Collisional broadening compensation using real or near-real time validation in spectroscopic analyzers
A technology for spectrometers and analytes, applied in the field of collision broadening compensation using real-time or near-real-time verification in spectrometers, can solve the problems of not being able to provide measurement accuracy and not being suitable for gas analysis applications in the chemical process industry
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
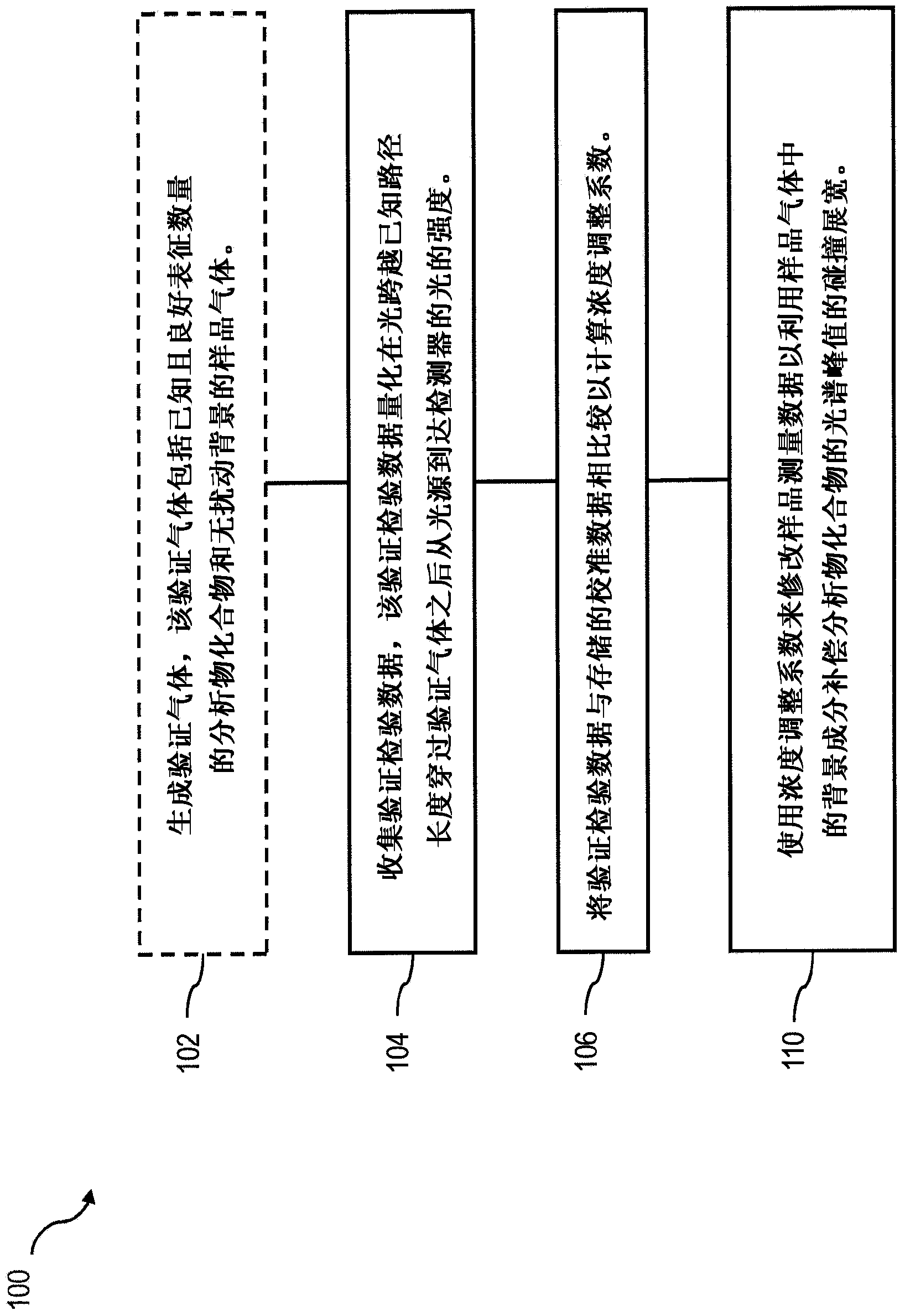
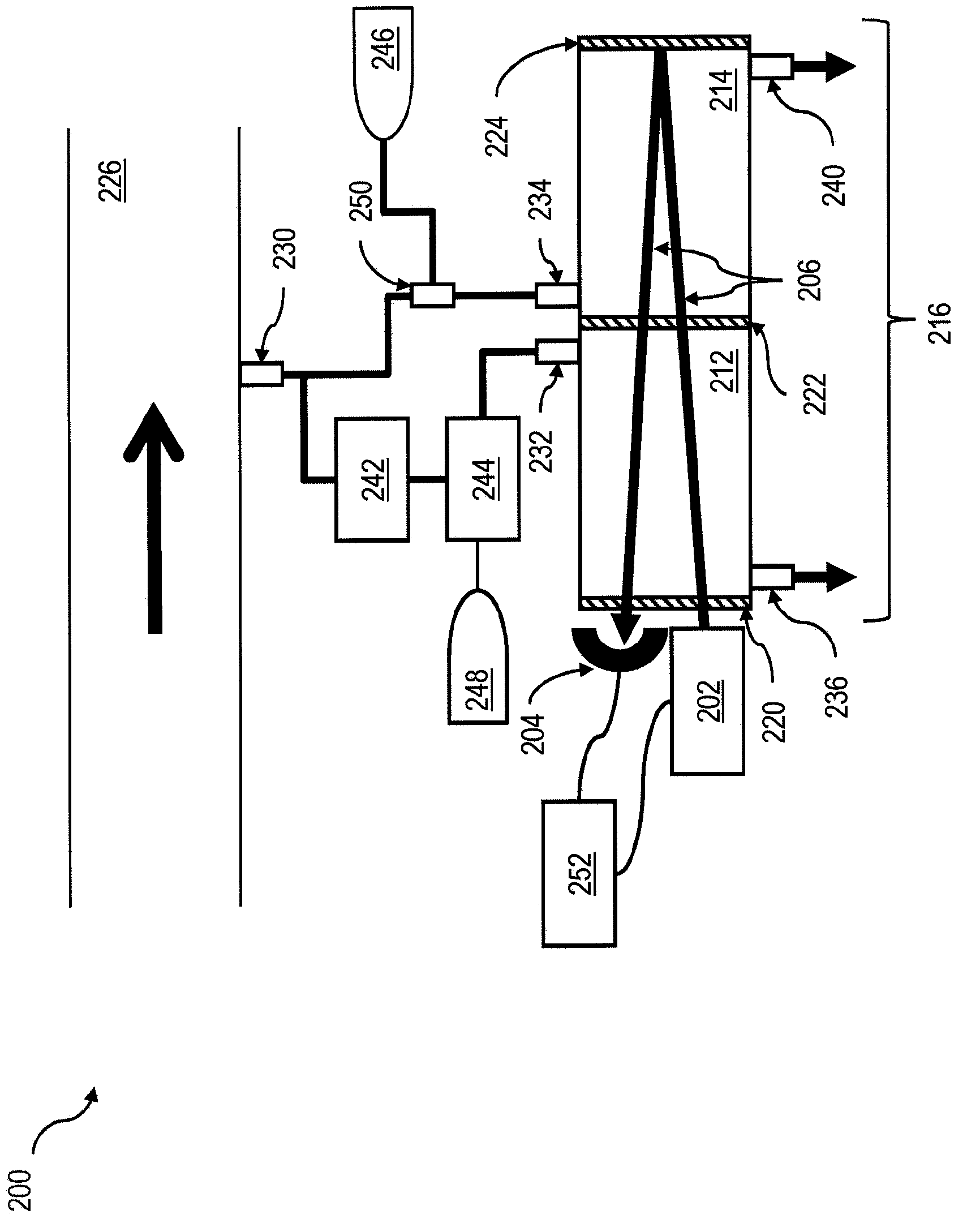
