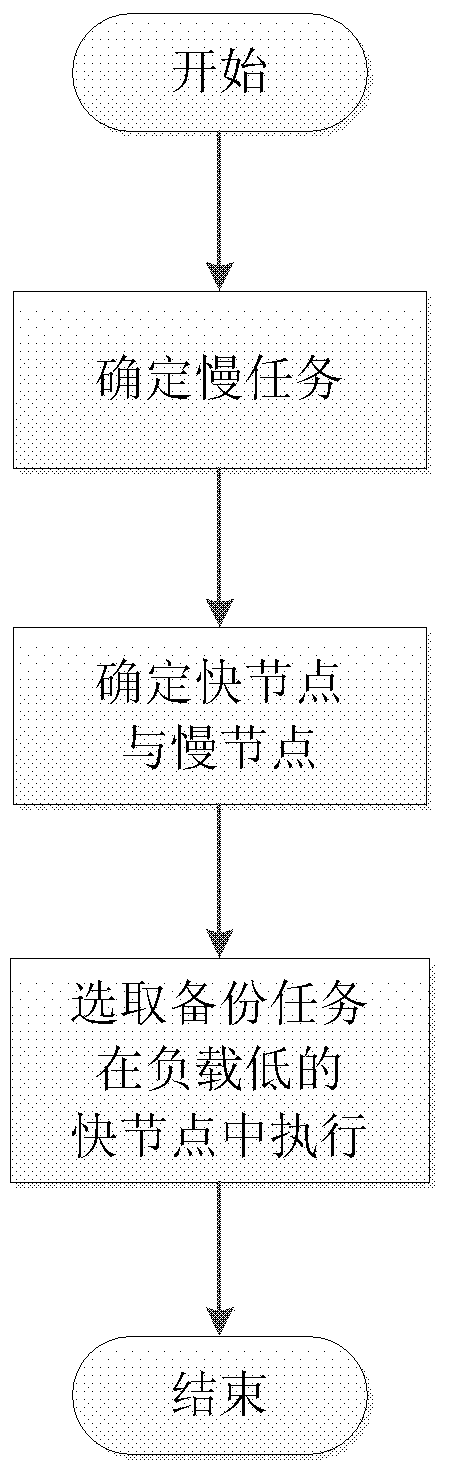
[0037] see figure 1 , which shows the overall flowchart of the speculative Hadoop scheduling method proposed by the present invention. The methods include:
[0038] S1: The method starts to determine whether the task is a slow task;
[0039] Whether a task is a slow task is judged according to the remaining execution time of the task. Specifically, assuming that the current execution progress of the task is A, and the task has been running for t, the remaining time of the task can be calculated as t1=t / A-t. Estimate the remaining completion time of the task based on the progress of the task and the running time, sort the tasks based on the remaining completion time, and select the task with the longest remaining completion time as the slow task; put the backup task of the slow task into the slow task queue.
[0040] S2: Determine which nodes in the cluster are fast nodes;
[0041] The criteria for judging are as follows: if there are a lot of slow tasks on a certain node, t...
Embodiment 2
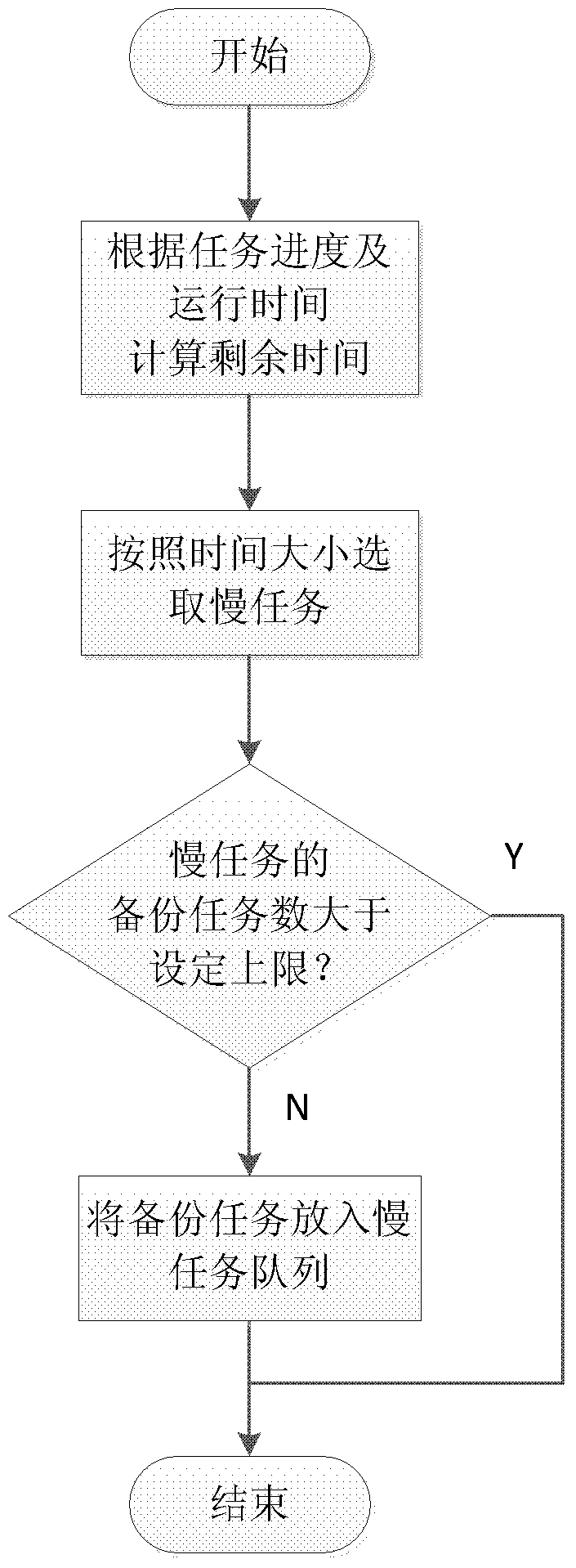
[0046] The step process of determining the slow task proposed by the present invention is as follows: figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0047] S11: Calculate the remaining execution time of the task according to the running progress and running time of the task;
[0048] Specifically: assuming that the current execution progress of the task is A, and the running time of the task is t, the remaining time of the task can be calculated as t1=t / A-t.
