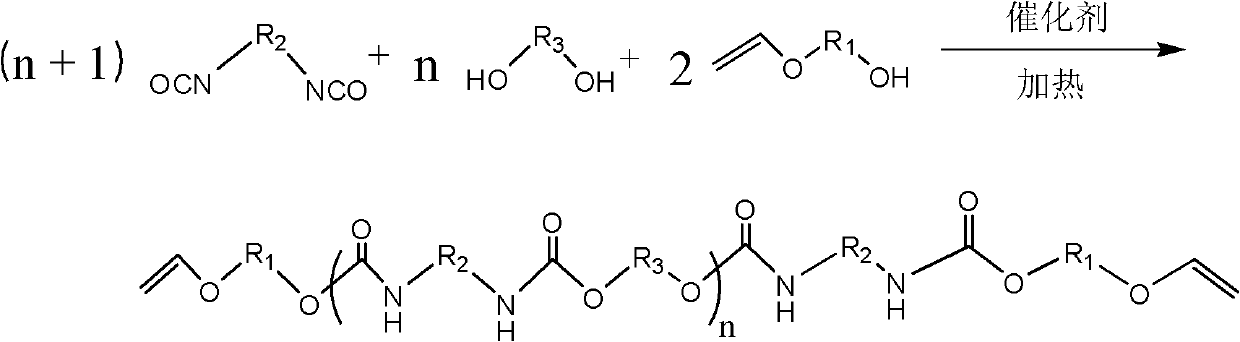
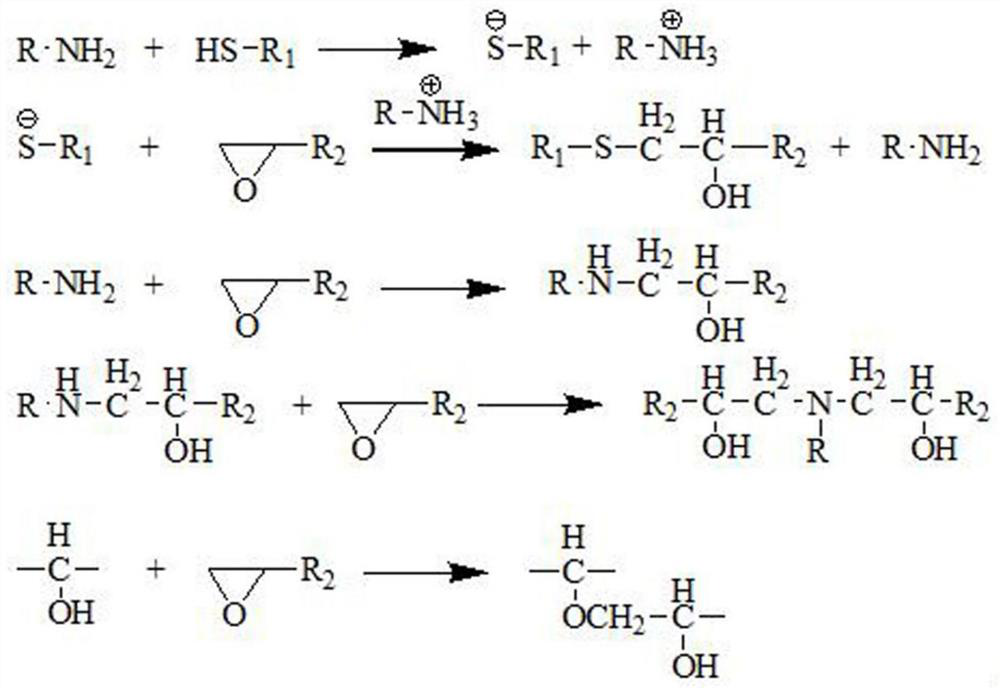
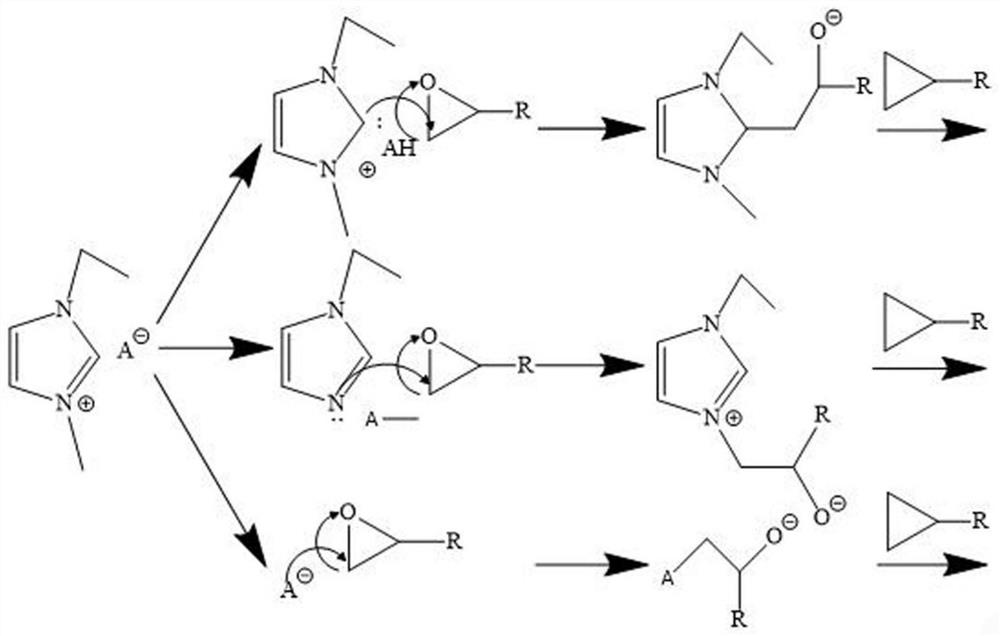
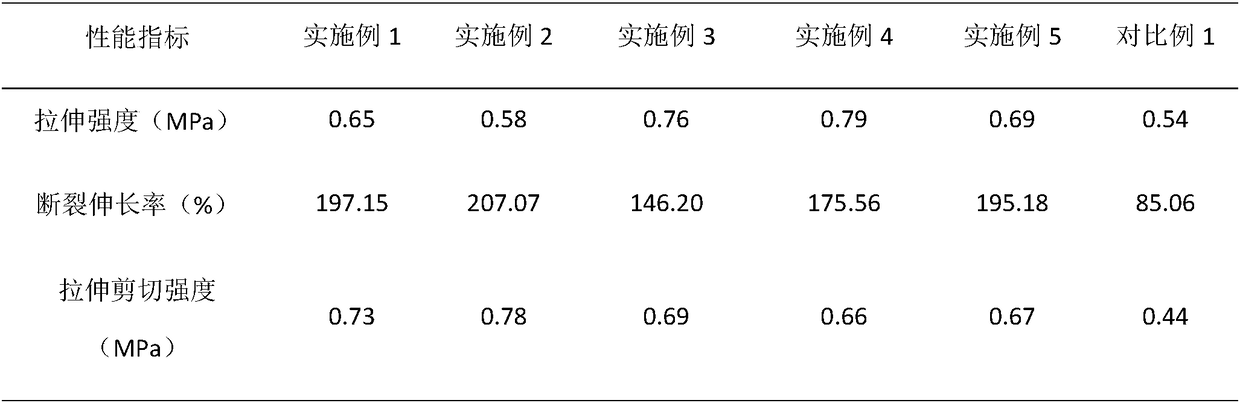
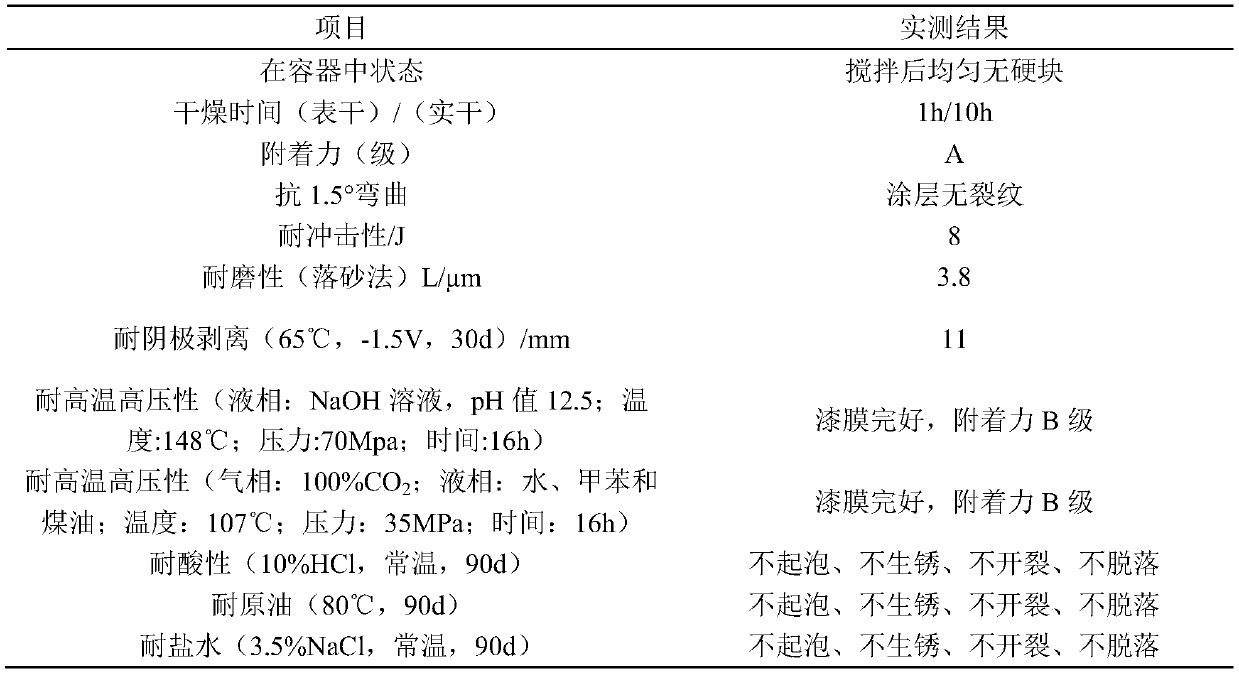
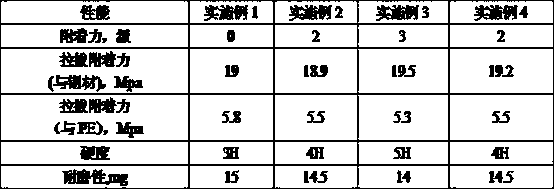
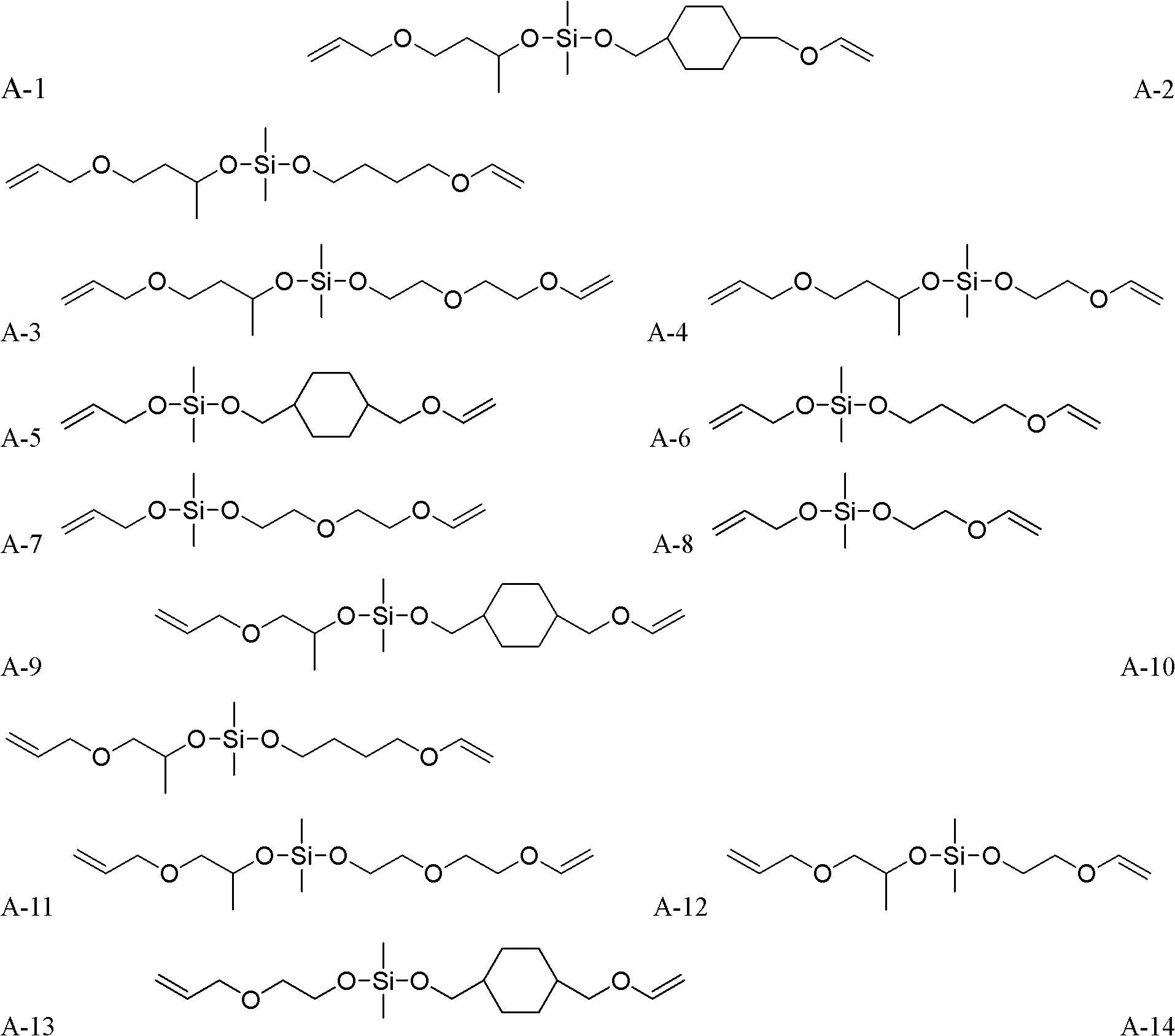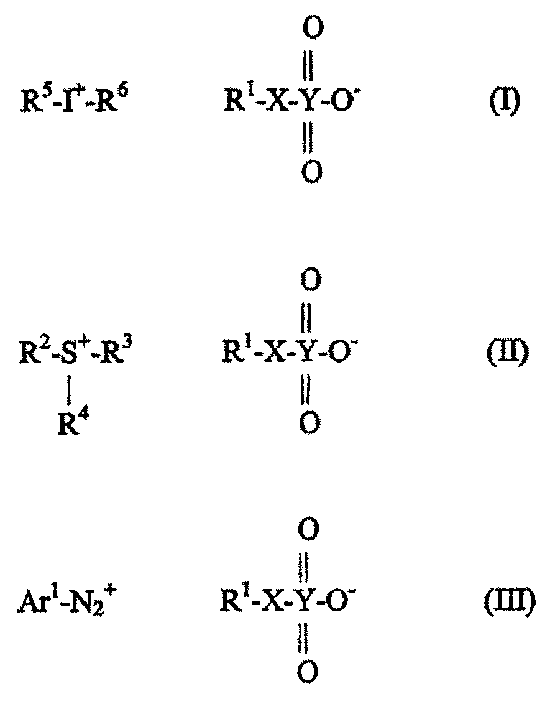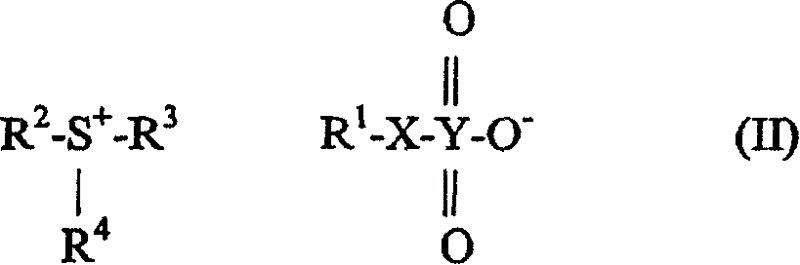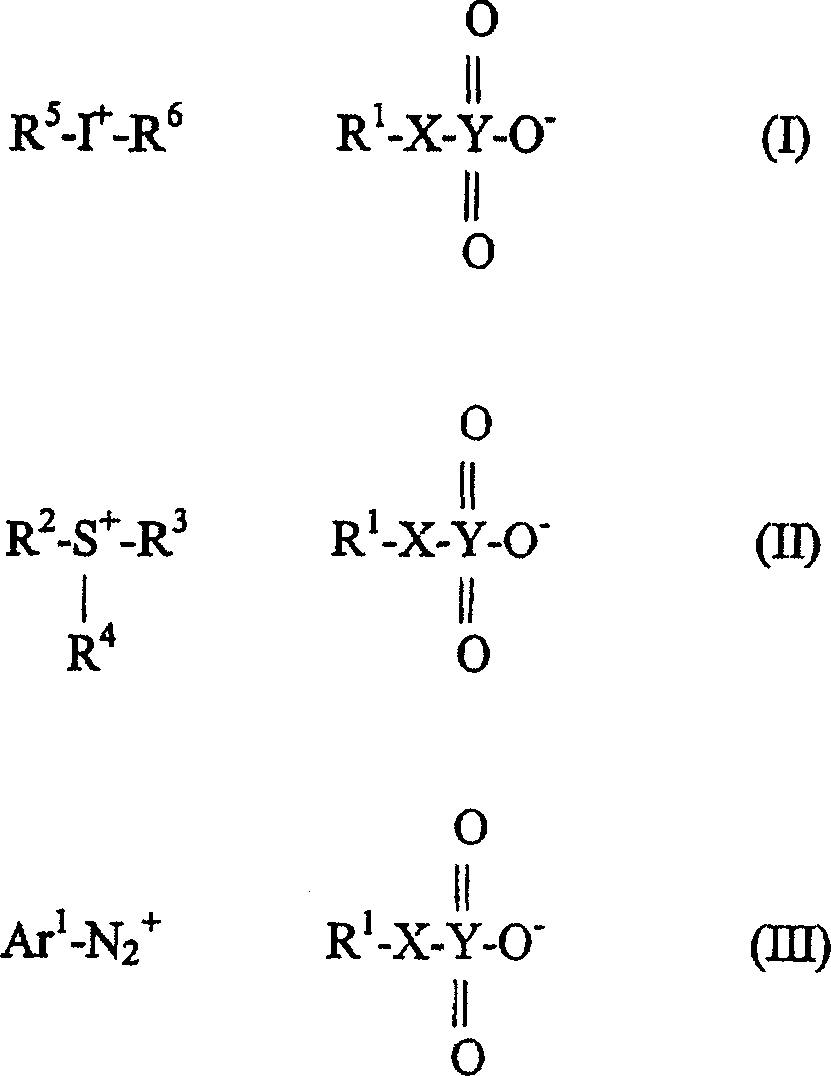Patents
Literature
131results about How to "Improve cure rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Elastic photosensitive resin for 3D printing of digital light processing (DLP) and preparation method of elastic photosensitive resin
The invention belongs to the field of a high molecular material, and particularly relates to photo-cured elastic photosensitive resin with wavelength being 405 nanometers for 3D printing of digital light processing (DLP). The elastic photosensitive resin comprises the following raw materials based on parts by weight: 10-50 parts of elastic acrylate, 30-70 parts of active diluents, 1-10 parts of photoinitiator, 0.01-0.05 part of flatting agent, 0.01-0.05 part of dispersning agent and 0.01-0.05 part of polymerization inhibitor. The elastic photosensitive resin can be directly used for 3D printing of DLP or can be mixed with other existing photosensitive resin, a product with a complicated structure and certain elasticity can be printed, meanwhile, the elastic photosensitive resin has the characteristics of small volatile odor, rapid formation speed, small product shrinkage rate, high formation accuracy and the like.
