Method for repairing bone tissue by utilizing 3D printing double-component hydrogel
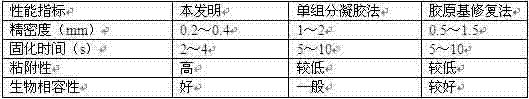
A 3D printing and hydrogel technology, used in tissue regeneration, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of inability to achieve precise and dense bone repair, slow curing of repaired bone, hindering the healing of bone damage, etc. Curing rate and adhesion properties, dense bone repair, effect of enhancing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
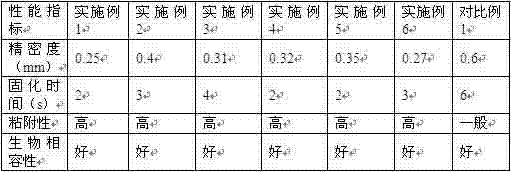
Embodiment 1
[0039] The two-component hydrogel is composed of hydrogel A and hydrogel B;
[0040] The mass ratio of hydrogel A and hydrogel B used for printing is 4:3;
[0041]In hydrogel A, each component is: methacryloyl glycinamide hydrogel 45kg, monetite 13kg, calcium sulfate 15kg, nonionic surfactant 0.4kg, ethyl acetate 26.6kg;
[0042] In hydrogel B, each component is: silica gel 28kg, silicic acid 22kg, polylactic acid short fiber 28kg, zwitterionic surfactant 0.4kg, ethanol 21.6kg;
[0043] The nonionic surfactant is coconut oil glucoside; the short polylactic acid fiber is poly d-lactic acid fiber; the zwitterionic surfactant is lecithin;
[0044] The preparation process is:
[0045] (1) In a high-speed mixer, use non-ionic surfactants to treat monetite and calcium sulfate on the surface, add them to ethyl acetate after discharging, stir and disperse evenly, and then mix with methacryloylglycine The amide hydrogel is mixed to obtain stable hydrogel A; the high-speed mixer is a...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The two-component hydrogel is composed of hydrogel A and hydrogel B;
[0051] The mass ratio of hydrogel A and hydrogel B used for printing is 3:2;
[0052] In hydrogel A, each component is: methacryloyl glycinamide hydrogel 40kg, monetite 10kg, calcium sulfate 14kg, nonionic surfactant 0.5kg, ethyl acetate 35.5kg;
[0053] In hydrogel B, each component is: silica gel 22kg, silicic acid 18kg, polylactic acid short fiber 28kg, zwitterionic surfactant 0.2kg, ethanol 31.8kg;
[0054] The nonionic surfactant is lauryl glucoside; the short polylactic acid fiber is poly L-lactic acid fiber; the zwitterionic surfactant is an amino acid active agent;
[0055] The preparation process is:
[0056] (1) In a high-speed mixer, use non-ionic surfactants to treat monetite and calcium sulfate on the surface, add them to ethyl acetate after discharging, stir and disperse evenly, and then mix with methacryloylglycine The amide hydrogel is mixed to obtain stable hydrogel A; the high-sp...
Embodiment 3
[0061] The two-component hydrogel is composed of hydrogel A and hydrogel B;
[0062] The mass ratio of hydrogel A and hydrogel B used for printing is 4:3;
[0063] In hydrogel A, each component is: methacryloyl glycinamide hydrogel 50kg, monetite 15kg, calcium sulfate 17kg, nonionic surfactant 0.4kg, ethyl acetate 17.6kg;
[0064] In hydrogel B, each component is: silica gel 30kg, silicic acid 26kg, polylactic acid short fiber 30kg, zwitterionic surfactant 0.4kg, ethanol 13.68kg;
[0065] The nonionic surfactant is cetearyl glucoside; the short polylactic acid fiber is poly dL-lactic acid fiber; the zwitterionic surfactant is a betaine type active agent;
[0066] The preparation process is:
[0067] (1) In a high-speed mixer, use non-ionic surfactants to treat monetite and calcium sulfate on the surface, add them to ethyl acetate after discharging, stir and disperse evenly, and then mix with methacryloylglycine The amide hydrogel is mixed to obtain stable hydrogel A; the hi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com