Prostatic cancer marker lncRNA MALAT-1 and application thereof
A prostate cancer and sequence technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve problems such as elevated PSA
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
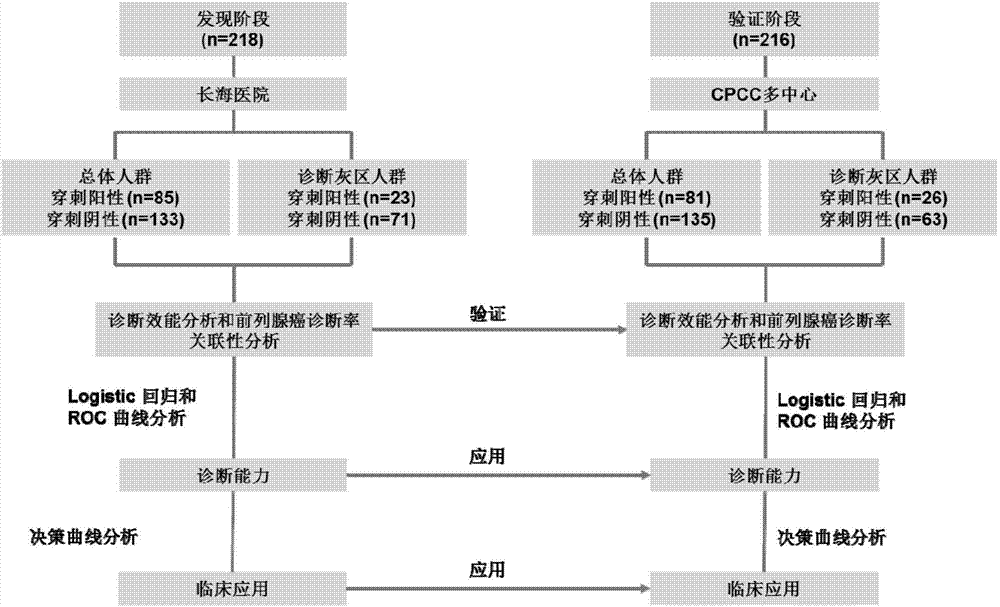
[0100] Summary of clinical specimen information
[0101] In this study, 536 consecutive clinical cases were selected, of which 29 cases were excluded due to insufficient RNA isolation in urine sediment, and 73 cases were excluded due to insufficient collection of prostate cells in urine sediment. Therefore, the final cases of this study The number is 434 cases, of which 218 cases were in the discovery group and 216 cases in the verification group. The clinical information of all cases is summarized in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that in the overall population of the discovery group, PCa-related risk factors (age, total PSA, prostate volume, PSA free ratio, and digital rectal examination) were significantly higher in the tumor group than in the negative biopsy group. However, in the "diagnostic gray zone" of PSA, serum total PSA could not distinguish the tumor group from the biopsy-negative group. Thereafter, the present inventors also obtained the same conclusion in...
Embodiment 2
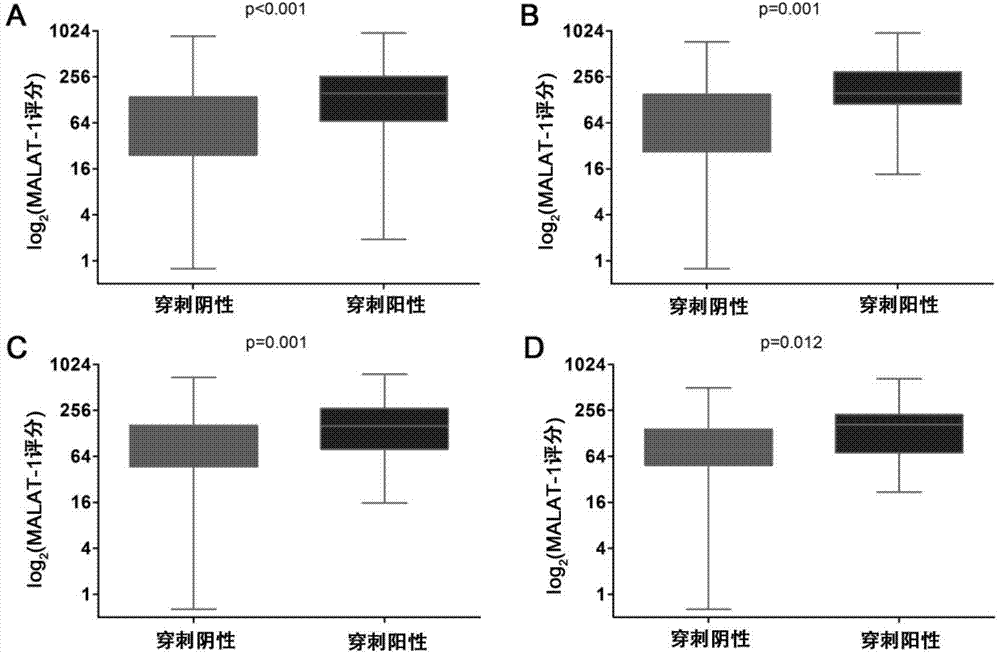
[0103] The urine MALAT-1 score can clearly distinguish the tumor group from the biopsy-negative group and is highly correlated with the detection rate of PCa