Owner:广州谱睿汀新材料科技有限公司 +1
Anti-static optical adhesive
InactiveCN104293253AWith anti-static functionAchieve synergyNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesGraft polymer adhesivesPolyesterWater baths
The invention discloses an anti-static optical adhesive which is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 1-5% of an antistatic agent, 30-60% of polyurethane acrylate, 20-50% of an acrylate monomer, 5-10% of unsaturated polyester, 0-2% of a photoinitiator (excluding 0%), 3-6% of a crosslinking agent and 1-5% of a coupling agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) adding polyurethane acrylate, part of the acrylate monomer and unsaturated polyester into a reaction kettle, stirring and heating in a water bath to a stable backflow state; (2) uniformly mixing residual raw materials, putting into the reaction kettle and stirring for polymerization reaction; and (3) finishing the polymerization reaction to obtain the anti-static optical adhesive. The anti-static optical adhesive disclosed by the invention is a colorless transparent viscous liquid matter, has the characteristics of being anti-static, high in light transmittance, high in curing speed, low in cure shrinkage rate and low in haze and the like and can be widely applied to fitting an optical protective thin film base material and a release film.
Owner:TIANNUO PHOTOELECTRIC MATERIAL
3D printing device and method for high-molecular-weight silicone rubber
ActiveCN107283819AExtended service lifeQuality improvementAdditive manufacturing with liquidsApplying layer meansEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a 3D printing device and method for high-molecular-weight silicone rubber. A hundred-micron-level micropore nozzle with the high shearing rate and high extruding strength and for screw extruding force is adopted in a 3D printing head system, the flowing viscosity of the high-molecular-weight silicone rubber is greatly reduced, and 3D printing forming of a high-molecular-weight, high-compression-modulus and long-service life silicone rubber material is achieved. The extrusion and expansion stability of the material on the hundred-micron-level micropore nozzle is improved, the dimensional precision of a 3D printing fluid line is accurately controlled, and high quality, high precision and high efficiency in the 3D printing process are achieved. A photo-thermal two-order curing material 3D printing manner is adopted, the curing rate and dimensional precision of the 3D printing material are greatly increased, the high quality and stability of the 3D printing high-molecular-weight silicone rubber material are improved, and the macro-performance and structure adjustability of the 3D printing material are achieved.
