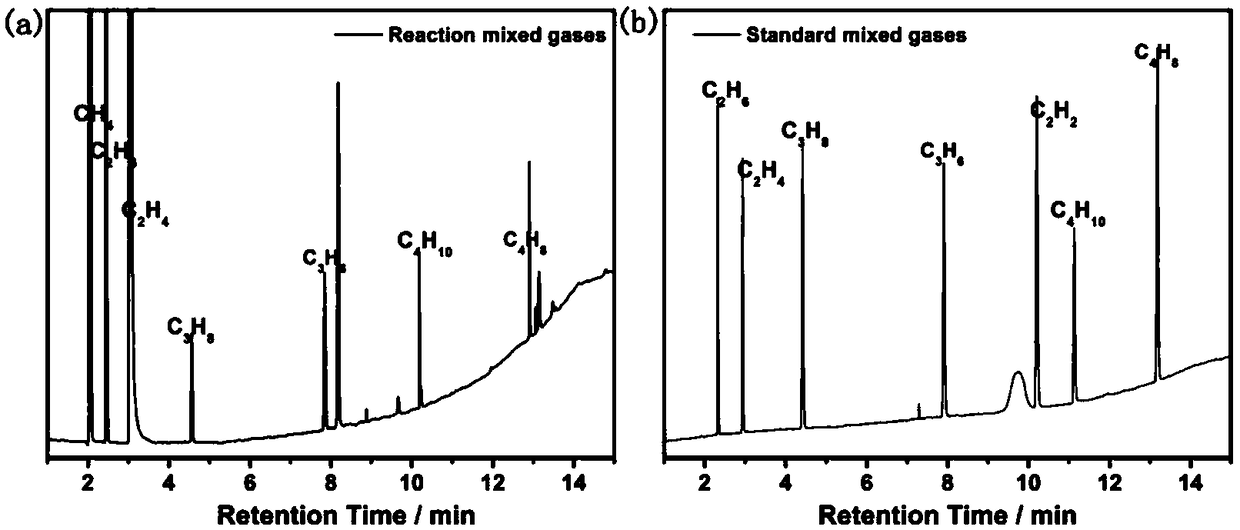
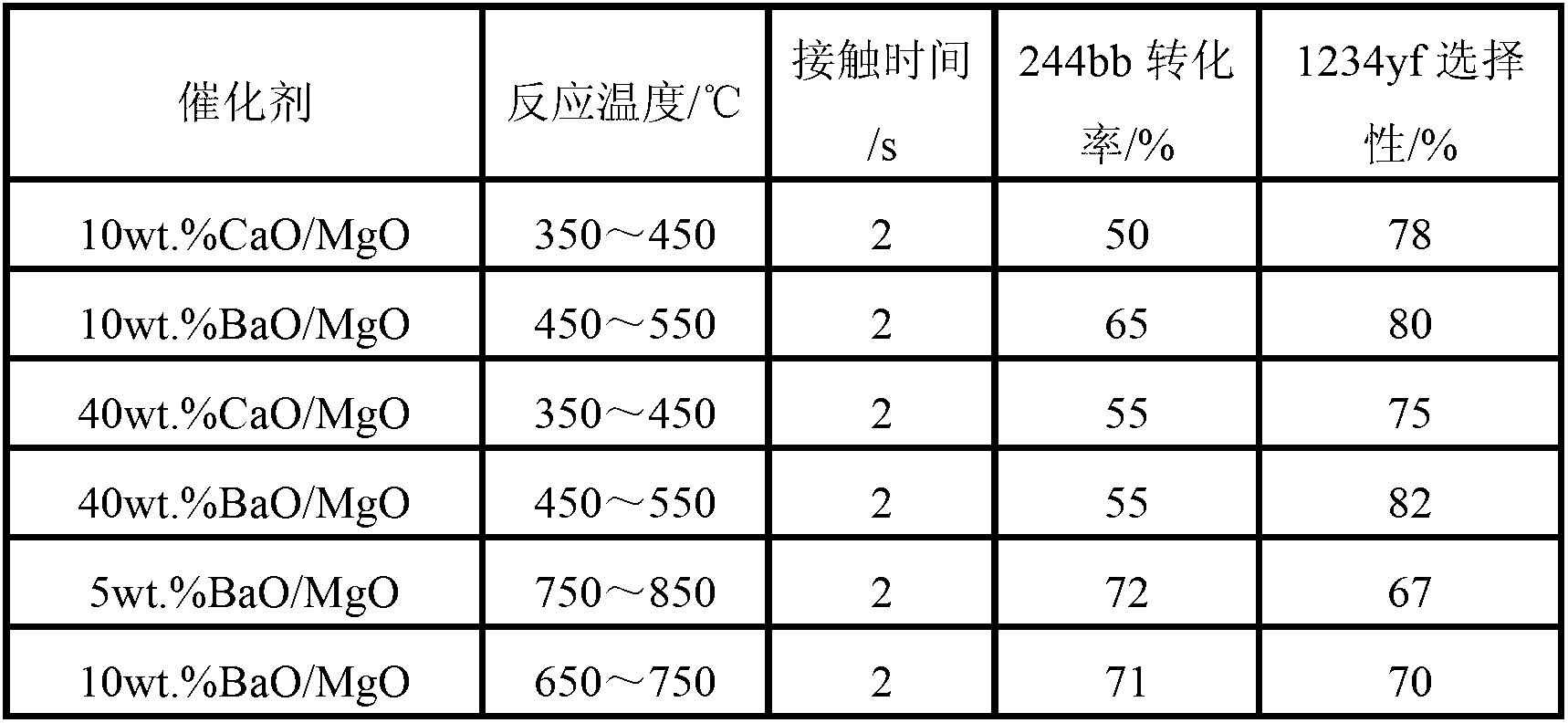
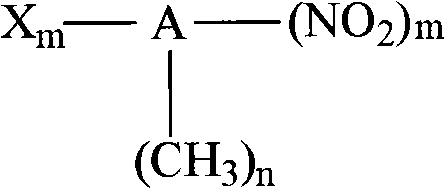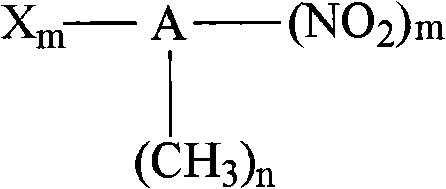Patents
Literature
152 results about "Dehydrohalogenation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dehydrohalogenation is an elimination reaction that eliminates (removes) a hydrogen halide from a substrate. The reaction is usually associated with the synthesis of alkenes, but it has wider applications.
