Thin-film transistor, preparation method of thin-film transistor, array substrate and display device
A thin-film transistor and thin-film technology, applied in transistors, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of destroying the performance of the active layer and affecting the performance of thin-film transistors, so as to avoid direct damage and ensure performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
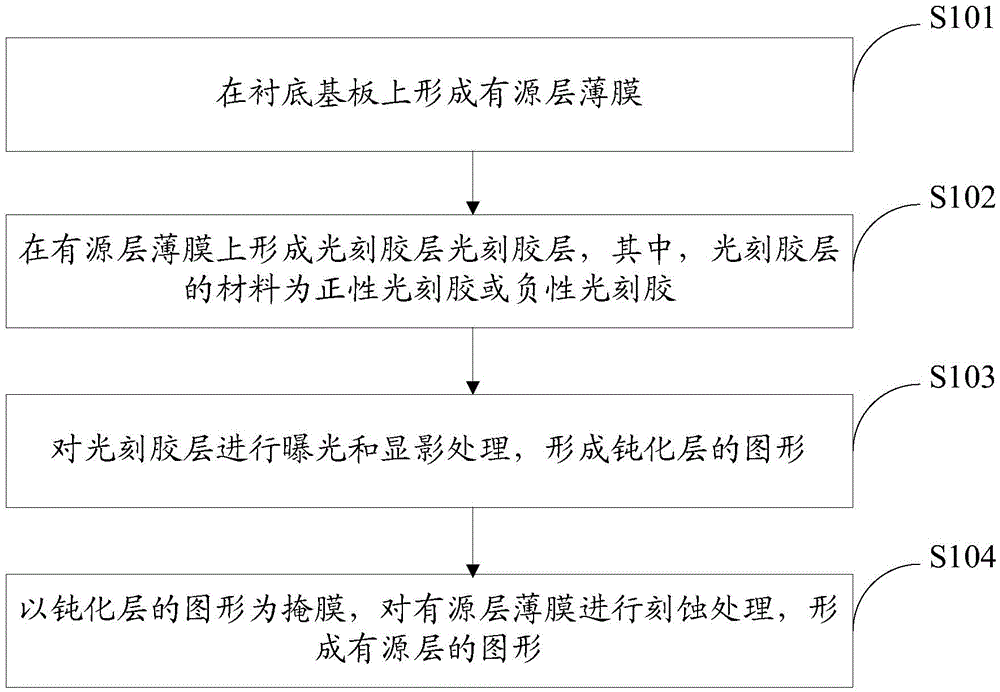
[0042] A method for manufacturing a thin film transistor provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes forming patterns of a gate electrode, a source electrode, and a drain electrode on a base substrate, and further includes:
[0043] Forming the pattern of the active layer and the pattern of the passivation layer covering the active layer through a patterning process; wherein,
[0044] The material of the passivation layer is negative photoresist or positive photoresist, the active layer and the gate electrode are insulated from each other, and the active layer is electrically connected to the source electrode and the drain electrode respectively.
[0045] In the above-mentioned preparation method provided by the embodiment of the present invention, since the material of the passivation layer is a negative photoresist or a positive photoresist, the pattern of the active layer and the passivation layer covering the active layer are formed through a patterning proc...
example 1
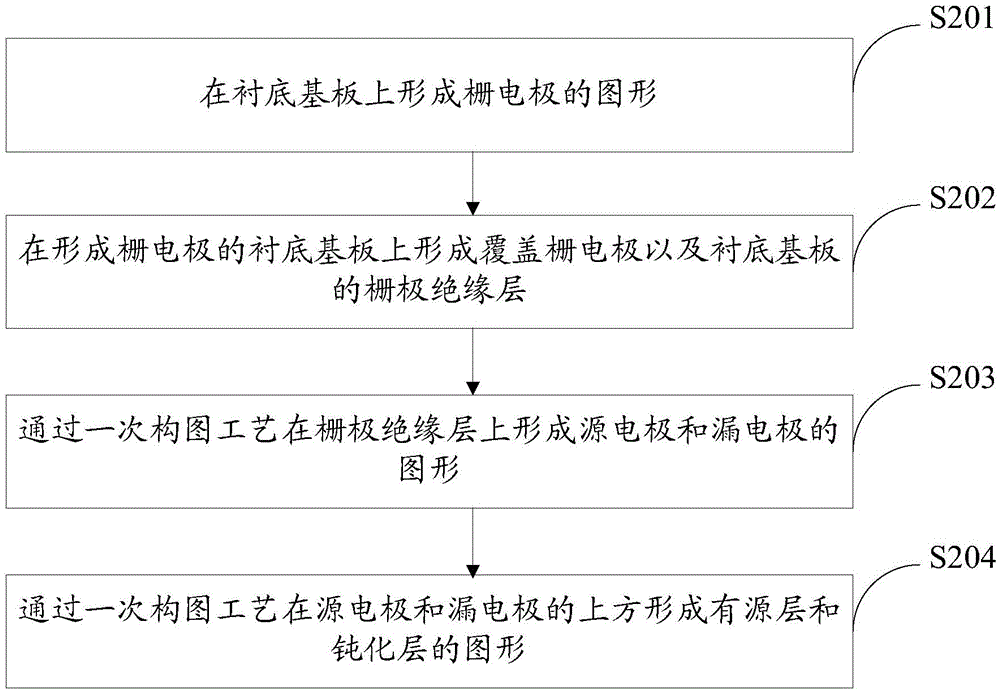
[0076] A thin-film transistor with a bottom-gate structure is prepared, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0077] (1) Form the pattern of the gate electrode 01 on the base substrate 1, such as Figure 4a shown;
[0078] Specifically, during specific implementation, a gate electrode layer may be formed on the substrate by means of thermal evaporation or sputtering, and then a pattern of the gate electrode may be formed by a photolithography process, which is not limited herein.