Owner:XIAN LIANCHUANG ADVANCED MFG A SPECIALIZED INCUBATOR CO LTD
Polyurethane sealant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105199657AImprove cure rateFast curing rateNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesOther chemical processesElastomerTriol
The invention discloses a polyurethane sealant and a preparation method thereof. The sealant is prepared from a prepolymer, a plasticizer, pigment and filler, a thickening agent, and a silane coupling agent, wherein the prepolymer is composed of polyether diol, polyether triol, butanediol, diphenylmethane diisocyanate, dibutyltin dilaurate, an oxazolidine latent curing agent, an acid catalyst and a defoaming agent. After the sealant is cured, the tensile strength of an elastomer is more than or equal to 8MPa, and the elongation at break is more than or equal to 450%. The sealant not only has good curing rate at normal temperature, but also has high curing rate in low temperature and low humidity conditions. The polyurethane sealant is suitable for elastic bonding of high mechanical property, for example, elastic bonding for glass installation of automobiles, trains, ships, planes, cable cars and the like. The polyurethane sealant is suitable for rapid bonding in low temperature and low humidity environments and other elastic bonding of high mechanical property.
Owner:三友(天津)高分子技术有限公司
Synthesis method of allyl oxetane compound for ultraviolet light curing
InactiveCN104892549AIncrease profitThe feeding process is simple and easyOrganic chemistrySynthesis methodsReaction temperature
The invention relates to a synthesis method of an allyl oxetane compound for ultraviolet light curing. The synthesis method comprises: in the presence of an aqueous solution or suspension of an alkali, under continuous vigorous stirring, adding a 3-hydroxymethyl oxetane compound and 3-halo-propylene, adding an appropriate amount of a phase transfer catalyst, carrying out a phase transfer catalysis reaction for 24-30 h at a reaction temperature of -5-5 DEG C, and then carrying out dehydrohalogenation esterification so as to obtain the product. According to the present invention, the allyl oxetane compound having extremely low viscosity and capable of concurrently being used for free radical and cation curing can be prepared, and the synthesis method has characteristics of simple and easy-performing related reactions, no requirement of heating, less by-products, environmental protection, high yield, high equipment utilization rate, and easy large-scale industrial production of the allyl oxetane compound.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Antibacterial and anti-fingerprint paint for mobile phones
PendingCN110791194AImprove cure rateImprove adhesionAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesPolymer scienceMeth-
The invention discloses an antibacterial and anti-fingerprint paint for mobile phones. The paint comprise the following raw materials by weight: 20-38 parts of a urethane acrylate oligomer, 10-30 parts of epoxy acrylic resin, 2.5-5.5 parts of an antibacterial agent, 15-28 parts of trimethylolpropane triacrylate, 5-9 parts of N-vinyl pyrrolidone, 13-30 parts of 1, 6-hexanediol diacrylate, 3-4.8 parts of a photoinitiator, 8-14 parts of nano-filler, and 0.5-1.3 pars of an assistant. The antibacterial and anti-fingerprint paint for mobile phones provided by the invention has good antibacterial properties and scratch resistance, and excellent antifouling and anti-fingerprint properties.
Owner:SHAOXING XUYUAN NEW MATERIAL TECH
Antibacterial low-melting-point hot melt adhesive and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105542698ALow melting pointCrystallize fastNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesPolyesterPolymer science
The invention relates to an antibacterial low-melting-point hot melt adhesive. The antibacterial low-melting-point hot melt adhesive is processed from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40-80 parts of a polyester hot melt adhesive, 20-30 parts of polyamide resin, 3-8 parts of paraffin, 0.5-1 part of an antioxidant 164 and 0.5-1 part of an inorganic antibacterial agent. A preparation method of the antibacterial low-melting-point hot melt adhesive comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing the polyester hot melt adhesive, the polyamide resin, the paraffin, the antioxidant and the inorganic antibacterial agent according to the formula ratio, adding the mixture into a screw extruder granulator, carrying out melt blending extrusion, cooling and granulating the extruded mixture, and carrying out vacuum drying on the aggregates to remove moisture, so as to obtain the antibacterial low-melting-point hot melt adhesive. By mixing the low-melting-point polyester hot melt adhesive with the polyamide resin, the paraffin, the antioxidant and the inorganic antibacterial agent, the prepared hot melt adhesive is stable in binding power, high in curing speed and convenient to use and does not easily mildew, the environmental influence is low, and particularly, the curing rate is prior to that of the hot melt adhesive in the prior art in a low-temperature environment; the production efficiency is greatly improved, the cooling curing time is substantially shortened after the coating of the hot melt adhesive, and the coating efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:佛山市高达树脂有限公司
Anti-cracking, wear-resistant and seepage-proof compound mortar and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses anti-cracking, wear-resistant and seepage-proof compound mortar. The anti-cracking, wear-resistant and seepage-proof compound mortar is prepared from raw materials in parts by weight as follows: 20-30 parts of long and short reinforcing fiber, 15-20 parts of a waterproof additive, 10-20 parts of gelatine powder, 10-16 parts of a composite aid, 10-14 parts of glass beads, 65-75 parts of Portland cement, 55-65 parts of fine sand, 35-45 parts of composite filling sand, 1-2 parts of triethanolamine and 1-3 parts of sodium tripolyphosphate. The compound mortar has excellent anti-cracking, wear-resistant and efflorescence preventing properties and has better water resistance, seepage-proof property and adhesion force, relatively excellent impact resistance and thermal insulation and sound insulation effects and a certain pollutant air absorption function; besides, according to the provided preparation method, the material cost is lower, raw materials are easy to obtain, the process is simple, and the compound mortar has higher practical value and excellent application prospects.