Process for producing fluoropropenes
InactiveUS7230146B2Simplifies isolationPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offPreparation by halogen halide additionHalogenHydrogen
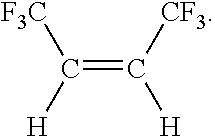
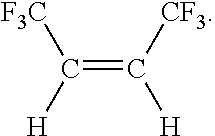
Dehydrohalogenation processes for the preparation of fluoropropenes from corresponding halopropanes, in which the fluoropropenes have the formula CF3CY═CXNHP, wherein X and Y are independently hydrogen or a halogen selected from fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine; and N and P are independently integers equal to 0, 1 or 2, provided that (N+P)=2.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Process for manufacture of fluorinated olefins
A process for the production of fluorinated olefins, preferably fluorinated propenes, by contacting a feed stream containing a fluorinated olefin and hydrogen with a first amount of catalyst to produce the hydrofluorocarbon, wherein a first exit stream contains unreacted fluorinated olefin and hydrogen; contacting the first exit stream with a second amount of catalyst to produce a hydrofluorocarbon, wherein the second amount of catalyst is preferably greater than the first amount of catalyst; and contacting the hydrofluorocarbon with a catalyst for dehydrohalogenation to produce a product stream of fluorinated olefin.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Process for manufacture of fluorinated olefins
A process for the production of fluorinated olefins, preferably fluorinated propenes, by contacting a feed stream containing a fluorinated olefin and hydrogen with a first amount of catalyst to produce the hydrofluorocarbon, wherein a first exit stream contains unreacted fluorinated olefin and hydrogen; contacting the first exit stream with a second amount of catalyst to produce a hydrofluorocarbon, wherein the second amount of catalyst is preferably greater than the first amount of catalyst; and contacting the hydrofluorocarbon with a catalyst for dehydrohalogenation to produce a product stream of fluorinated olefin.