Block-division low-power-consumption magnetic memory cache framework design method
A technology of magnetic memory and architecture design, applied in the direction of digital memory information, static memory, memory system, etc., can solve the problem of high write power consumption of on-chip cache, and achieve the effect of reducing write power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
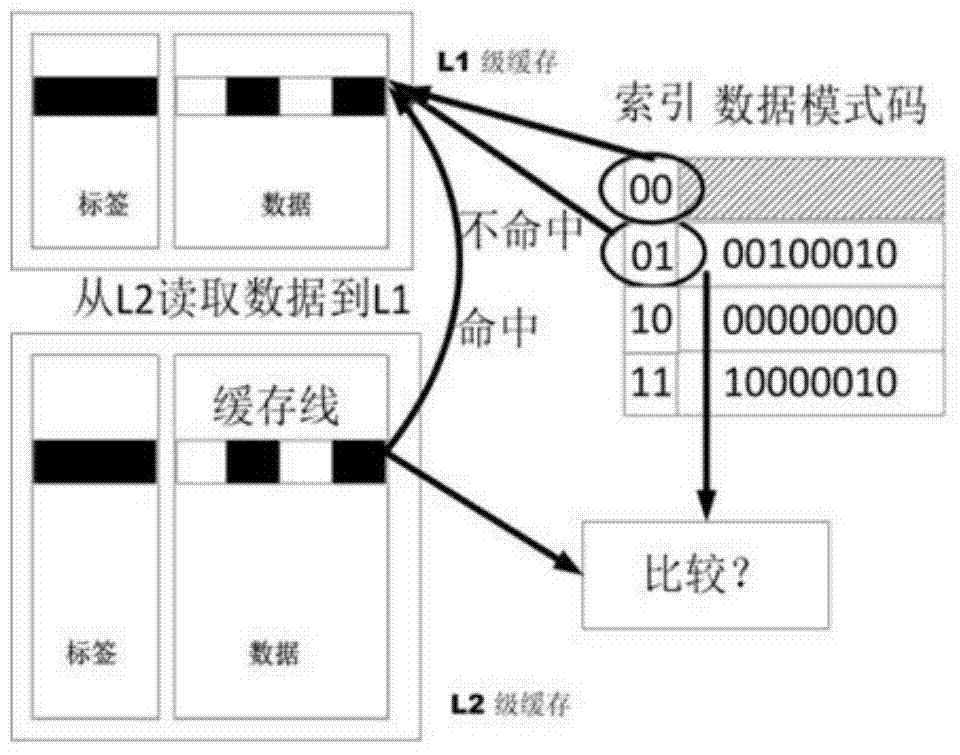
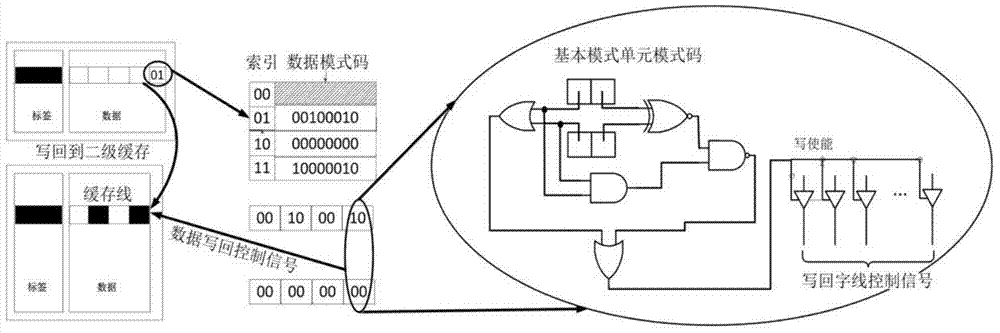
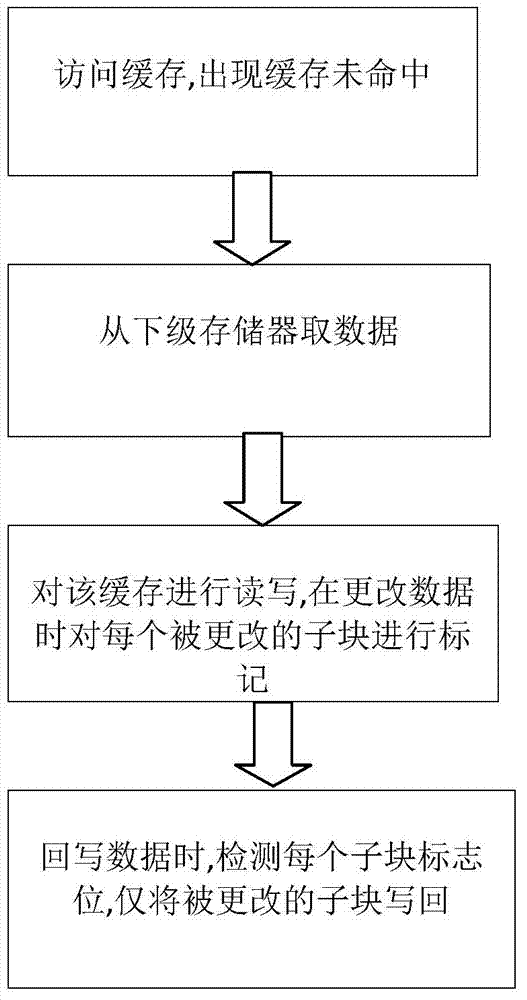
[0023] The invention aims to solve the problem of excessive writing energy consumption caused by using non-volatile memory such as STT-MRAM as an on-chip cache. By analyzing the characteristics of data written in the L1 and L2 caches, a single block in the L1 cache is divided into several sub-blocks. In addition to storing the content of the original block, each block also sets an additional index bit. The purpose of the index bit will be described later. Each sub-block has three modes: 0 (all bits in the block are 0), 1 (all bits in the block are 1), 2 (other modes that are neither 0-mode nor 1-mode). The mode is expressed in units of blocks. For example, if a block is divided into four sub-blocks, the mode of the block is composed of four sub-patterns. These four sub-patterns correspond to a sub-block respectively, and each sub-pattern is 0, 1, and 2. one of the . In this way, each block has a corresponding unique combination mode.
[0024] See figure 2 , the present inv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com