Engine oil control valve with guiding structure
A technology of oil control valve and guide structure, which is applied to non-mechanically actuated valves, valve devices, mechanical equipment, etc. Reduced load, reduced friction and wear, reduced wear effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
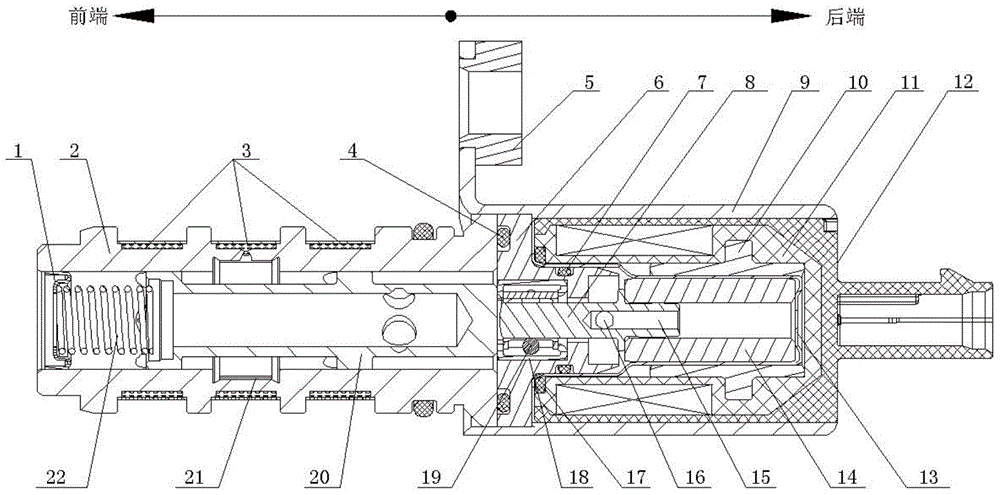
[0028] Such as figure 1 The shown oil control valve with guiding structure mainly includes spring seat 1, valve sleeve 2, pole shoe 6, magnetic core shaft 8, valve housing 9, electromagnetic solenoid assembly 12, magnetic core 14 and valve core 20 and a one-way valve 21, wherein the electromagnetic solenoid assembly 12 includes a skeleton 11 and a back yoke sleeve 10, the spring seat 1 is fixedly connected with one end of the valve sleeve 2, and the other end of the valve sleeve 2 is fixedly connected with the valve casing 9, The valve core 20 is installed in the inner cavity of the valve sleeve 2, and a spring 22 is arranged between the valve core 20 and the spring seat 1; They are respectively fixedly connected to both ends of the inner chamber of the valve housing 9, and an elastic washer 17 is arranged between the larger end of the pole shoe 6 and the skeleton 11 on the electromagnetic solenoid assembly 12. The main function of the elastic washer 17 is Prevent the electro...
Embodiment 2
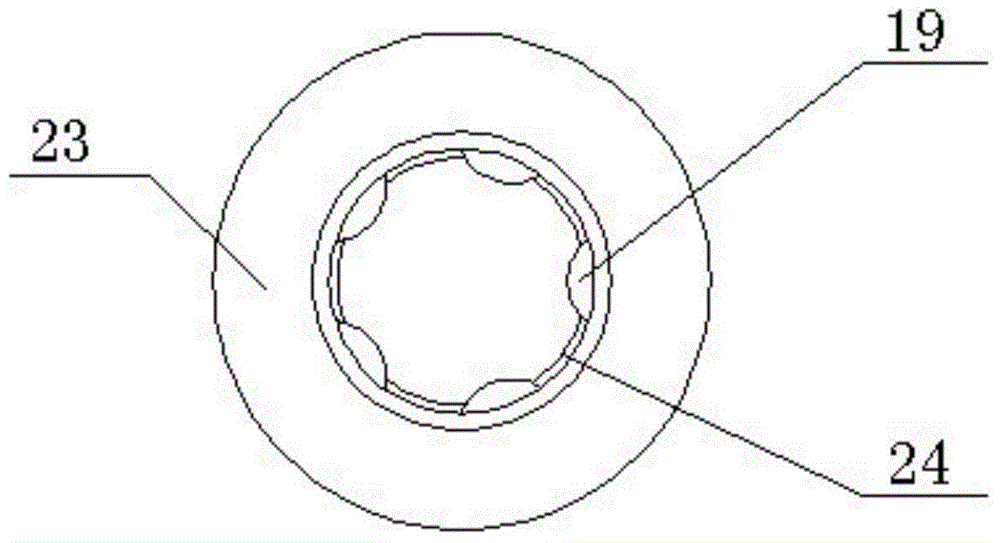
[0032]The difference from Embodiment 1 is that the bearing sleeve 23 of the first guide bearing 18 is omitted, and the ball 19 is arranged directly in the pole shoe 6 . Specifically, as Image 6 , Figure 7 As shown, a number of guide grooves 26 arranged circumferentially along the tail end of the pole shoe 6 are provided at the relatively large end of the pole piece 6, and balls 19 that can roll axially along the guide groove 26 are installed in the guide groove 26, and pass through The bottom plane of the guide groove 26 and the end surface of the tail end of the pole shoe 6 are riveted to limit the axial movement stroke of the ball 19 . The magnetic core 14 is supported on the guide sleeve 13 and is supported on the ball 19 through the front end of the magnetic core shaft 8 . In this way, when the magnetic core 14 moves axially under the drive of electromagnetic force and spring force, the magnetic core 14 is supported and guided by the guide sleeve 13 and forms sliding f...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Different from the above-mentioned embodiment 1 and embodiment 2, as Figure 8 , Figure 9 As shown, a second guide bearing is set between the magnetic core shaft 8 and the guide sleeve 13, and the open end of the guide sleeve 13 extends to the outside of the larger end of the pole piece 6. The structure of the second guide bearing is as follows Figure 10 , Figure 11 As shown, it includes a bearing frame 27 and a ball 19. The main part of the bearing frame 27 is ring-shaped, and several guide grooves 25 are provided on it. One end of the bearing frame 27 protrudes from several rings. The main part of the bearing frame 27 is evenly distributed in the circumferential direction. The L-shaped claws 28 are used to ensure that the bearing frame 27 is evenly stressed in the axial direction. The ball 19 is installed in the guide groove 25 and can roll axially along the guide groove 25 , and its axial rolling stroke is the axial length of the guide groove 25 . A ring groove...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com