Loopback technique for IQ imbalance estimation for calibration in OFDM systems
一种平衡、复用信号的技术,应用在正交频分复用系统,无线OFDM系统领域,能够解决增加模拟设计复杂性、ADC设计复杂性和功率消耗多等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
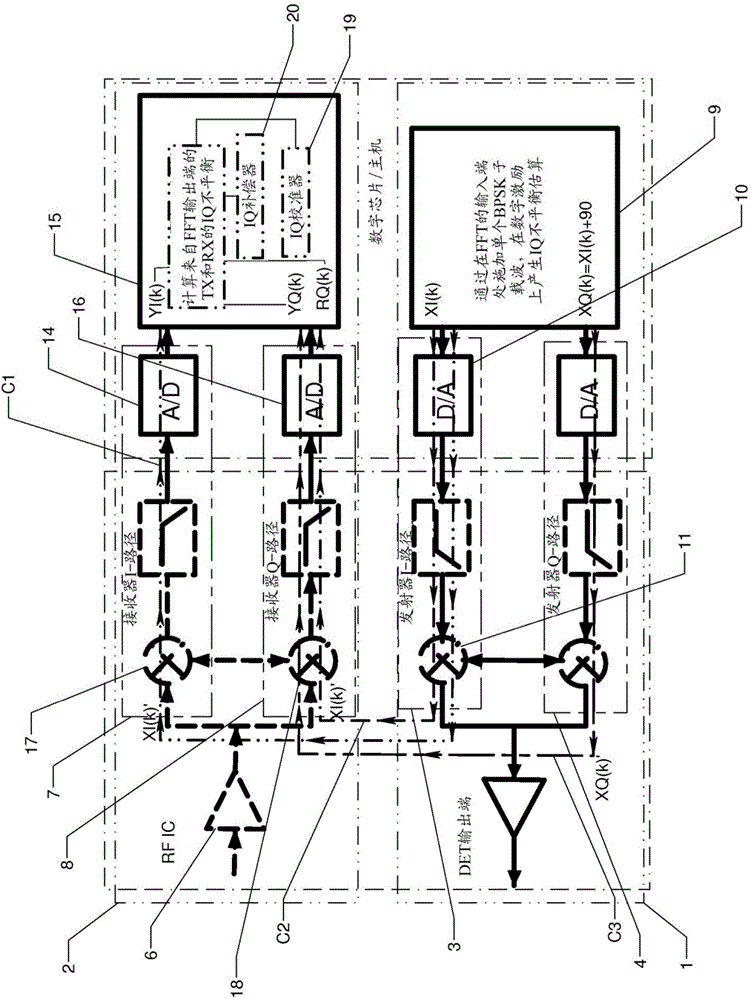
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
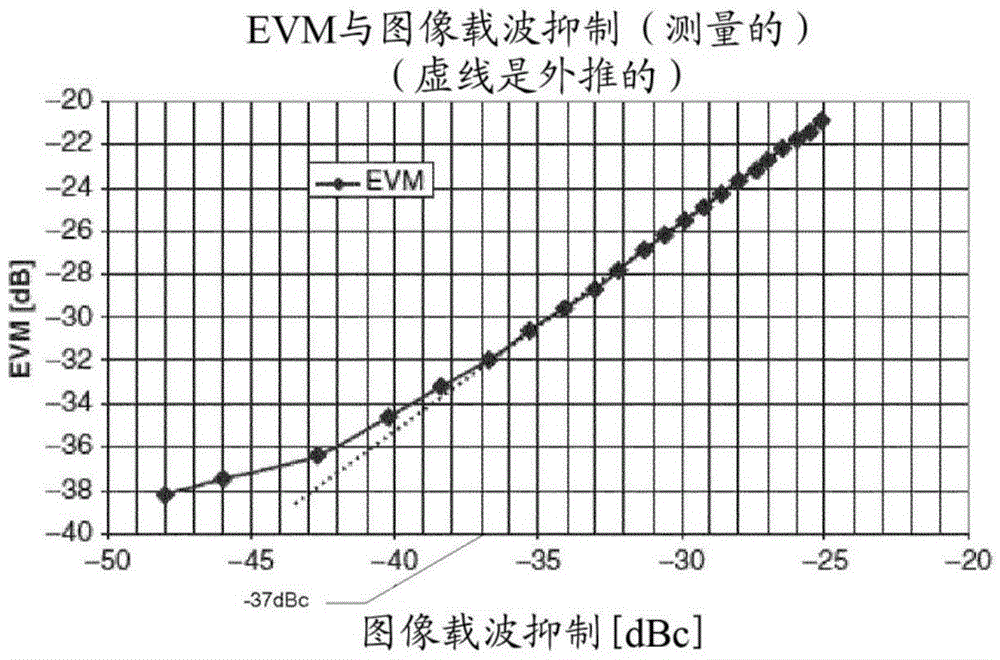
[0043] figure 1 Shows the relationship between EVM and image carrier suppression rate in an example of a 54-Mbps 802.11a based implementation. The figure shows the measured EVM of an "ideal" transmitter as a function of its image carrier suppression. The reduction in EVM at low signal levels is due to the limitations of the VSA (Vector Signal Analyzer) at low power