Freeform surface building grid division method based on self-defined element method
A grid division and self-definition technology, applied in 3D modeling, image data processing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to meet the aesthetic requirements of grid architecture, grid unevenness, and relying on the design experience of engineers to meet Aesthetic requirements and visual effects, diverse grid forms, flexible and controllable methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
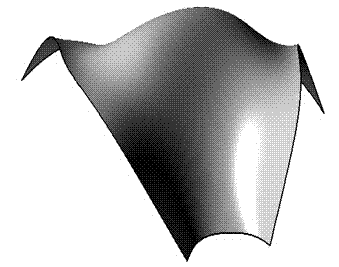
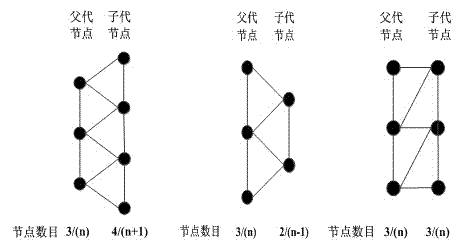
[0030] A free-form surface building model, such as figure 1 Shown. Surface size along the parametric domain u The direction changes regularly, and the custom unit types such as figure 2 Shown.
[0031] According to the surface size characteristics, select the parameter domain u The direction is used as the node advancing direction.
[0032] The number of advance steps is 27, and the parameter line of the node of each generation is obtained. The initial number of nodes is determined to be 10, along with u =0 Parameter line layout, dichotomy loop adjusts the node parameter coordinates, so that the surface distance under the initial node Riemann metric is equal.
[0033] Select the element type according to the surface features of the parametric line where the upper and lower nodes are located. When the surface is expanded, the meristematic unit is automatically selected to increase the number of nodes in the next generation; when the surface is contracted, the symbiotic unit is auto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com