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Preparation of fluorinated olefins via catalytic dehydrohalogenation of halogenated hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20090043136A1Physical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offHalohydrocarbonHydrogen atom
A process for making a fluorinated olefin having the step of dehydrochlorinating a hydrochlorofluorocarbon having at least one hydrogen atom and at least one chlorine atom on adjacent carbon atoms, preferably carried out in the presence of a catalyst selected from the group consisting of (i) one or more metal halides, (ii) one or more halogenated metal oxides, (iii) one or more zero-valent metals / metal alloys, (iv) a combination of two or more of the foregoing.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Functionalized Copolymers of Terminally Functionalized Perfluoro (Alkyl Vinyl Ether) Reactor Wall for Photochemical Reactions, Process for Increasing Fluorine Content in Hydrocaebons and Halohydrocarbons and Olefin Production
InactiveUS20070265368A1Preparation by hydrogen halide split-offCatalyst activation/preparationVinyl etherHalohydrocarbon
A photochemical reaction apparatus including a reactor and a light source situated so that light from the light source is directed through a portion of the reactor wall is disclosed. The apparatus is characterized by the portion of the reaction wall comprising a functionalized copolymer of a terminally functionalized perfluoro(alkyl vinyl ether). Also described is a photochemical reaction process using said reactor. The functional group of the copolymer of the apparatus and the process