Owner:HEFEI GUANGMIN BUILDING MATERIAL CO LTD
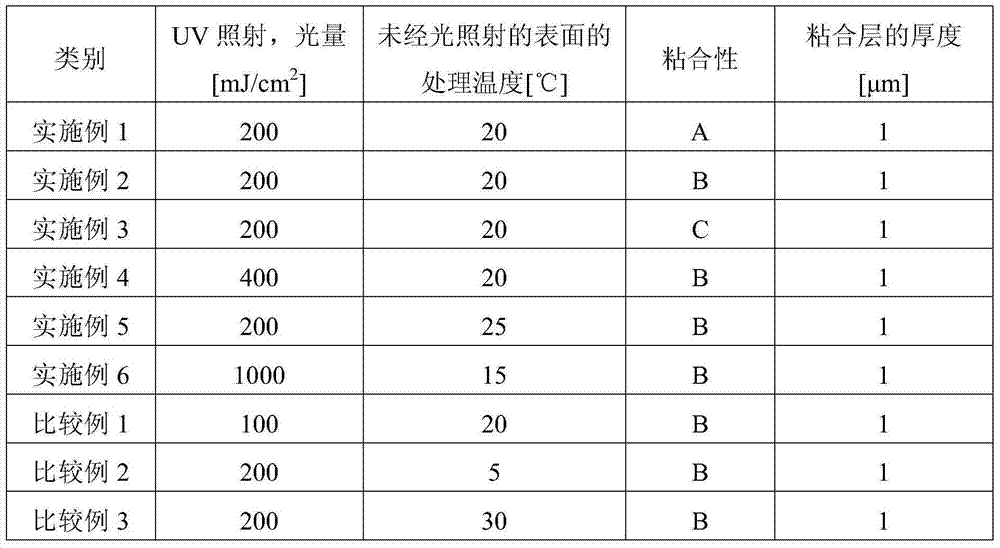
Method for manufacturing double-sided polarizing plate and double-sided polarizing plate manufactured by same
InactiveCN104246556AImprove cure rateImprove adhesion strengthLamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentPolarizerMechanical engineering
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a double-sided polarizing plate and a double-sided polarizing plate manufactured using the same, the method comprising the steps of: stacking transparent films on both surfaces of a polarizer via adhesive layers; radiating active energy rays at a quantity of light of 200mJ / cm2 or higher through an energy source which is positioned in one direction with reference to the polarizer; and processing the surface of the transparent film, which is positioned opposite the energy source, at 10 DEG C to 25 DEG C.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
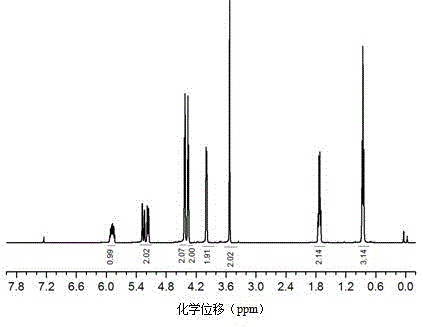
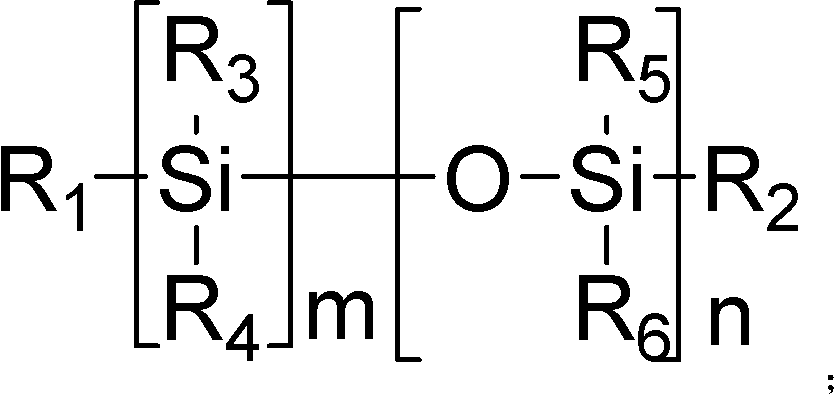
Method for synthesizing silicon-containing polymerizing monomer terminated by vinyl ether and allyl ether
ActiveCN102140116AImprove uniformityHigh yieldGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsPhotomechanical apparatusVinyl etherEnd-group
The invention relates to the design and synthesis of a silicon-containing polymerizing monomer terminated by vinyl ether and allyl ether, which is prepared by using chlorosilane or chloro siloxane, hydroxyalkyl ethenyl ether and hydroxyalkyl allyl ether as raw materials. The reaction synthesis method is simple, the reaction conditions are mild, the purification is easy, and the yield is as high as over 80 percent. The synthesized monomer is a mixed polymerizing photocurable monomer and a novel photopolymerizing material which can be used for making an imaging information recording material. In the invention, the problems of complex preparation process, low yield, high cost, environment pollution and the like of the conventional silicon-containing photopolymerizing monomer are solved effectively, and a novel monomer is developed for making photocurable materials and photoimaging information recording materials.
Owner:HUBEI GURUN TECH CO LTD
One-component polyurethane foam caulking agent
InactiveCN109749040AGood toughness strengthHigh tensile strengthPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPolyolPlasticizer
The invention discloses a one-component polyurethane foam caulking agent, which comprises the following components in parts by weight: 30.0-60.0 parts of polyether polyol, 2.0-6.0 parts of catalysts,1.0-4.0 parts of curing agents, 2.0-6.0 parts of plasticizers and 20.0-40.0 parts of solvents. The one-component polyurethane foam caulking agent has good flexibility and tensile strength, uniform foam holes, and can be used in a low-temperature environment; a DMDEE catalyst is contained inside the agent, and has soft activity and good storage stability, and thus the surface drying rate, curing rate and foaming rate of OCF can be effectively promoted; a CP52 plasticizer is contained inside the agent, and has good compatibility, and thus the viscosity and brittleness of the OCF is reduced, andthe flexibility is increased; and a ketoimine curing agent is added inside the agent, and thus the viscosity of the OCF can be reduced, the agent can be quickly wet cured, and the tensile strength isimproved.
Owner:东元科技有限公司
Polyurethane acrylate prepolymer and preparation method thereof as well as paint prepared by same
ActiveCN103030768AExcellent toughnessExcellent cure ratePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPrepolymerHydroquinone Compound
The invention discloses a polyurethane acrylate prepolymer and a preparation method thereof, as well as paint prepared by the polyurethane acrylate prepolymer. The prepolymer comprises the following components in part by mass: 900-1100 parts of hexamethylene diisocyanate, 2-5 parts of dibutyl tin laurate, 400-600 parts of polyethylene glycol, 1-3 parts of hydroquinone and 1000-1300 parts of hydroxyethyl acrylate. According to the invention, the paint prepared by the polyurethane acrylate prepolymer is high in curing rate, can effectively improve gloss, flexibility and adhesion level of floorboards, and is excellent in use effect.
Owner:JIUSHENG WOOD
Substrate, gene chip and preparation method thereof and target detection method
ActiveCN101824477AHigh sensitivityHigh detection throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEthylenediaminePolyamide
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and provides a substrate for a biological chip. The substrate is formed by jointing a polyamide-amine dendritic macromolecule on a solid support through a covalent bond; the polyamide-amine dendritic macromolecule is a dendritic macromolecule which radiates 64 amino terminals with ethidene diamine as a center, and a molecular weight is 14,214 to 14,220; and the polyamide-amine dendritic macromolecule is activated by an aldehyde group. The substrate for the biological chip adds reaction points through the multiple amino terminals of the dendritic macromolecule, so that the sensitivity of the biological chip is enhanced. The invention also provides a gene chip prepared from the substrate, a method for preparing the gene chip and a method for detecting a target by using the gene chip.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low viscosity curable compositions
InactiveCN101085856AGood dispersionImprove cure rateOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPolyesterDispersity
A low viscosity capillary flow underfill composition having improved filler dispersion and cure rate. One embodiment of the composition comprises one or more epoxy resins, such as cycloaliphatic epoxy resins, one or more catalysts, such as super acid catalysts and one or more inert components, which may comprise diluents such as non-electrically conductive fillers. Further embodiments of the invention include compositions further comprising low viscosity non-epoxy reactive diluents, such as vinyl ether, and polyols such as polyester polyols. A further embodiment is a method of assembling an electronic component utilizing the low viscosity underfill composition of the present invention. A still further embodiment is an electronic device or component containing the underfill composition of the present invention.
Owner:NAT STARCH & CHEM INVESTMENT HLDG CORP
High-toughness and high-flame-retardant polyurethane circuit board material
InactiveCN107674408AIncrease crosslink densityImprove toughnessGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPolyesterEpoxy
The invention discloses a high-toughness and high-flame-retardant polyurethane circuit board material which comprises polyester polyol, 2, 6-diisopropyl benzene isocyanate, dimethyl-biphenyl diisocyanate, terephthalyl alcohol, 1, 4-butanediol, 4, 4'-diamino-3, 3'-dichlorodiphenylmethane, dibutyltin dilaurate, catalyst DMP (dimethyl phthalate)-30, bicyclopentadiene dioxide epoxy resin, polyvinyl chloride, maleic anhydride, nano-calcium carbonate, alpha, omega-dihydroxy polydimethylsiloxane, 1-oxygen-4-hydroxymethyl-2, 6, 7-trioxa-1-phospha-dicyclo[2.2.2] octane and phosphorus-containing flame retardants. The high-toughness and high-flame-retardant polyurethane circuit board material has excellent flame resistance and toughness and is good in heat resistance and long in service life.
