Asymmetric double-stator cylindrical permanent magnet linear motor
A permanent magnet linear motor, cylindrical technology, applied in electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve the problems of reduction, poor heat dissipation, thrust density limitation, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing consumption, avoiding heat dissipation difficulties, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
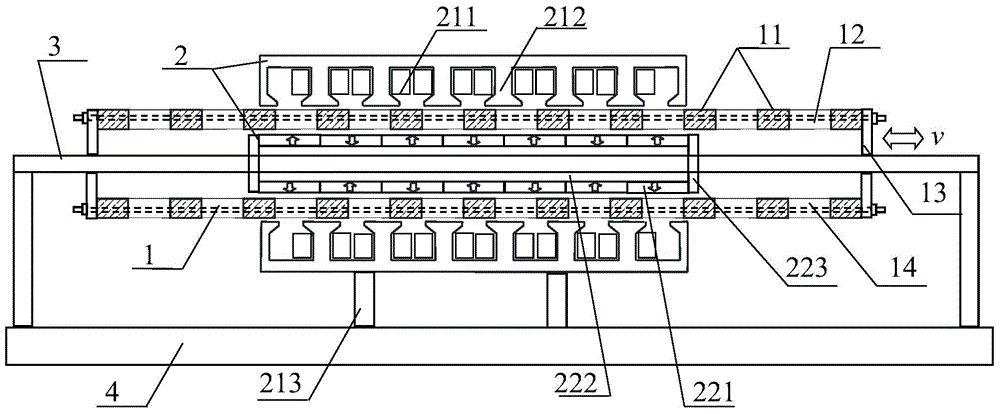
[0033] Such as figure 2 As shown, the overall schematic diagram of the asymmetric double-stator cylindrical permanent magnet linear motor of this embodiment, the magnetic pole part of the short stator is installed on a long shaft 3 inside, fixed by bolts 223 at both ends, and the two ends of the long shaft are supported by brackets It is fixed on the working platform 4; the long moving part is filled with liquid non-magnetic material and then separated after solidification, or directly separated by a non-magnetic ring. The hole is opened in the magnet block and fixed by long bolts 14, and then in the long Sliding bearings 13 are installed at both ends of the mover 1, and the air gap with the short stator pole part 22 is kept constant; the armature part of the short stator is directly fixed on the working platform 4 through the bracket 213, and the air gap with the long mover 1 is kept constant .
[0034] The asymmetric dual-stator cylindrical permanent magnet linear motor ad...
Embodiment 2
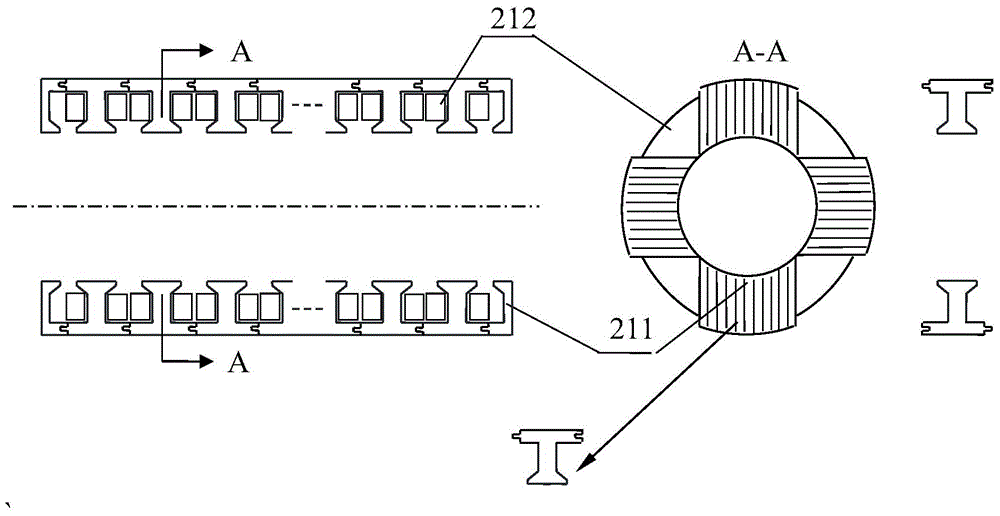
[0040] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the feature of this embodiment is that the number of magnet blocks of the long mover is different from the number of slots of the armature of the short stator by 2, and the rest are the same as in Example 1, and the radial magnetization structure is also adopted. In this embodiment, the asymmetrical double stator The working principle of the cylindrical permanent magnet linear motor is the same as that of the first embodiment. With the change of the position of the mover, the flux linkage in the armature winding is positive and negative alternating, which is basically sinusoidal and bipolar flux linkage.
Embodiment 3
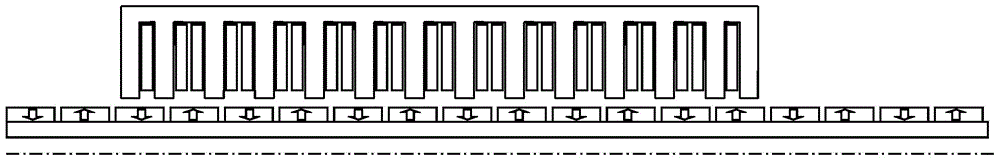
[0042] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the characteristic of this embodiment is that the number of permanent magnets of the short stator is twice the number of teeth of the armature of the short stator.
[0043] The working principle of the asymmetric double-stator cylindrical permanent magnet linear motor in this embodiment is the same as that in Embodiment 1. With the change of the position of the mover, the flux linkage in the armature winding is positive and negative alternating, which is basically sinusoidal. Bipolar magnetic linkage.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com