Light emitting element, manufacturing method thereof, and display device
A light-emitting element and manufacturing method technology, applied to electrical components, laser parts, lasers, etc., can solve problems such as radius shape bending, complex structure of super light-emitting diodes, and changing the direction of emitted light
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
[0047] 3. Example 2 (Methods of Manufacturing Light-Emitting Elements According to Second and Fourth Embodiments of the Present Invention) and the like.
[0048] [Explanation of the entire light-emitting element according to the first embodiment and the second embodiment of the present invention, the method of manufacturing the light-emitting element according to the first embodiment to the fourth embodiment of the present invention, and the display device of the present invention]
[0049] A method for manufacturing a light-emitting element according to the first embodiment or the second embodiment of the present invention is preferably implemented in the following form, wherein,
[0050] In the process (a), the first compound semiconductor layer, the active layer, the first layer of the second compound semiconductor layer, and the 2A layer of the second compound semiconductor layer, the first etch stop layer, the the 2B layer of the second compound semiconductor layer, the s...
example 1
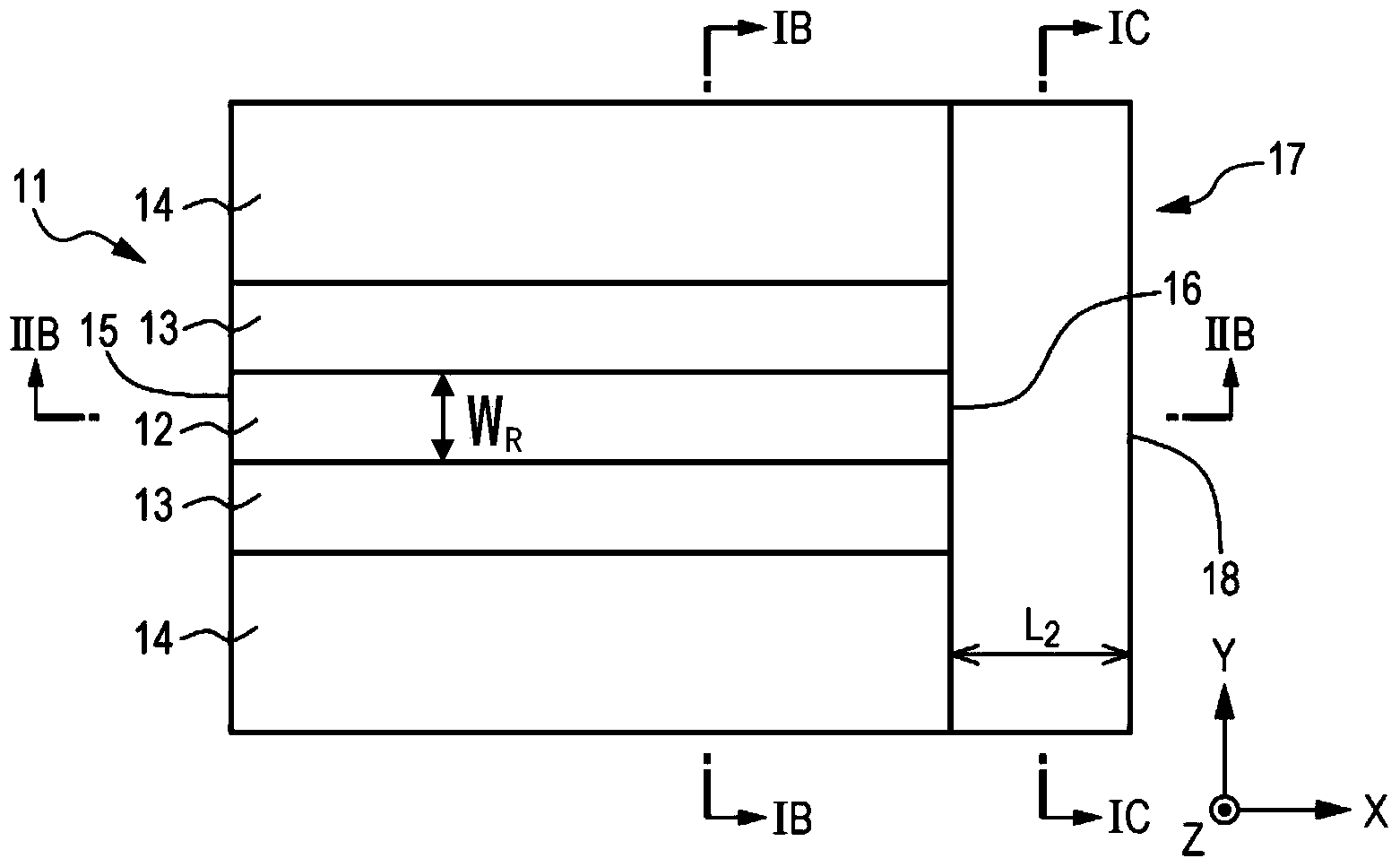
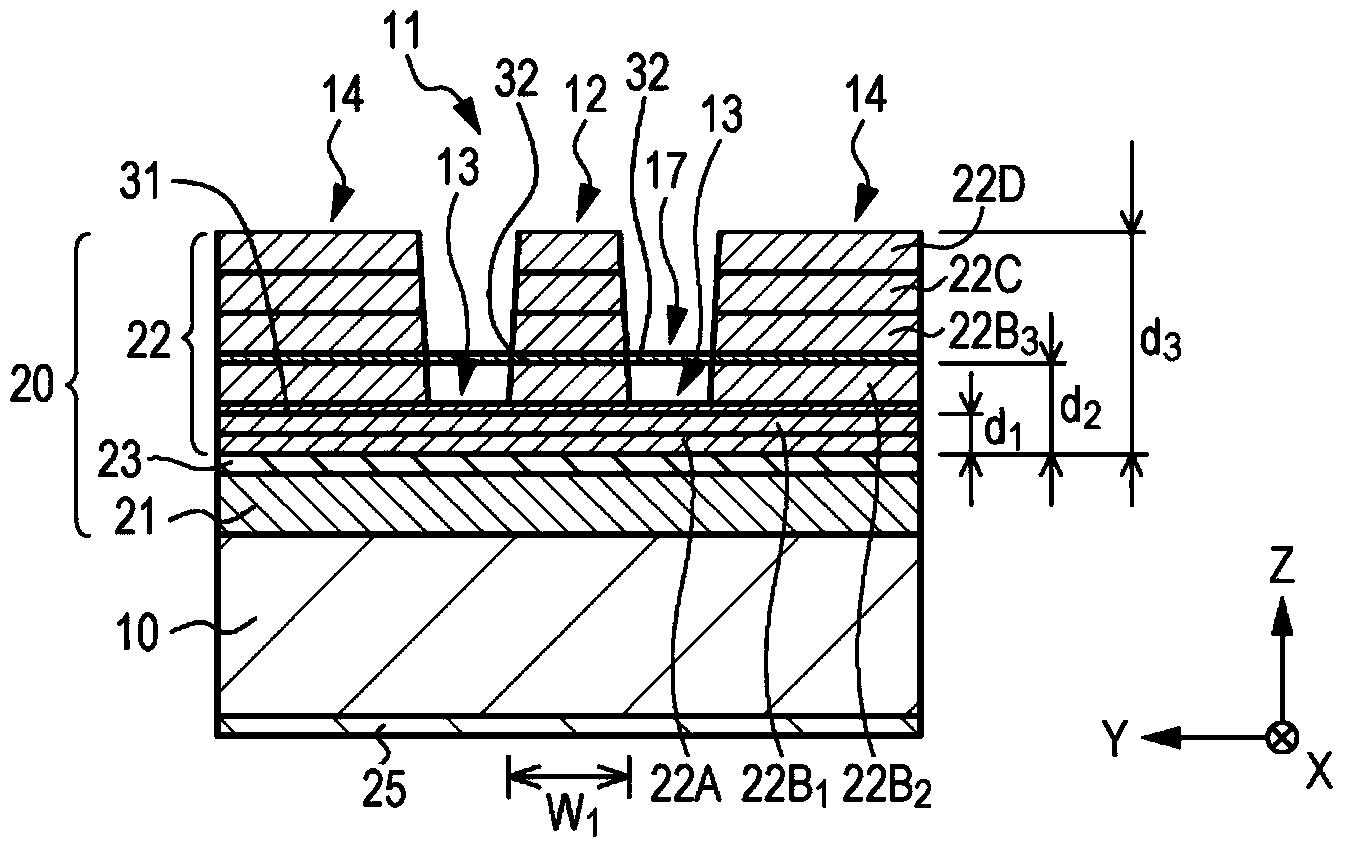
[0095] Example 1 relates to the light emitting element according to the first embodiment and the second embodiment of the present invention, and the method of manufacturing the light emitting element according to the example 1 and the third embodiment of the present invention. Figure 1A A schematic plan view showing a laminated structure constituting the light-emitting element of the first embodiment, Figure 1B showing along Figure 1A A schematic cross-sectional view of a laminated structure etc. obtained by middle arrow IB-IB, Figure 1C showing along Figure 1A A schematic cross-sectional view of a laminated structure and the like obtained by middle arrows IC-IC. also, Figure 2A A perspective view showing a laminated structure of the light-emitting element of Example 1, etc., Figure 2B showing along Figure 1A The schematic cross-sectional view of the laminated structure obtained by the middle arrow IIB-IIB, image 3 a schematic partial cross-sectional view showing...