Owner:ANHUI RUIFA COMPOSITES MFG
Solar component package material capable of being cured through ultraviolet
InactiveCN102585755AGood compatibilityImprove absorption rateNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPhotosensitizerAging resistance
The invention relates to a solar component package material capable of being cured through ultraviolet, comprising the following components in percentages by mass: 40-55% of bisphenol A epoxy resin, 1.5-2.5% of polyurethane acrylate prepolymer, 0.1-0.5% of organic light stabilizer, 40-50% of activated diluents agent, 1-8% of photosensitizer and 0.1-5% of processing aid. With the adoption of the solar component package material, the absorption rate of the package material in an ultraviolet band is increased, the ultraviolet ageing resistance of the package material is reinforced, the service life is prolonged, additional laminating steps are not needed, the package material can be quickly solidified under the condition of ultraviolet radiation, so that the production efficiency is improved, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD
Temperature response type polymeric biomedical adhesive and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN106267324AImprove performanceGood biocompatibilityImpression capsSurgical adhesivesTemperature responseSide effect
The invention provides a temperature response type polymeric biomedical adhesive and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of adhesive application materials. According to the invention, by taking a polyhydroxy or poly-amino hyperbranched polymer as an initiator, tetrahydrofuran as a solvent, and amino acids with N-carbonyl anhydride at the tail end as functional monomers, under the protection of nitrogen, polymerization reaction is performed for 48-72 hours at room temperature, and after reaction is ended, a crude product is precipitated by using a mixed solution of triethylamine-ethyl alcohol, so as to obtain the polymeric biomedical adhesive which has the bonding strength of 90-130Kpa at 37+ / -0.5 DEG C. In addition, by taking amino acids which are needed for the human body as raw materials, the polymeric biomedical adhesive has good biocompatibility and no side effects, and can be degraded and metabolized in tissues.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Selected acid generating agents and their use in processes for imaging radiation-sensitive elements
InactiveCN1656426ALoss minimizationImprove efficiencyOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesArylSulfur
An acid generating agent useful for imaging photosensitive elements selected from compounds of formulae (I), (II) and (III). wherein R<1 >is selected from the group consisting of an unsubstituted and substituted hydrocarbon or aryl group; wherein X is selected from the group consisting of oxygen, sulfur and selenium; wherein Y is selected from the group consisting of sulfur, selenium and tellurium; wherein Ar<1 >is selected from the group consisting of an unsubstituted and substituted aryl group; wherein R<2>, R<3 >and R<4 >are individually selected from the group consisting of an unsubstituted and substituted hydrocarbon or aryl group or any two of them are bonded together to form a ring structure; and wherein R<5 >and R<6 >are individually selected from the group of an unsubstituted and substituted hydrocarbon or aryl group, or are bonded to each other to form a ring structure.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Polyurethane oligomer taking vinyl ether as end group and synthesis method
InactiveCN102558491AReduce pollutionImprove cure rateCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationSolubilityVinyl ether
A polyurethane oligomer taking vinyl ether as an end group and a synthesis method are disclosed, wherein the structural formula (I) of the compound is FORMULA; and the synthesis method comprises the following process steps of: dripping polyol in diisocyanate and mechanmically stirring; controlling a temperature to be 0-90 DEG C and reacting for 1-6 hours; adding a catalyst and heating to 60-120 DEG C after the reaction is finished; dripping the mixed solution of hydroxyalkyl vinyl ether diluted by a solvent; and continuing to react with stirring for 2-7 hours after the dripping is finished. The synthesis method has the advantages of being simple in process, high in production rate, low in cost, and reduced in environmental pollution. The product prepared by the method can be used as a coating without being purified, as well as is great in dissolubility, simple in synthesis process, easy in control for conditions, and excellent in practical application value.
Owner:HUBEI GURUN TECH CO LTD
Weather-resistant fadeproof organic paint for colored steel plates
ActiveCN103992711AHigh mechanical strengthGood radiation resistanceCoatingsPolyvinylidene fluorideSolvent
The invention provides a weather-resistant fadeproof organic paint for colored steel plates, which is characterized by comprising the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20-35 parts of polyacrylic resin, 20-30 parts of polyvinylidene fluoride resin, 3-5 parts of polymethyl siloxane, 5-8 parts of titanium white, 5-8 parts of aluminum powder, 2-3 parts of graphite powder, 2-3 parts of leveling agent, 4-6 parts of Ti2AlC / TiAl composite material, 0.5-2 parts of organobentonite, 0.5-1 part of stabilizer, 0.2-1 part of dispersing agent, 0.5-1 part of defoaming agent and 30-40 parts of solvent. The paint has the advantages of high coating adhesion firmness, high flexibility, high binding force, high impact resistance, high acid / alkali resistance, high aging resistance, high glossiness, high curing rate, high water resistance, high durability, high compatibility, favorable weather resistance, small influence of film thickness difference on color difference, and the like, and thus, is a weather-resistant fadeproof organic paint for colored steel plates with excellent comprehensive properties.
Owner:SHANDONG HUIJIN COLOR STEEL
Long-acting anti-corrosion solvent-free universal epoxy coating and preparation method thereof
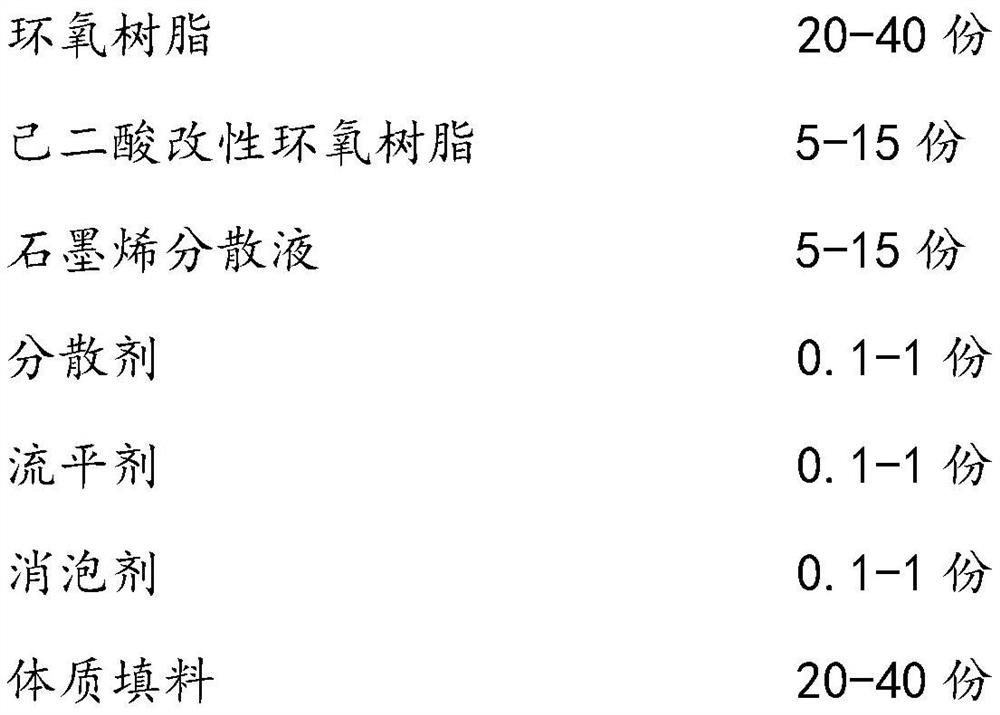
ActiveCN112029382AImprove cure rateLong application periodAnti-corrosive paintsEpoxy resin coatingsEpoxyPolymer science
The invention relates to the technical field of anti-corrosion coatings, and particularly relates to a long-acting anti-corrosion solvent-free universal epoxy coating and a preparation method thereof.The long-acting anti-corrosion solvent-free universal epoxy coating comprises a first component and a second component, wherein the first component comprises epoxy resin, adipic acid modified epoxy resin and graphene dispersion liquid; and the second component comprises an amine mixed curing agent and an amino silane coupling agent. The coating provided by the invention effectively solves the problems of large internal stress, poor coating flexibility and corrosion resistance, easiness in oil surface and gloss loss in a low-temperature environment and a high-humidity environment and the likeof an existing solvent-free epoxy coating system, has excellent corrosion resistance, good recoatability, excellent matching performance with various finishing paints, good weather resistance and thelike, has good film-forming property in low-temperature and high-humidity environments, has no oil surface or gloss loss, and achieves the technical goals of universality of the whole ship and universality in four seasons.