is selected from —SO2F, —SO2CI, —SO3H, —CO2R (where R is H or C1-C3 alkyl), —PO3H2, and salts thereof. A process for increasing the flourine content of at least one compound selected from hydrocarbons and halohydrocarbons, comprising: (a) photochlorinating said at least one compound, and (b) reacting the halogenated hydrocarbon in (a) with HF. A process for producing an olefinic compound, comprising: (a) photochlorinating at least one compound selected from hydrocarbons and halohydrocarbons containing at least two carbon atoms and at least two hydrogen atoms to produce a halogenated hydrocarbon containing a hydrogen substituent and a chlorine substituent on adjacent carbon atoms; and (b) subjecting the halogenated hydrocarbon produced in (a) to dehydrohalogenation.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Use of copolymers of perfluoro(alkyl vinyl ether) for photochemical reactions
InactiveUS7943015B2Impression capsPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offVinyl etherHalohydrocarbon
A photochemical reaction apparatus including a reactor and a light source situated so that light from the light source is directed through a portion of the reactor wall is disclosed. The apparatus is characterized by the portion of the reaction wall comprising a copolymer of a perfluoro (alkyl vinyl ether). The perfluoro (alkyl vinyl ether) is selected from the group consisting of CF30CF═CF2, C2F5OCF═CF2, C3F7OCF═F2, and mixture thereof. Also disclosed is a photochemical reaction process wherein light from a light source is directed through said reactor wall to interact with reactants in said reactor. A process for increasing the fluorine content of at least one compound selected from hydrocarbons and halohydrocarbons, comprising: (a) photochlorinating said at least one compound; and (b) reacting the halogenated hydrocarbon produced