example 3
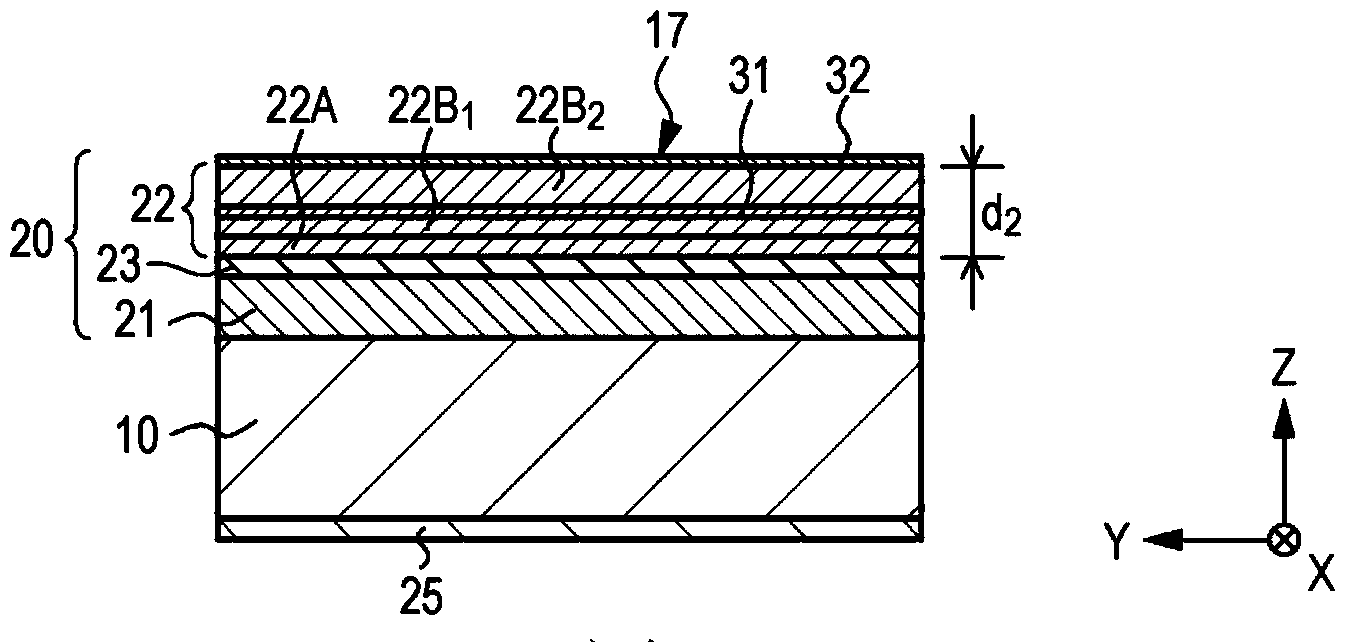
[0147] Example 3 is a variation of Examples 1 and 2. As a schematic partial sectional view of the light propagation region 17 of the light emitting element of Example 3 Figure 9 As shown, in Example 3, the first dielectric film 24 is formed on at least one side surface of the ridge-ridge structure portion 12 and the top surface of the ridge-ridge-corrugation adjacent portion 13 (see image 3 ), and a second dielectric film 24A made of a material different from that of the first dielectric film 24 is formed on the top surface of the light propagation region 17 . Specifically, the first dielectric film 24 is made of Ta 2 o 5 made, the second dielectric film 24A is made of SiO 2 production.
[0148] The composition and structure of the light emitting element of Example 3 may be the same as those of Examples 1 and 2 except for the above-mentioned points, and thus no detailed description will be provided. As described above, by making the material of the first dielectric film ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com