Owner:XIAMEN SUNRUI SHIP COATING
Preparation method for deep-layer curing type fixed abrasive polishing pad
The invention relates to a preparation method for a fixed abrasive polishing pad, and belongs to the technical field of chemical-mechanical polishing dressing preparation. Zirconium propoxide solution serves as a precursor, composite epoxy resin and acetone serve as mediums, and after high-refractive fiber is prepared by electrostatic spinning, the high-refractive fiber and Sic abrasive grit are mixed and ball-milled and blend with other materials; and in the process of ultraviolet light polymerization, ultraviolet light penetrates into a deep layer of the fixed abrasive polishing pad to conduct ultraviolet curing under the influence of high-refractive materials, the curing rate and the homogeneous curing degree of the fixed abrasive polishing pad are effectively improved, and the using performance of the polishing pad is effectively improved. According to the preparation method for the fixed abrasive polishing pad, the hardness of a pencil in a dry state is 3-4 H, the hardness of a pencil in a hygrometric state is 3 H / 3-5 B, the swelling ratio is 2.67-3.56%, and a long service life and a high working efficiency are achieved.
Owner:东莞市均新胜光电科技有限公司
Epoxy resin adhesive for electronic devices and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111808566AImprove uniformityHigh mechanical strengthEpoxynovolac adhesivesBulk chemical productionPolymer scienceManufacturing technology
The invention discloses an epoxy resin adhesive for electronic devices, and belongs to the technical field of adhesives. The epoxy resin adhesive comprises a component A and a component B, wherein thecomponent A is 25-35 parts of a composite ionic liquid curing agent; the component B is prepared from 65 to 75 parts of epoxy resin, 0 to 2 parts of an accelerant, 0 to 2 parts of a diluent, 0 to 2 parts of a plasticizer and 0 to 1 part of a filler. The epoxy resin adhesive prepared by the method is long in working life and high in reaction activity, can be quickly cured within 3 minutes at roomtemperature, remarkably shortens the forming period, and completely meets the requirement of a quick manufacturing technology in the field of electronic device bonding on the production efficiency.
Owner:郯城博化化工科技有限公司 +1
Ultraviolet curable adhesive for thermosensitive substrate with high performance
InactiveCN104312428AHigh sticking residueGood storage stabilityCoatingsEnvironmental resistanceAdjuvant
The invention relates to the technical field of adhesives and particularly relates to an ultraviolet curable adhesive for a thermosensitive substrate with high performance. The ultraviolet curable adhesive for a thermosensitive substrate with high performance is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-60 parts of acrylate modified polysiloxane prepolymers, 1-2 parts of pigment, 2-5 parts of photopolymerization initiator, 10-20 parts of reactive diluent and 1-5 parts of adjuvant. The ultraviolet curable adhesive is capable of saving energy sources, simplifying the process and improving the quality of a product, beneficial to environment protection and wide in development prospect.
Owner:CHENGDU NASHUO TECH
Latent curing type single-component polyurethane adhesive and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109251715AImprove mechanical propertiesGood adhesionPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPolyurethane adhesivePolyol
The invention provides a latent curing type single-component polyurethane adhesive, the adhesive is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 80-120 parts of polyether polyol, 20-40 parts of isocyanate, 3-10 parts of a chain extender and 0.5-2 parts of a latent curing agent, a preparation method of the adhesive comprises the following steps: preparing a polyurethane prepolymer, cooling the polyurethane prepolymer to 40-60 DEG C, slowly dropwise adding the chain extender into a four-neck flask containing the polyurethane prepolymer so as to obtain a reaction product, slowly dropwise adding the latent curing agent while stirring to the reaction product, and uniformly stirring to obtain the latent curing type single-component polyurethane adhesive.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Nanometer solvent-free epoxy anticorrosive paint and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111087894AGood flexibilityImprove antibacterial and antifouling abilityAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesPolymer scienceSolvent free
The invention relates to a nanometer solvent-free epoxy anticorrosive paint and a preparation method thereof. The paint comprises a first component and a second component in a weight ratio of 1: (0.1-0.3). The first component comprises 1 part of polyether modified epoxy resin, 0.8 to 1 part of novolac epoxy resin, 0.05 to 0.1 part of nanometer TiO2, 0.005 to 0.01 part of a corrosion inhibitor, 1.35 to 2.0 parts of a pigment and filler, 0.02 to 0.03 part of an antifoaming agent, 0.01 to 0.02 part of a dispersant and 0.01 to 0.02 part of a leveling agent. The second component comprises an epoxycuring agent. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing the novolac epoxy resin, the polyether modified epoxy resin, the antifoaming agent, the dispersant and the leveling agent, adding the nanometer TiO2 and the pigment and filler, carrying out uniform mixing, adding the corrosion inhibitor, conducting uniform dispersing, and uniformly mixing the first component and the second component according to a weight ratio of 1: (0.1-0.3) to obtain the nanometer solvent-free epoxy anticorrosive paint.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Preparation method of photo-curable graphene solvent-free epoxy fiberglass reinforced plastic paint
InactiveCN109749568AImprove cure rateHigh degree of curingEpoxy resin coatingsPhotoinitiatorDefoaming Agents
The invention relates to a preparation method of a photo-curable graphene solvent-free epoxy fiberglass reinforced plastic paint, in particular to a photo-curable graphene solvent-free epoxy fiberglass reinforced plastic paint and a preparation method thereof. The photo-curable graphene solvent-free epoxy fiberglass reinforced plastic paint is made from, by percent, resin, a monomer (an active diluent), glass powder, a photoinitiator A, a photoinitiator B, a defoaming agent, an adhesion promoter, and graphene oxide. During curing, the graphene oxide is reduced into graphene, so that improved adhesion, wear resistance and the like are imparted to a coating; the photo-curable graphene solvent-free epoxy fiberglass reinforced plastic paint also has the advantages of high curing speed, excellent corrosion resistance, good mechanical properties, good construction operability and the like. The photo-curable graphene solvent-free epoxy fiberglass reinforced plastic paint is applicable to pipeline joint patch, station buried pipelines, pipeline crossing external protection, pipeline elbows of different diameters and the like.