[0104] In order to study whether the urine MALAT-1 score can be used as an effective PCa molecular marker, the inventors of this study detected the urine MALAT-1 score in the discovery group and the verification group, and made further statistical analysis. The study found that whether in the general population or in the PSA "diagnostic gray area" population, the expression of urine MALAT-1 score in tumor cases was significantly higher than that in negative cases, such as figure 2 The difference in the expression of urine MALAT-1 score between the tumor group and the biopsy-negative group, (A) the overall population of the discovery group, (B) the PSA "diagnostic gray area" population of the discovery group, (C) the overall population of the verification group , (D) Validation group PSA "diagnostic gray zone" populatio...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Logistic regression analysis of the diagnostic performance of urine MALAT-1 score for PCa
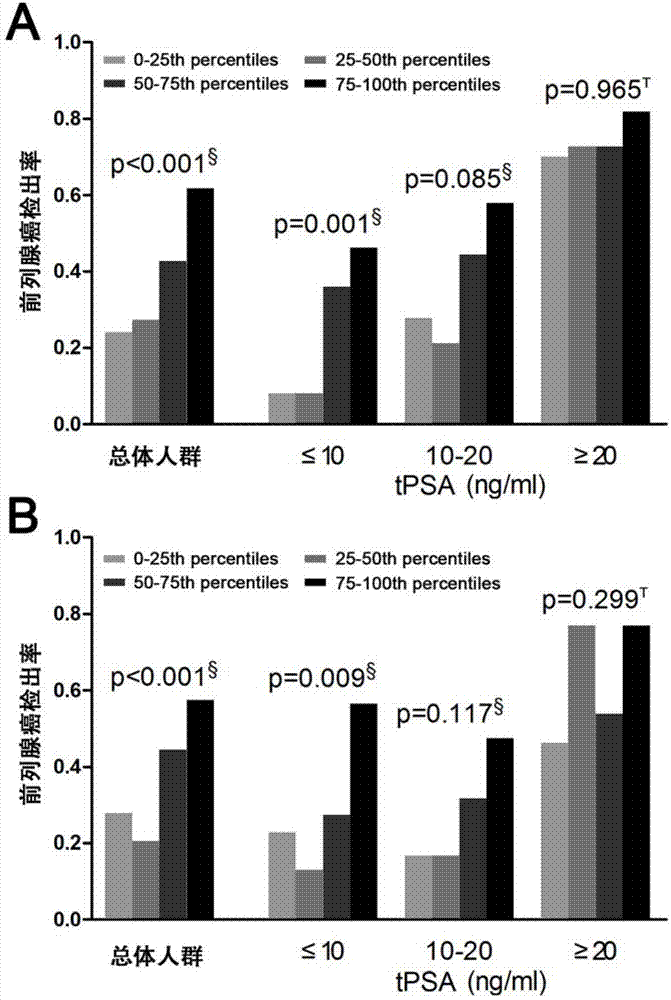
[0108] The inventors established univariate and multivariate logistic regression models, and proved that the urine MALAT-1 score and other risk factors are independent predictors of PCa in the general population, but total PSA cannot be the predictor of PCa in the PSA "diagnostic gray zone" population. Independent predictors of PCa, see Table 2, Table 3 and Figure 6 The area under the receiver operating curve shown was used to analyze the diagnostic performance of urine MALAT-1 score and other risk factors for PCa.
[0109] In the univariate logistic regression model, the diagnostic efficiency of urine MALAT-1 score for PCa in the general population was not statistically significant compared with total PSA, but it was significantly better than total PSA in the PSA "diagnostic gray area" population, see Figure 4 A. Figure 4C and Supplementary Table 2. At the same time, no mat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com