in (a) with HF. A process for producing an olefinic compound, comprising: (a) photochlorinating at least one compound selected from hydrocarbons and halohydrocarbons containing at least two carbon atoms and at least two hydrogen atoms to produce a halogenated hydrocarbon containing a hydrogen substituent and a chlorine substituent on adjacent carbon atoms; and (b) subjecting the halogenated hydrocarbon produced in (a) to dehydrohalogenation.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
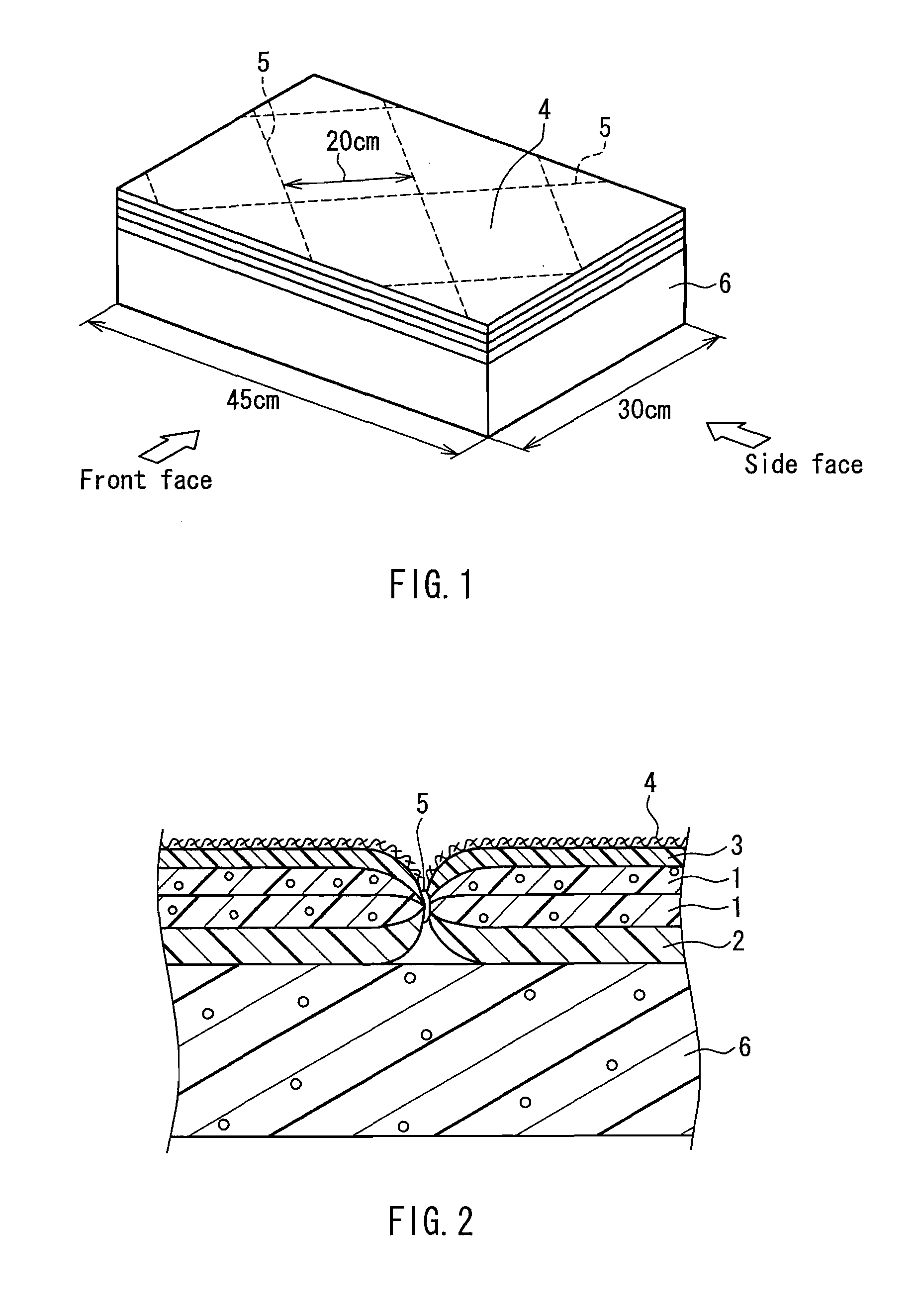
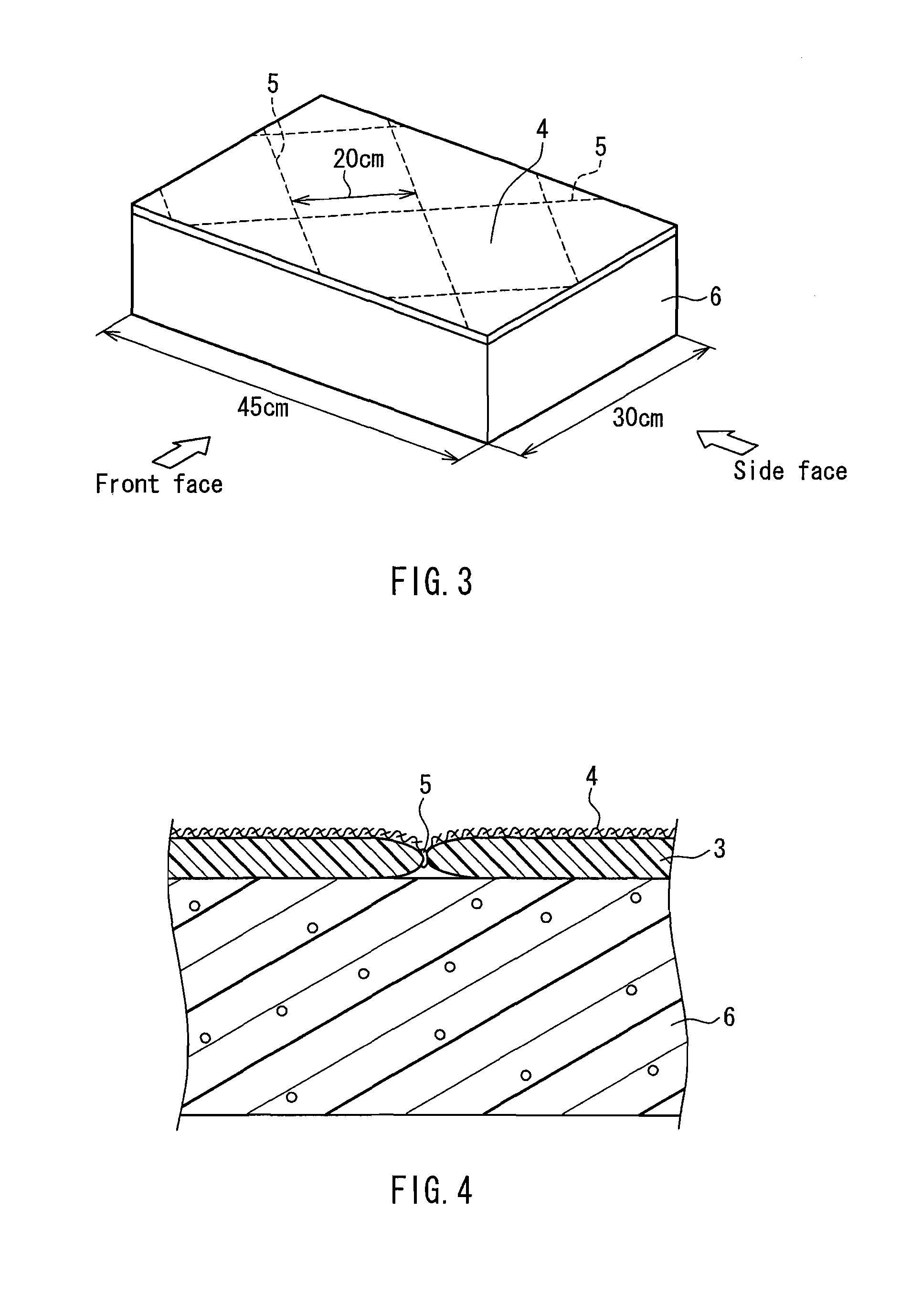
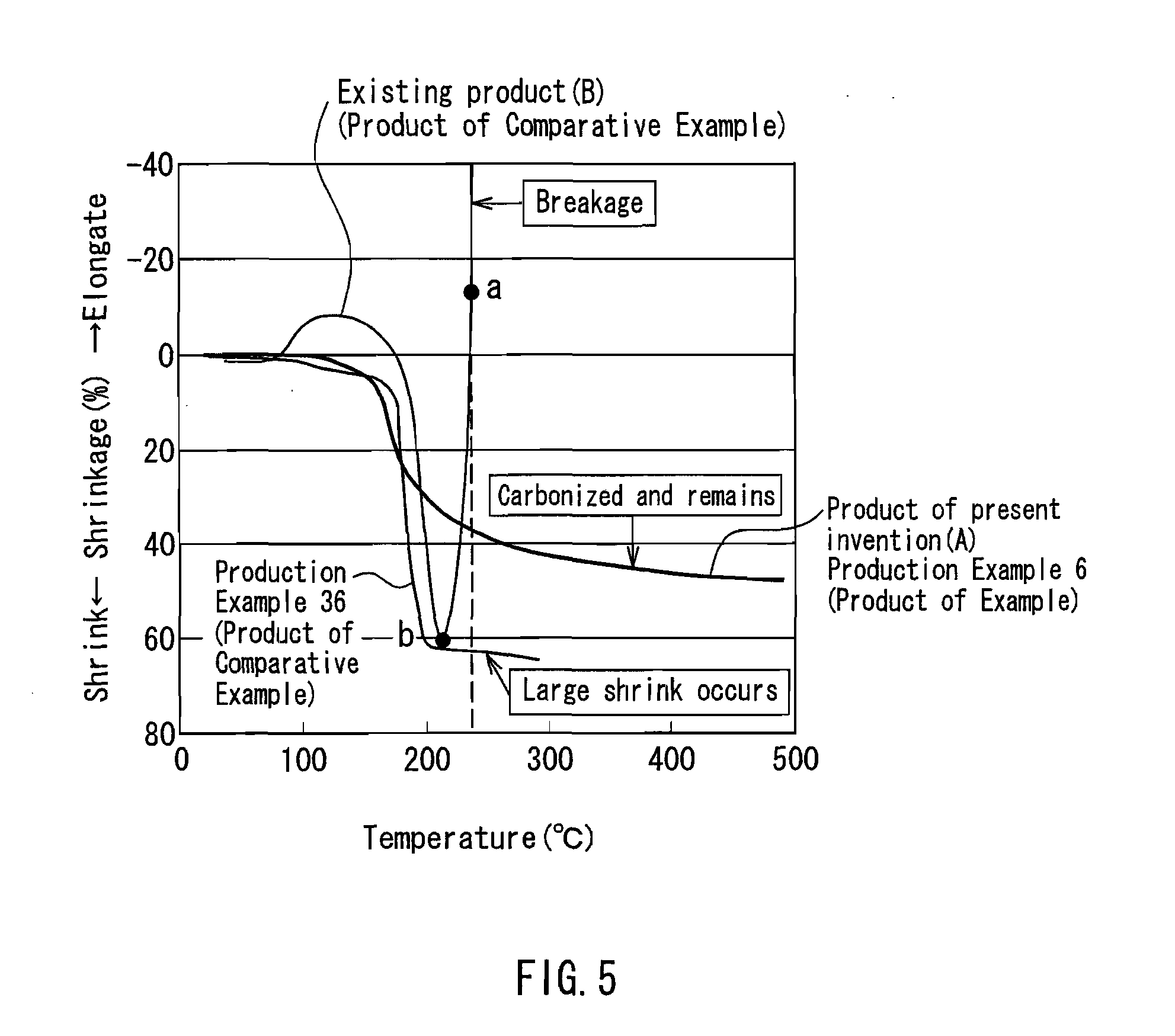
Flame retardant synthetic fiber, flame retardant fiber composite, production method therefor and textile product
ActiveUS20100029156A1High flame retardanceHigh flame shield propertyArtificial filament heat treatmentMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentHalogenChemistry
A flame retardant synthetic fiber and a flame retardant fiber composite that satisfy high flame retardance and high fire resistance, a method for producing the flame retardant synthetic fiber and the flame retardant fiber composite, and a textile product are provided. The flame retardant synthetic fiber of the present invention includes a polymer (1) containing 30 to 70 parts by mass of acrylonitrile, 70 to 30 parts by mass of a halogen-containing vinylidene monomer and / or a halogen-containing vinyl monomer, and 0 to 10 parts by mass of a vinyl-based monomer copolymerizable therewith, based on 100 parts by mass of the polymer, and at least one kind of a metal compound (2) that accelerates a dehalogenation reaction of the polymer (1) during burning and a carbonization reaction of the polymer (1) during burning, wherein the flame retardant synthetic fiber has a shrinkage variation of 45% or less when a temperature is raised from 50° C. to 300° C. under a load of 0.0054 mN / dtex.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Process for cis 1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoro-2-butene