[0049] S12: Determine the slow task according to the remaining execution time calculated in step S11;
[0050] Specifically, the tasks are sorted based on the calculated remaining completion time of each task, and the task with the longest remaining completion time is selected as the slow task.
[0051] S13: Determine whether the number of backup tasks of the slow task is greater than a set upper limit; if yes, the process ends; if not, put the backup tasks of the slow task into the slow task queue, and the process ...
Embodiment 3
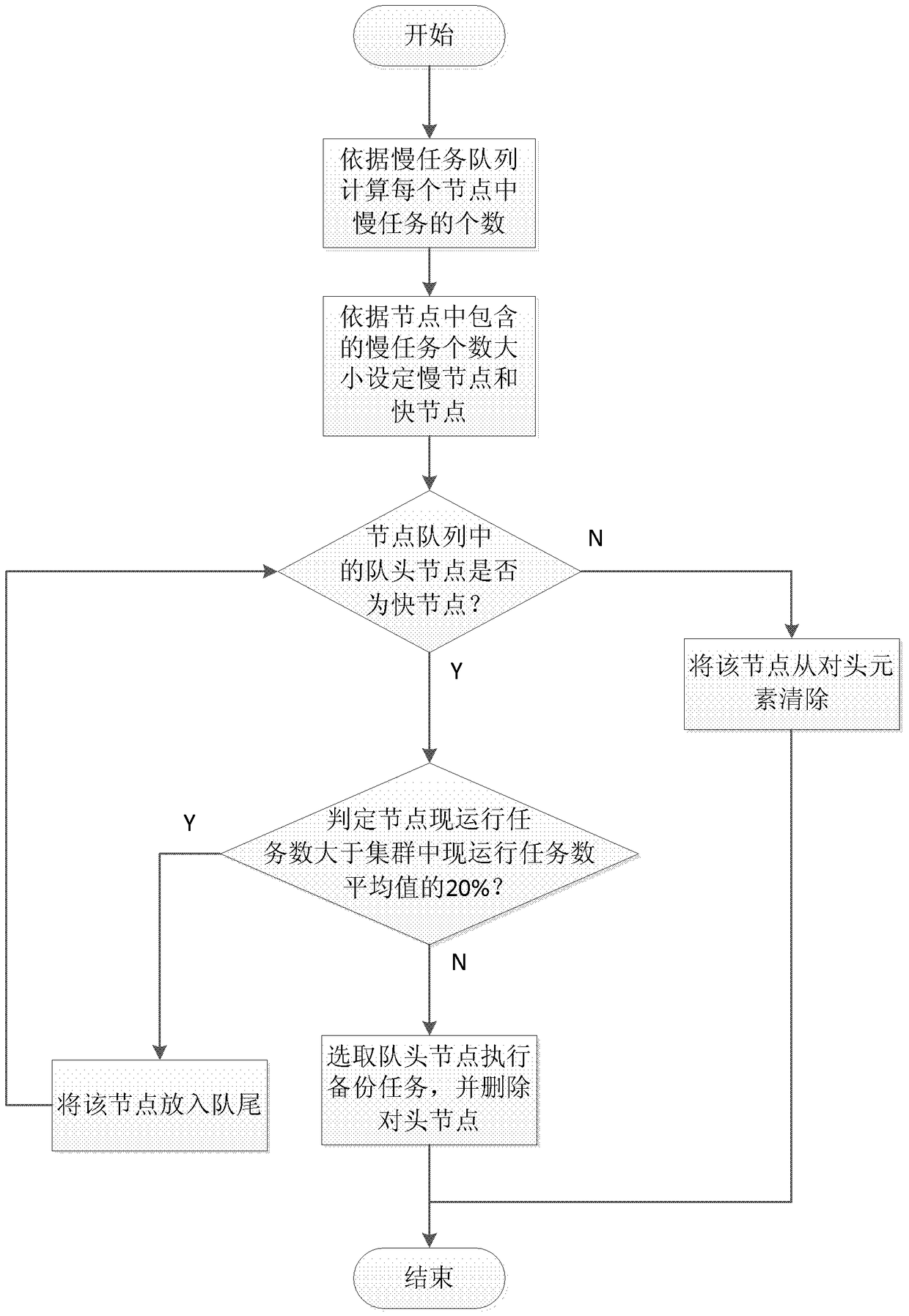
[0053] The flow chart of selecting the fast node to execute the backup task of the slow task is attached image 3 As shown, including the following processes:
[0054] S21: Determine whether the head node in the node queue is a fast node; if yes, execute step S22, otherwise execute step S25;
[0055] In the cluster system, all cluster node information is placed in the queue to form a node queue; when selecting a node in the cluster system to perform the backup task of the slow task, it is judged whether the head node in the current node queue is a fast node.
[0056] This step judges the slow node and the fast node according to the following principle: if there are many slow tasks on a node, the node is judged as a slow node; on the contrary, a node with few slow tasks is judged as a fast node.
[0057] S22: Judging whether the number of tasks currently running on the head node is greater than 20% of the average number of tasks running on all nodes in the cluster; if not, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com