Polymer drug-loaded materials for microvascular decompression surgery
A microvascular and polymer technology, applied in the field of polymer drug-loaded materials used in microvascular decompression surgery, can solve the problems of surrounding tissue adhesion, difficult to control aseptic meningitis, material displacement, etc., to reduce the recurrence rate and Complications, good brain histocompatibility, and the effect of improving surgical outcomes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1. Preparation of drug-loaded polymer PVA material
[0026] 1. Preparation of PVA decompression material
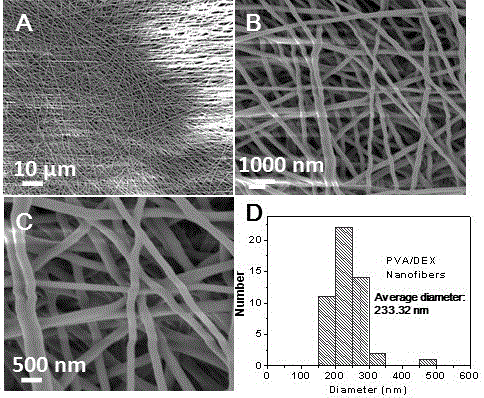
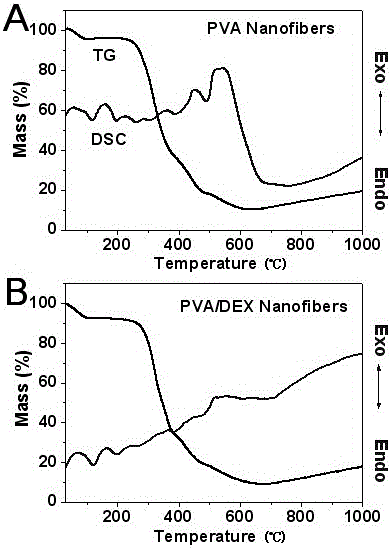
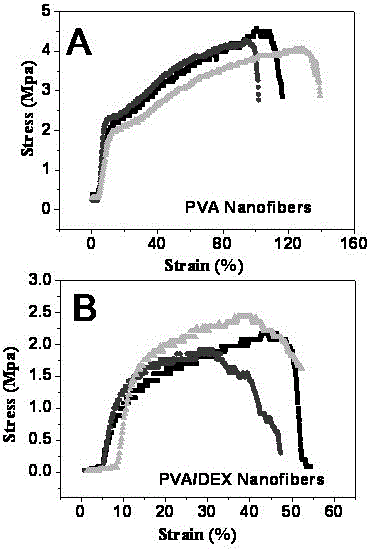
[0027] Weigh polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and dextran (DEX) powders into a 50 mL Erlenmeyer flask with a stopper, add an appropriate amount of distilled water, and heat with magnetic stirring to a constant temperature of 80 °C until the polymer is swollen and dissolved to obtain a concentration of 5 %~15% PVA aqueous solution. The PVA solution was sucked into a 5 mL glass syringe equipped with a 9# stainless steel needle, and the tip of the needle was ground flat as a spray needle, with an outer diameter of 1 mm and an inner diameter of 0.7 mm. The injection needle is connected to the positive pole of the high-voltage power supply, the collection device is connected to the negative pole of the power supply, and the injection voltage is set at 5 kV to 15 kV. The flow rate of the PVA solution was controlled by a syringe pump, the flow rate was 0.5 mL / h, and t...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2. Biocompatibility and its promoting effect on Schwann cell growth
[0035] Co-cultivation of drug-loaded polymer materials and Schwann cells: Take out the bilateral sciatic nerves of 3-day-old Wistar rats under sterile conditions, cut them into paste and put them into centrifuge tubes, add 0.125% trypsin + 0.03% IV Type collagenase, digest for 30-40min; centrifuge at 1500r / min for 5min; suspend the pellet with DMEM10%FCS medium, inoculate into culture dish, 37℃, volume fraction 5%CO 2 Incubate in a cell culture incubator. After 24 hours of culture, cytarabine with a final concentration of 10-5mmol / L was added to inhibit fibroblasts and glial cells, and the purity of Schwann cells identified by rabbit anti-S-100 polyclonal antibody was above 95%. 5-7 days after culture, press 1×10 6 Each / L concentration was passaged to a 0.5cm×0.5cm drug-loaded polymer material petri dish. On the seventh day after inoculation, the growth of Schwann cells in the experimental ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com