ActiveUS20110288346A1Preparation by dehalogenationPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offButeneHydrogen
Disclosed is a process for preparing cis-1,1,1,4,4,4-hexafluoropropene comprising the steps of (a) reacting CCl4 with a compound having the formula CF3CX═CXH, where each X is independently halogen or hydrogen, to form a compound having the formula CF3CXClCXHCCl3; (b) fluorinating the compound formed in step (a) to form a compound having the formula CF3CXHCXHCF3; (c) converting the compound formed in step (b) by a reaction selected from the group consisting of dehydrohalogenation, dehalogenation and both reactions, to form a compound having the formula CF3C≡CCF3; and (d) catalytically reducing the compound formed in step (c) with hydrogen to form the compound having the formula:
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Magnesium fluoride-based catalyst and application of magnesium fluoride-based catalyst
InactiveCN104437567AImprove thermal stabilityLarge specific surface areaPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHydrofluoric acidMagnesium fluoride
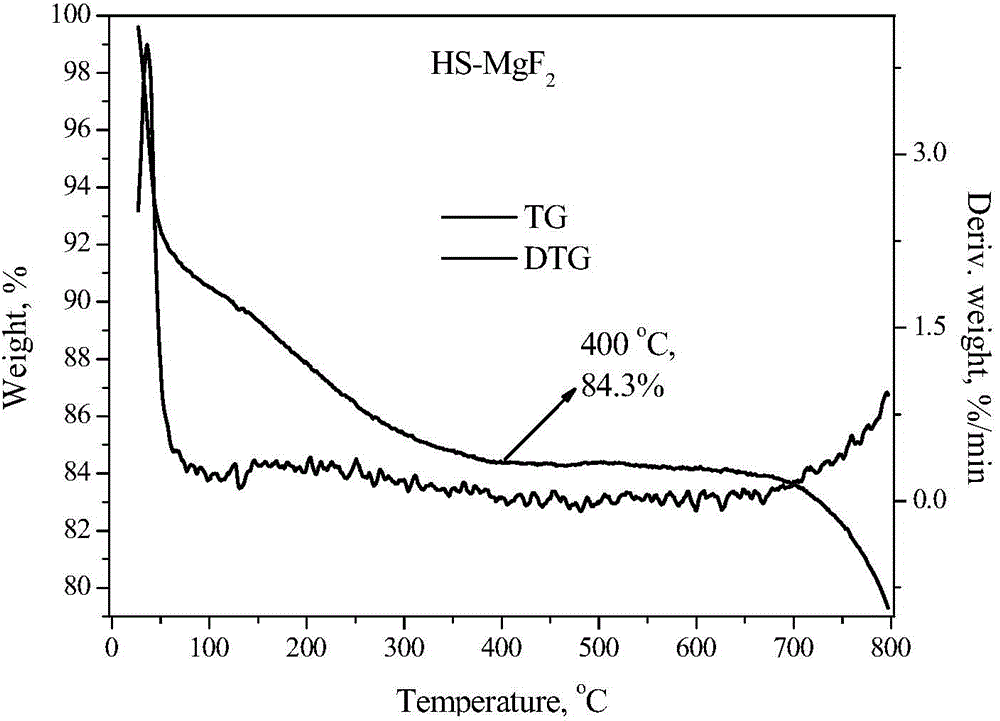
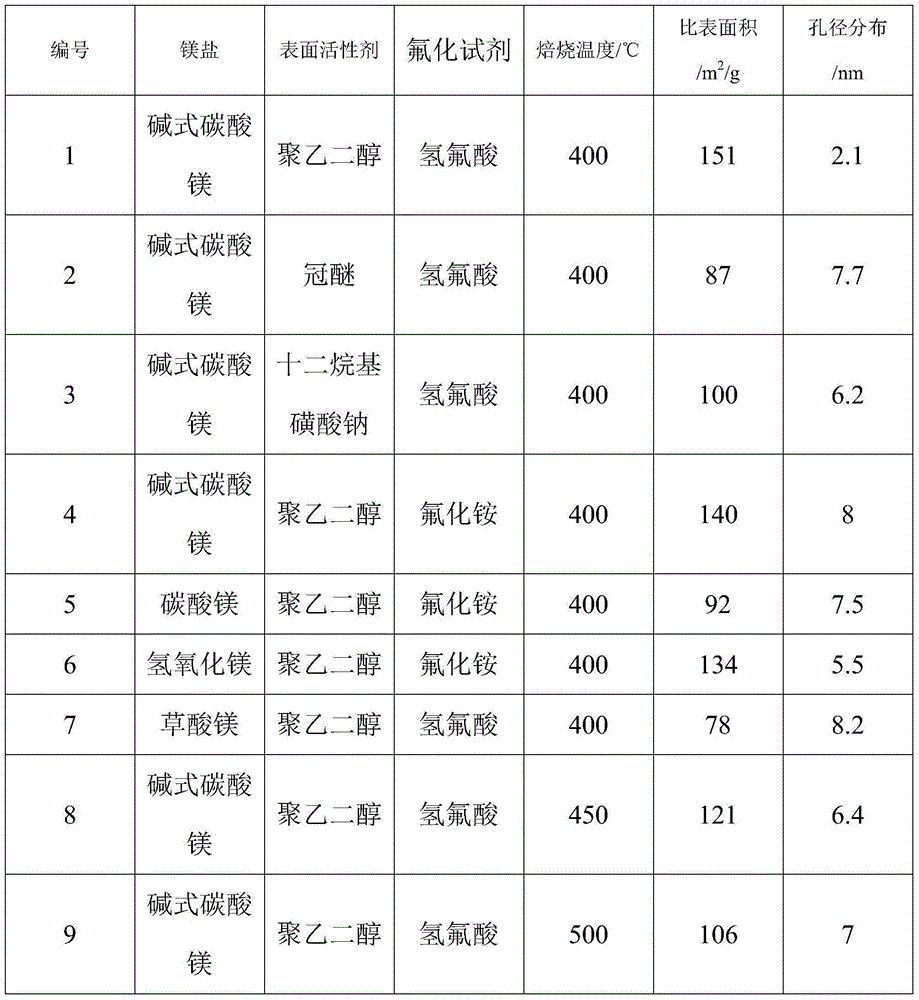
The invention discloses a magnesium fluoride-based catalyst which is stable at the temperature of over 400 DEG C and large in specific surface area and application of the magnesium fluoride-based catalyst. The invention aims at solving the problems such as low thermal stability and small specific surface area existing in the preparation of the magnesium fluoride-based catalyst in the prior art. The method for preparing the magnesium fluoride-based catalyst disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a