Reconfigurable variable length FIR filters for optimizing performance of digital repeater
A reconfiguration and filter technology, applied in digital technology networks, complex mathematical operations, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem that the FIR filter structure does not meet the needs of repeaters
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
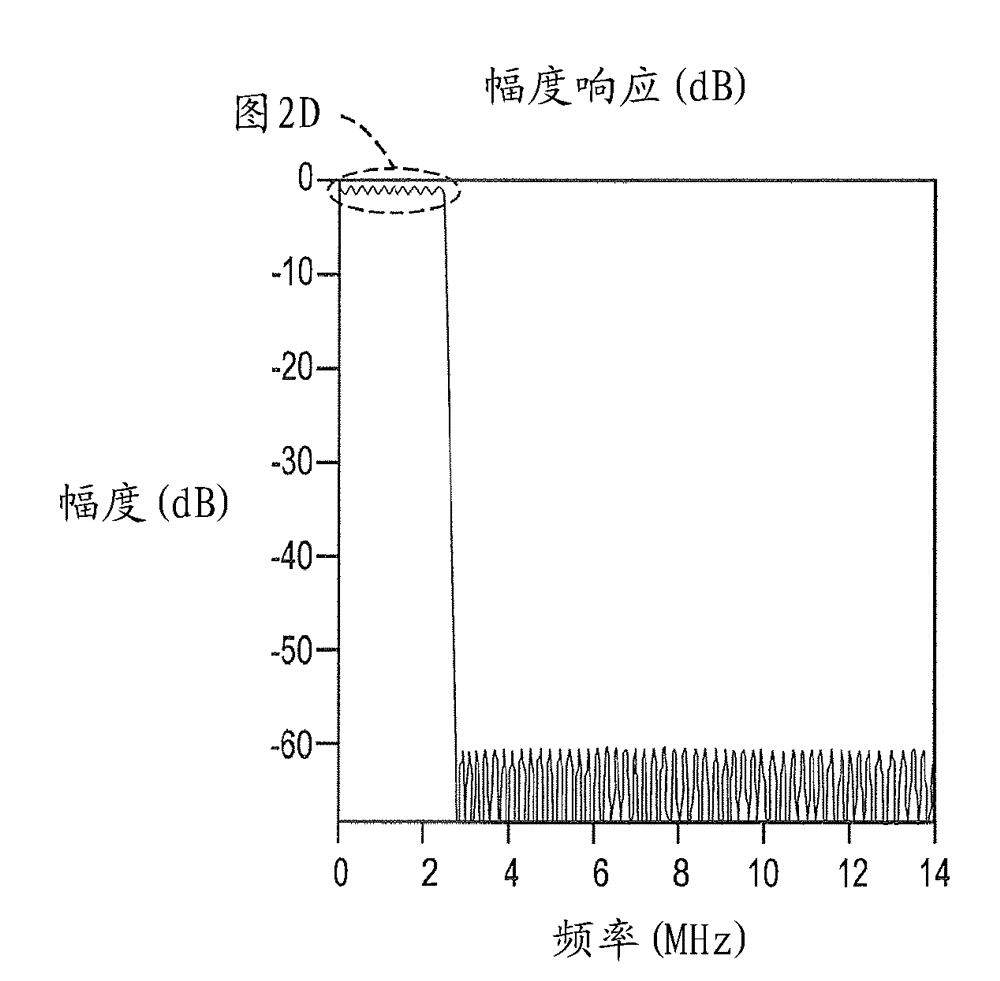
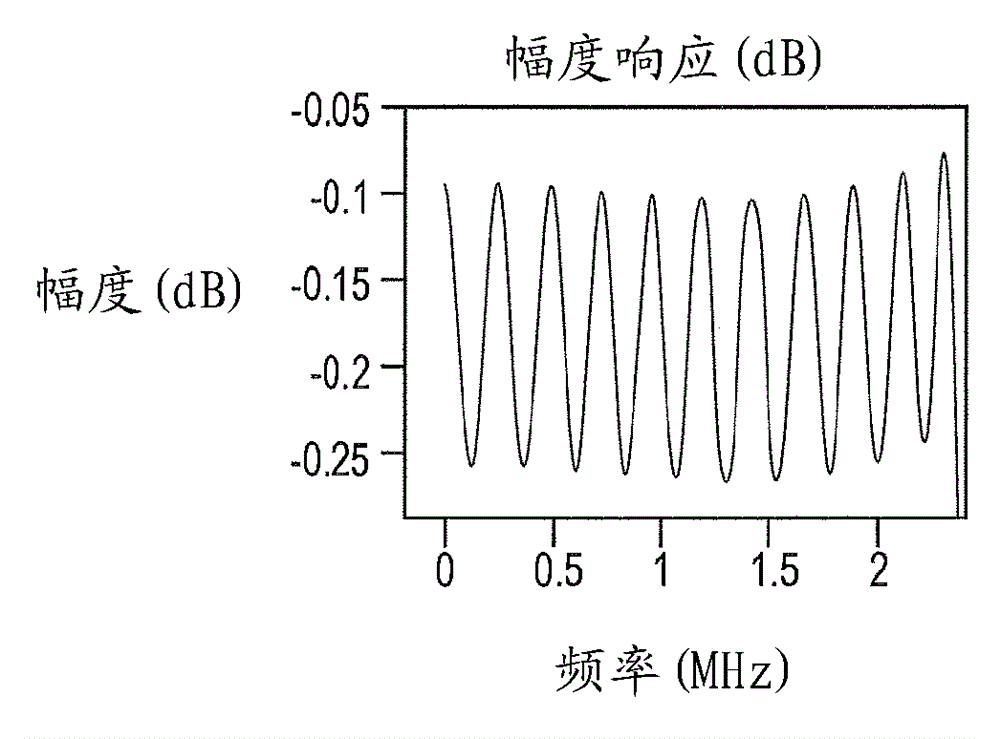
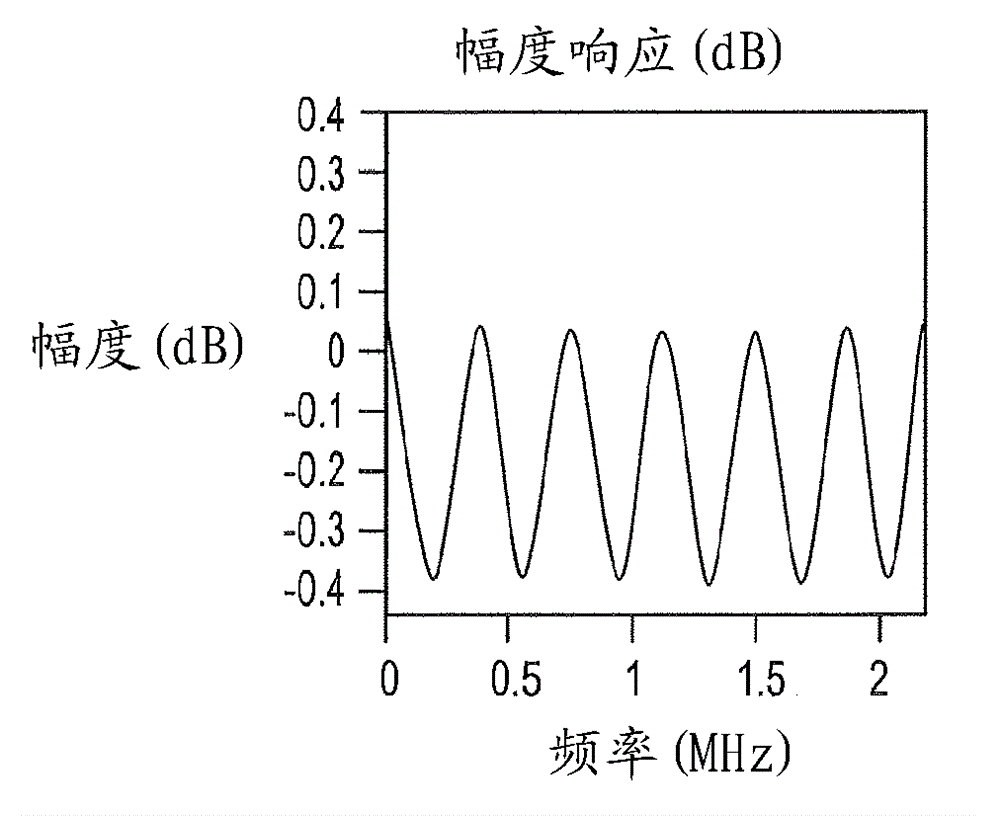
[0019] The present invention is directed to providing a digitizer 10 employing reconfigurable variable length FIR filters. refer to Figure 4 , showing the architecture of the repeater 10 . The repeater 10 includes two main blocks, the donor component 12 and the service component 14 . Each consists of: a) a duplexer 16, implemented using the same antenna for reception and transmission; b) a low noise amplifier (LNA) 18; c) a power amplifier (PA) 20; d) a radio frequency (RF) receive section 22; e) RF transmit section 24; f) analog-to-digital controller (ADC) 26, which converts analog signals into digital for further signal processing done in digital form; g) digital processing section 28 for sub- with filtering and gain control; h) a main control unit (MCU) 30 or main processing controller for receiving and sending instructions from and to other components of the repeater 10; and i) digital to analog (DAC) 32 to convert the digital signal back to analog after digital signal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com