levels. Dashed lines represent extrapolated values for ideal VSA. Only preamble based channel estimation is used for VSA for mapping.
[0044]In this example, it clearly appears that in order to meet the EVM requirement of a 54-Mbps 802.11a signal (EVM = -25dB), the image carrier suppression of the system must exceed about -29dBc.
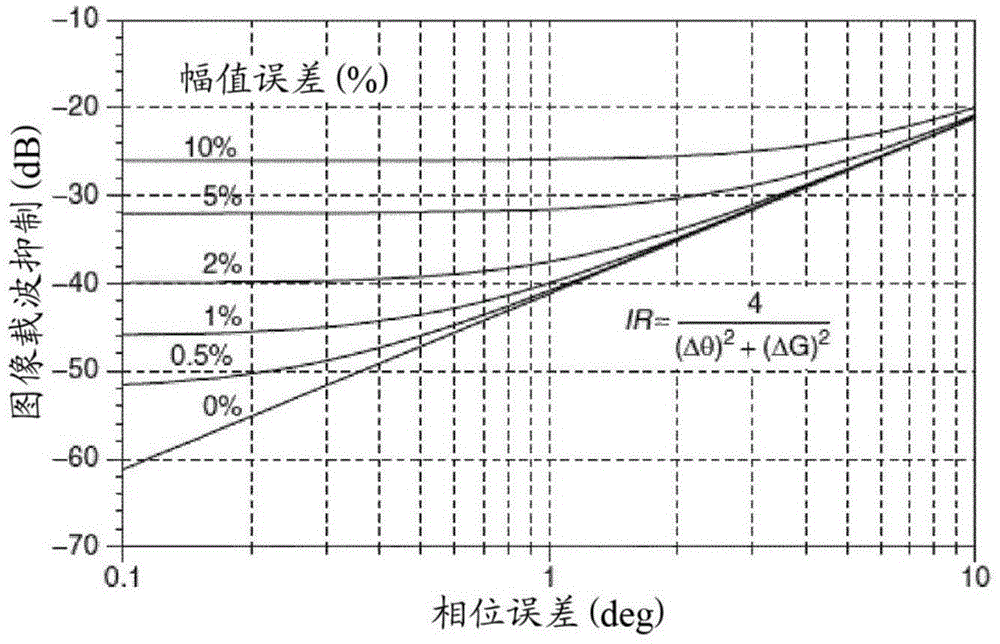
[0045] exist figure 2 , it can be seen that in order to achieve this image carrier suppression, a 5% magnitude error and a 2% phase error can be tolerated.
[0046] It should also be noted that in this example it is assumed that there are no other faults in the system. In realit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com