turbid liquid solution containing a magnesium metal insoluble salt and a surfactant, refluxing at the temperature of 100 DEG C, roasting under the condition of 400-550 DEG C for 4 hours, thereby obtaining magnesium oxide with the large specific surface area; (2) dropwise adding an aqueous solution of hydrofluoric acid or ammonium fluoride into the magnesium oxide base body obtained in the step (1) for fluorinating, roasting at the temperature of 400-500 DEG C for 4 hours, thereby preparing magnesium fluoride; and (3) dropwise adding the aqueous solution doped with components into the magnesium oxide base body obtained in the step (2), and finally roasting at the temperature of 400-500 DEG C so as to prepare the catalyst. According to the catalyst disclosed by the invention, high-efficiency dehydrohalogenation reaction can be realized by virtue of halofluoroalkane.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Mesoporous chromium-oxide-based catalyst for dehydrohalogenation reaction
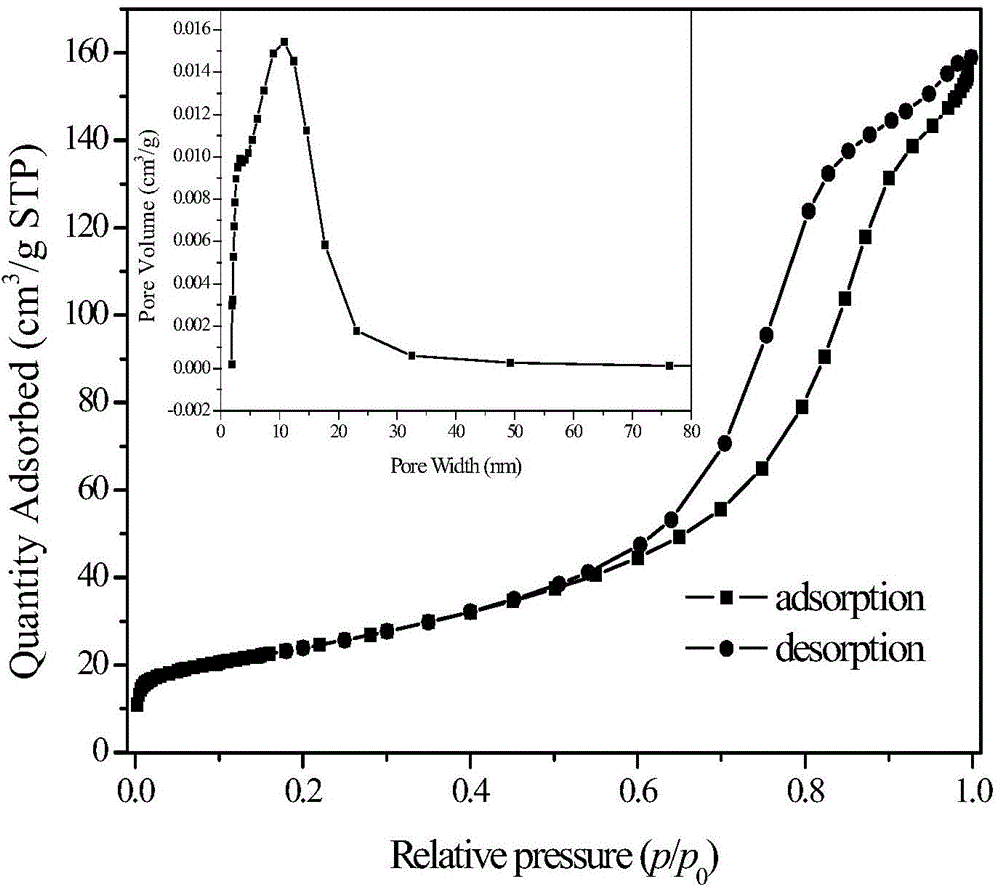
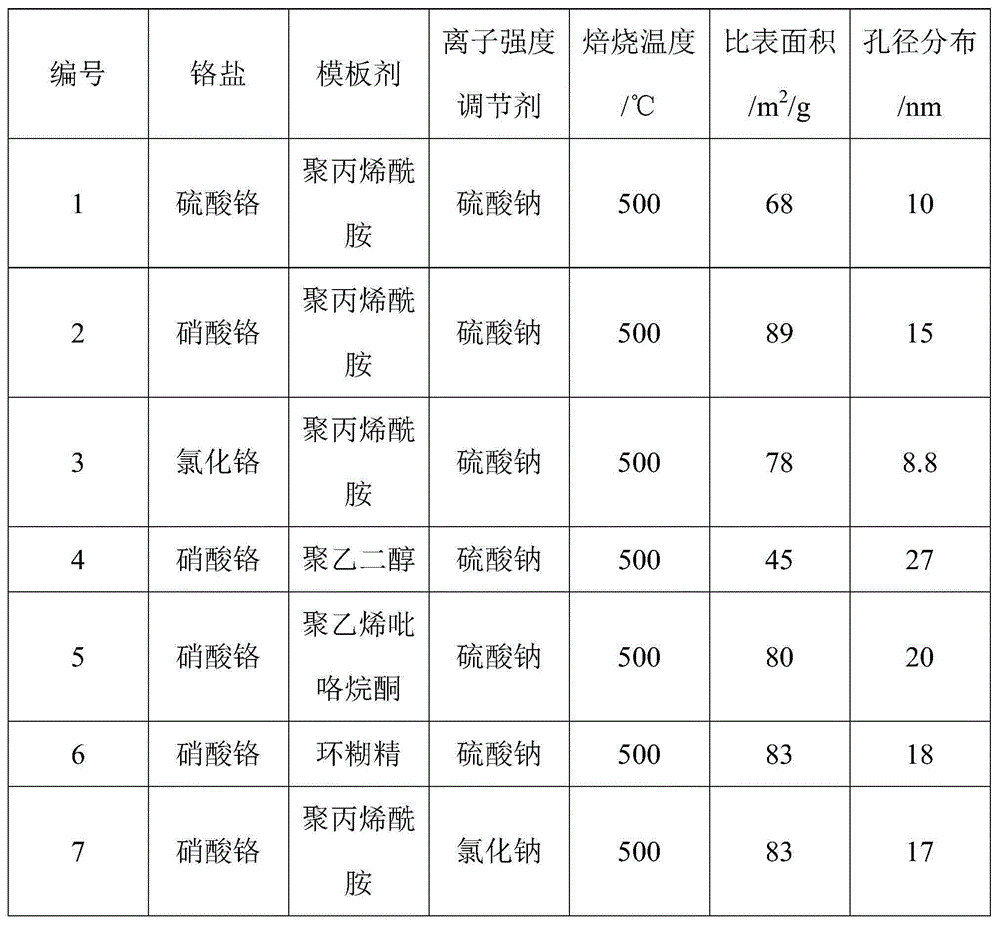
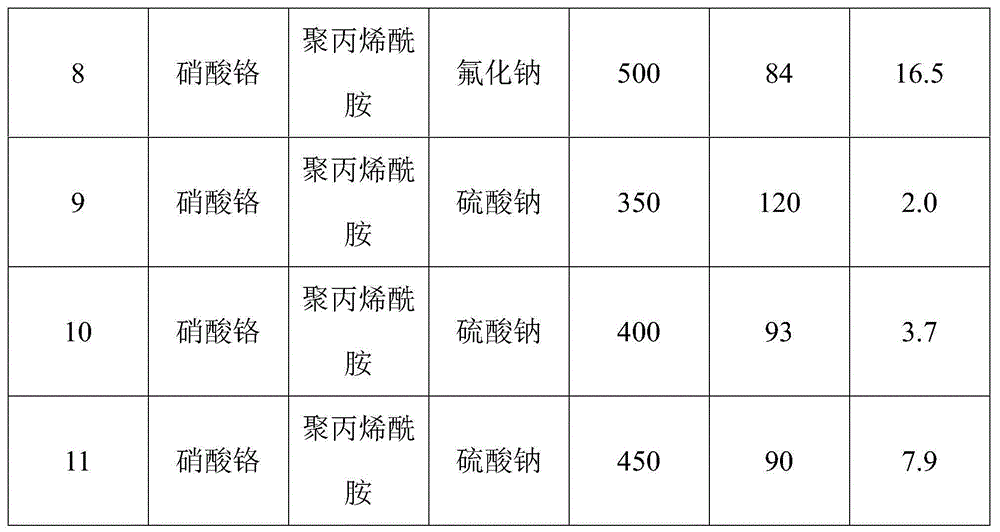
ActiveCN104475080ALarge specific surface areaRich mesostructurePreparation by hydrogen halide split-offMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsIonic strengthDehydrohalogenation
The invention discloses a mesoporous chromium-oxide-based catalyst for dehydrohalogenation reaction and a preparation method of the mesoporous chromium-oxide-based catalyst, and aims at solving the problems of small specific surface area, narrow porous structure and the like in preparation of the chromium-oxide-based catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing an aqueous solution containing chromium salt, a pH regulating agent, a template agent and an ion-strength regulating agent, flowing back at the temperature