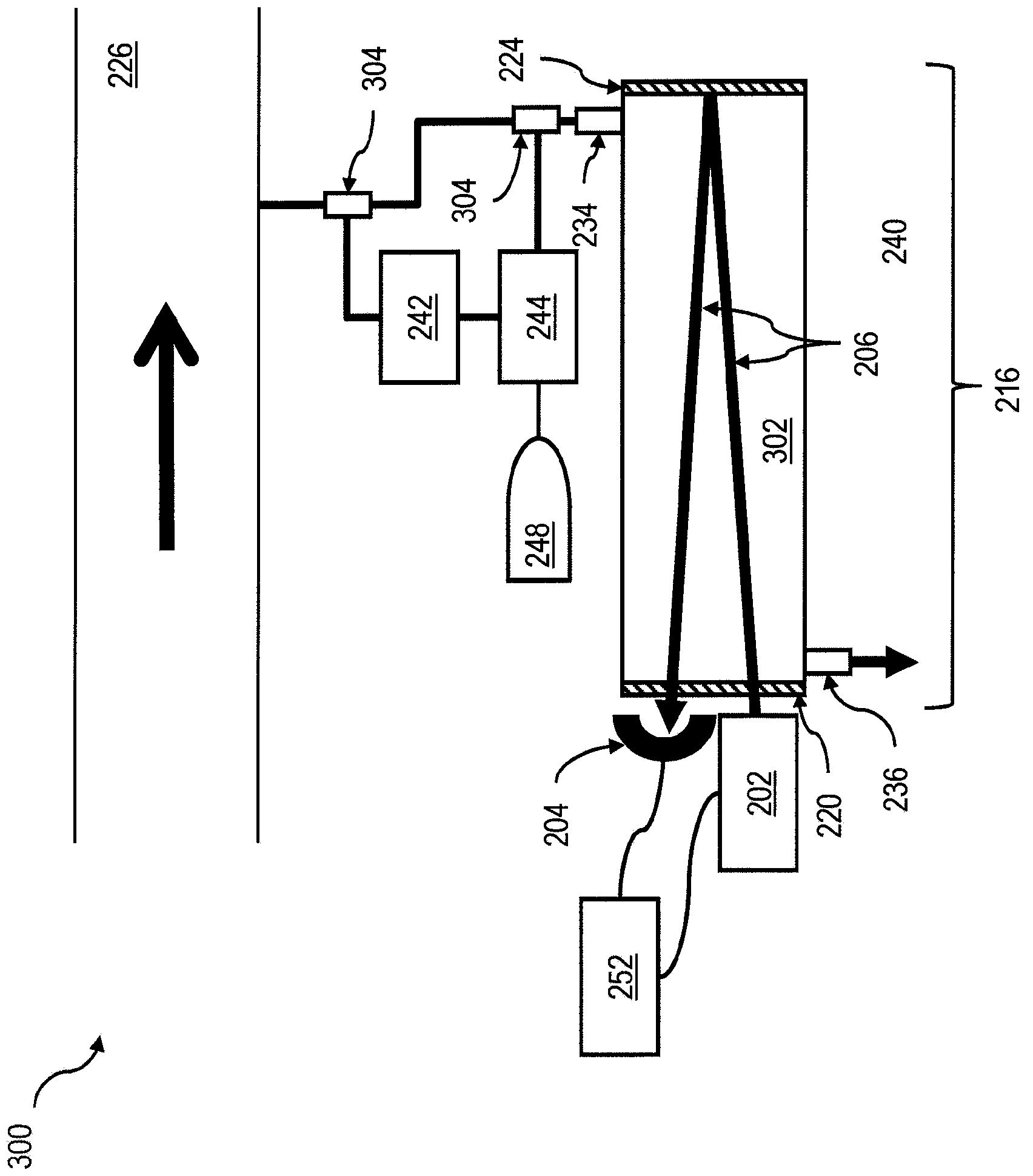
[0022] To address the foregoing and other potential problems with analytical validation of spectroscopic measurements, implementations of the present invention can provide trace gas generators that add known, temporally consistent and stable amounts of trace analytes to a gas stream to facilitate the gas flow. The flow is used as a verification flow for use in the verification of the spectrometer and compensation for collisional broadening effects that can affect the analysis. Methods consistent with implementations of the present invention can facilitate the on-site preparation of a standard verification gas for use in conjunction with a system that detects and / or quantifies parameters including its spectral absorptivity properties that may or may not be associated with one or more Trace analytes Concentrations of one or more trace analytes in a gas mixture that overlap those of other compounds in a complex and / or varying background. Such methods can also facilitate the measu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com