[0079] (2) Form a gate insulating layer 02 covering the gate electrode 01 and the base substrate 1 on the base substrate 1 on which the gate electrode 01 is formed, such as Figure 4b shown;
[0080] Specifically, in actual implementation, the gate insulating layer may be formed by evaporation, sputtering or spin coating, which is not limited herein.
[0081] (3) Form the patterns of the source electrode 03 and the drain electrode 04 on the gate insulating layer 02 through a patterni...
example 2
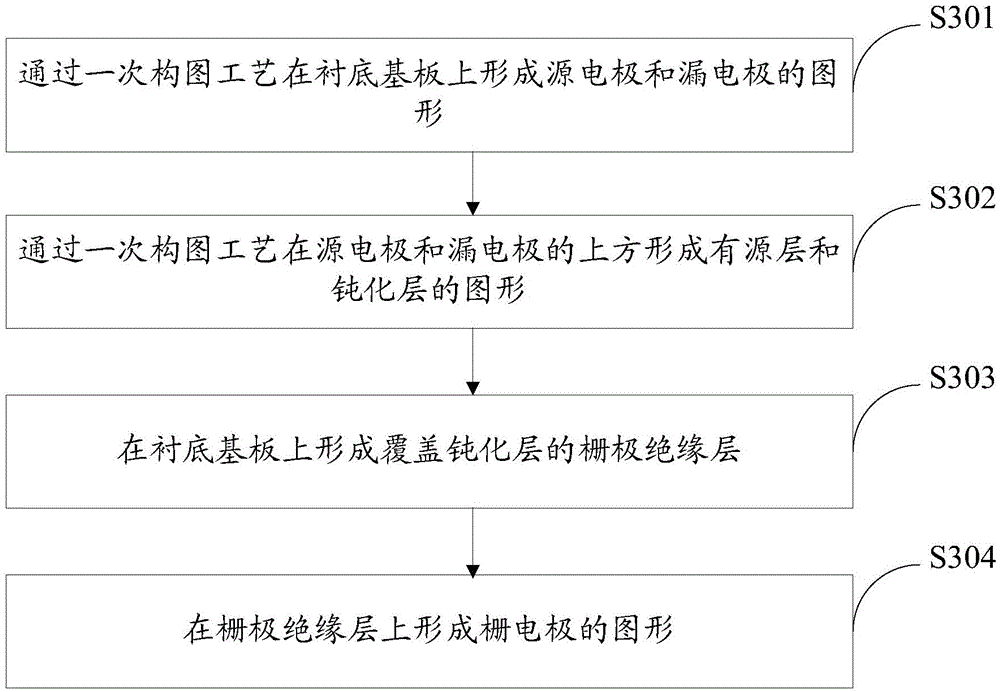
[0095] A thin film transistor with a top-gate structure is prepared, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0096] (1) Form the patterns of the source electrode 03 and the drain electrode 04 on the base substrate 1 through a patterning process, such as Figure 5a shown;
[0097] Specifically, in a specific implementation, the source and drain electrode layers may be formed on the base substrate by means of evaporation, spin coating or sputtering, and then the pattern of the source electrode and the drain electrode is formed by a photolithography process, which is not limited herein.
[0098] (2) Form the active layer film 05 above the source electrode 03 and the drain electrode 04, such as Figure 5b shown;
[0099] Specifically, during specific implementation, the thin film of the active layer may be formed by spin coating, which is not limited herein.
[0100] (3) a photoresist layer 06 with a negative photoresist material is formed on the active layer film 05, su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com