Owner:陕西燕园众欣石墨烯科技有限公司
Low-energy UV-curable circuit ink and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses low-energy UV-curable circuit ink and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of light-curable circuit inks. The low-energy UV-curable circuit ink is mainly made from, by weight, 22-28 parts of epoxy acrylate resin, 3-8 parts of 2-methyl-1-[4-(methylthio)phenyl]-2-(4-morpholinyl)-1-acetone, 1-3 parts of diphenyl(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine oxide, 32-38 parts of talcum powder, 3-4 parts of silicon dioxide, 0.5-1.5 parts of phthalo blue powder, 12-18 parts of hydroxyethyl methylacrylate, 7-12 parts of trimethylolpropane triacrylate, 2-6 partsof phosphates, 0.15-0.4 part of a defoaming agent, 0.2-0.5 part of a dispersing agent, and 8-12 parts of barium sulfate. The invention is intended to provide low-energy UV-curable circuit ink having scientific formulation and low energy and a preparation method thereof; the low-energy UV-curable circuit ink is applicable to circuit board production.
Owner:丰顺县三和电子材料有限公司
Expansion monomer modified light-cured resin and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses expansion monomer modified light-cured resin and a preparation method thereof, and aims to provide the expansion monomer modified light-cured resin and the preparation method thereof. The light-cured resin plays a very critical role in a light-cured rapid prototyping technology (SLA), the prototyping technology has the characteristics of low energy consumption, low cost, high prototyping precision and the like, and promotes the huge change of the manufacturing field. In the prior art, light-cured resin has the problem of volume shrinkage in the curing process, so that aformed product is large in shrinkage warping, low in precision and poor in mechanical property, and the performance of a final finished product is influenced. According to the invention, an expansionmonomer is introduced into a resin curing system; therefore, the volume shrinkage of the photo-cured resin during polymerization is counteracted by utilizing the polymerization expansion characteristic of the photo-cured resin, so that the prepared photo-cured composite resin has low shrinkage characteristic, good physical and chemical properties and thermodynamic properties, can be molded by adopting direct photo-curing rapid molding, 3D printing molding and the like, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:点铂医疗科技(常州)有限公司
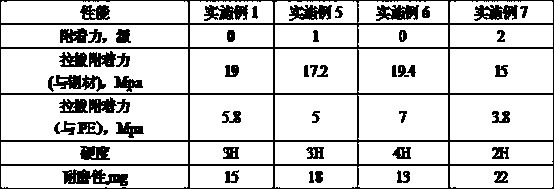
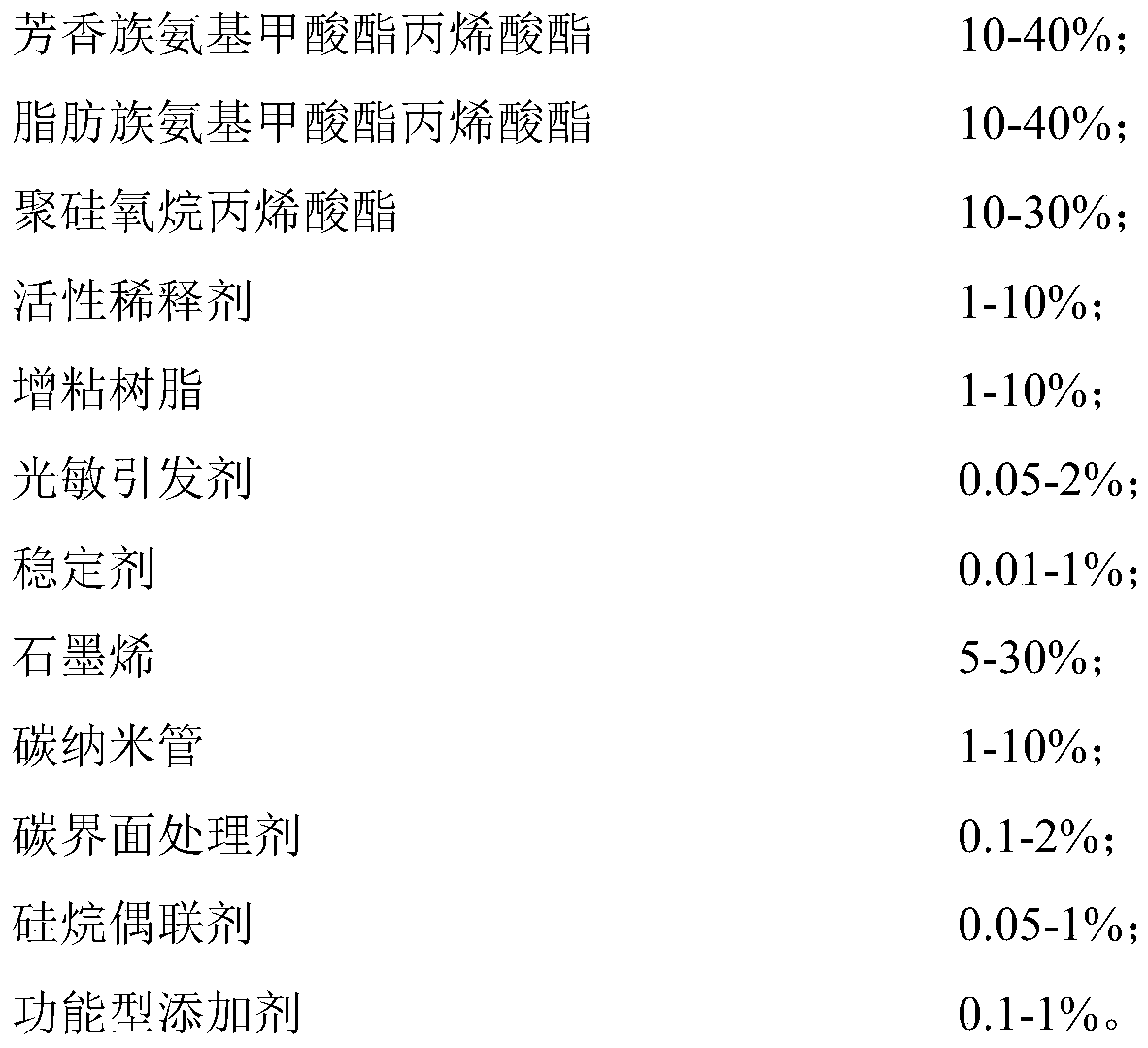
Graphene UV pressure-sensitive adhesive and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111139024AAppropriate weightAppropriate volumeNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesPolymer scienceCarbamate
The invention discloses a graphene UV pressure-sensitive adhesive and a preparation method thereof. The graphene UV pressure-sensitive adhesive has a formula comprising the following raw materials: aromatic carbamate acrylate, aliphatic carbamate acrylate, polysiloxane acrylate, an active diluent, tackifying resin, a photosensitive initiator, a stabilizer, graphene, a carbon nanotube, a carbon interface treating agent, a silane coupling agent and a functional additive. The graphene UV pressure-sensitive adhesive provided by the invention is light in weight, viscoelastic, fine and uniform in cross-section foam pores, is firm in bonding with a base material due to the interaction between a graphene nanometer film and an organic silicon material base body, excellent in compression resistance,impact resistance and thermal stability, and applicable to lightweight application scenes like sealed damping, microwave absorption, electromagnetic shielding and heat dissipation protection. Compared with the prior art, the graphene UV pressure-sensitive adhesive provided by the invention has the following physical properties: the electromagnetic and thermal simultaneous shielding performance isachieved; proper weight ratio and volume ratio are controlled; good curing rate and curing degree are achieved; and excellent mechanical strength and reliable stability are achieved through the synergistic effect of all the components.
Owner:SUZHOU TONGLI PHOTOELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com