of 100 DEG C, roasting under the condition of 350-500 DEG C so as to obtain a mesoporous chromium-oxide base body; and (2) dipping the aqueous solution doped with components into the chromium-oxide base body obtained in the step (1) and finally roasting at the temperature of 400-550 DEG C to prepare the catalyst. The mesoporous chromium-oxide-based catalyst disclosed by the invention can be used for achieving the high-efficiency dehydrohalogenation reaction of fluorochloroalkylene.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Catalyst for greenly synthesizing halogenated arylamine by means of high-efficiency catalytic hydrogenation of halogenated aromatic nitro compound and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101658788AImprove performanceImprove stabilityOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationNitro compoundActive component
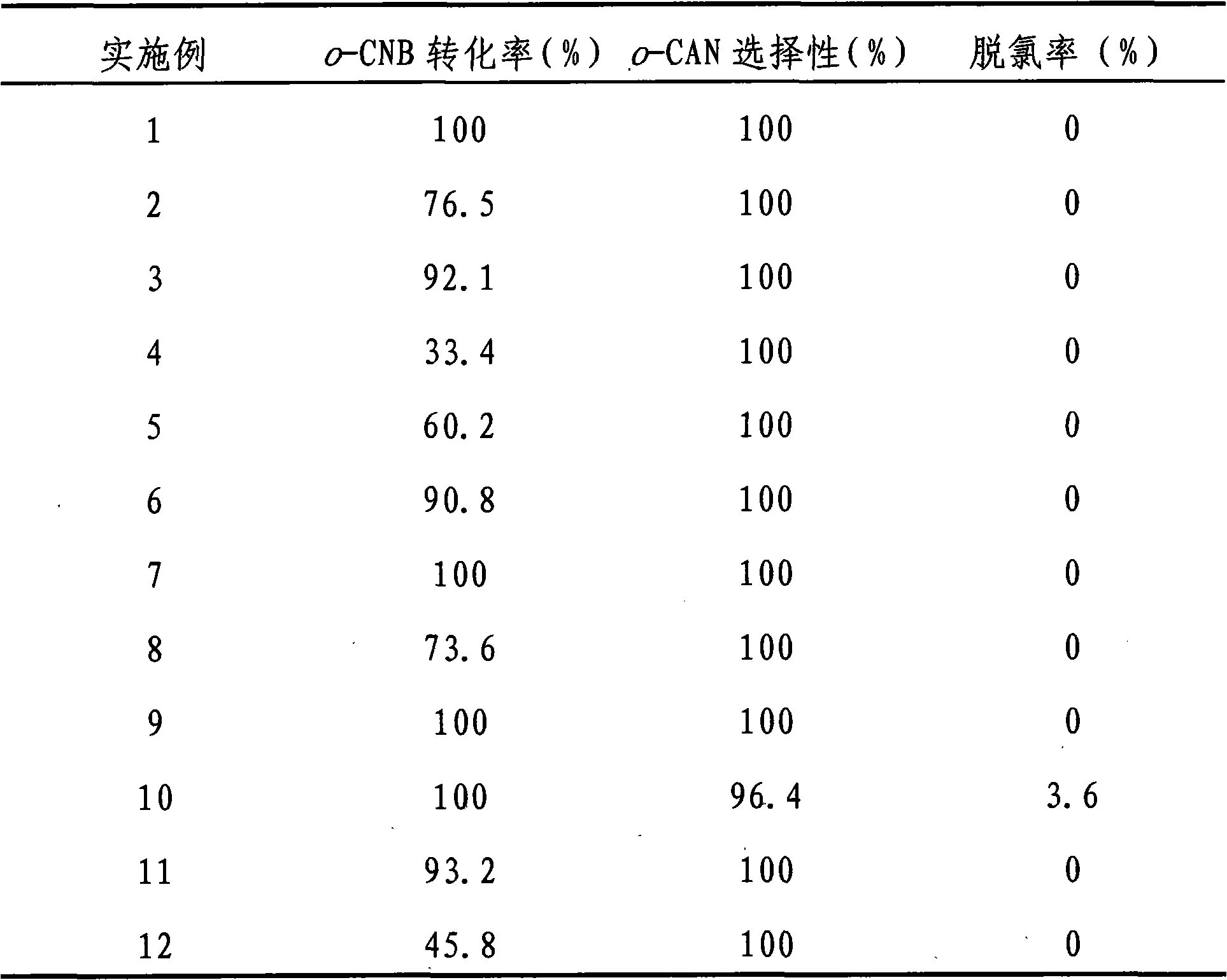
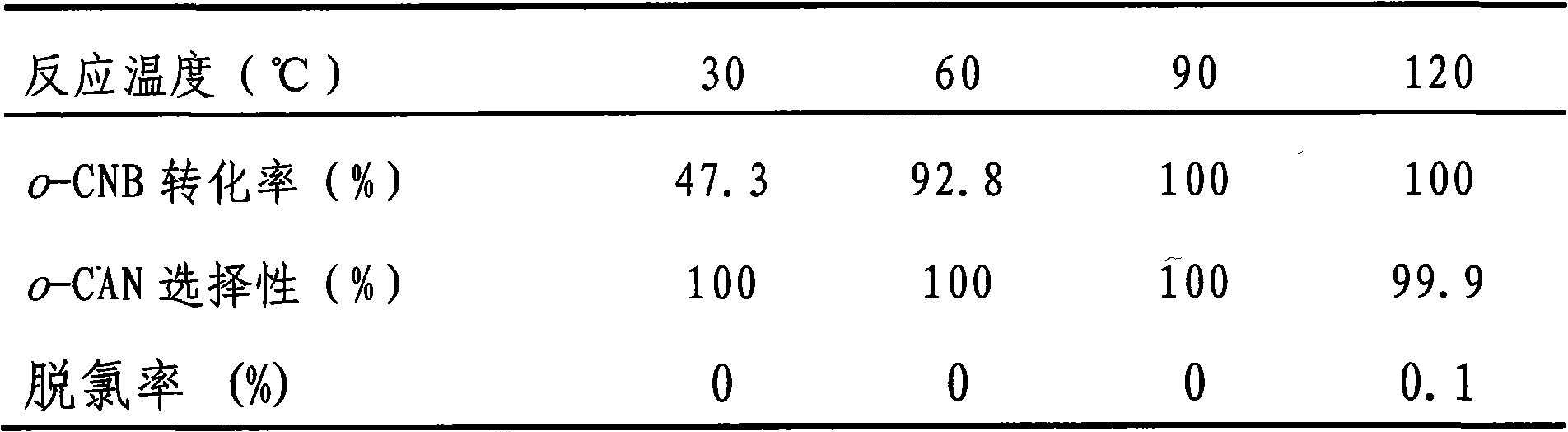
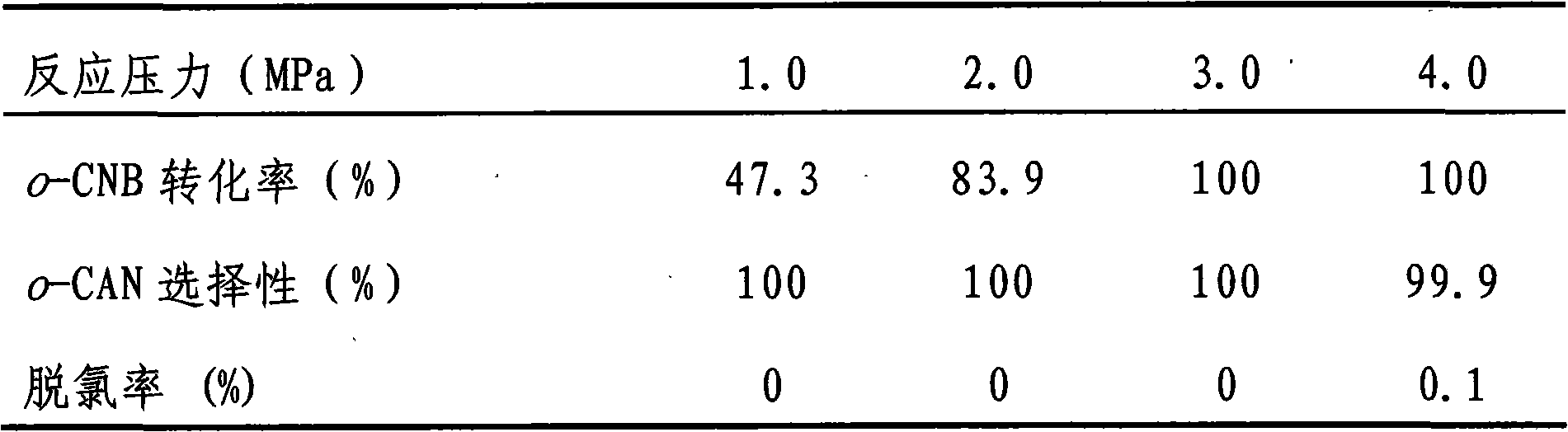
The invention discloses a catalyst for greenly synthesizing halogenated arylamine by means of catalytic hydrogenation of a halogenated aromatic nitro compound. The catalyst comprises a carrier and anactive component and is characterized in that TiO2, ZrO2, neutral Al2O3 or active carbon is used as the carrier, and a bi-component metal consisting of Au and Pt, Pd, Ir or Ru is used as the active component, wherein the metal accounts for 0.1-2.0% of the carrier in terms of weight percent and the two metal elements (the Au and the Pt, Pd, Ir or Ru) in the bi-component metal keep a weight ratio of1.0:0.1-0.5. The catalyst is highly active and selective during the preparation of the halogenated arylamine by means of catalyzing the hydrogenation of the halogenated aromatic nitro compound, can achieve 100% of raw material conversion rate and 100% of target product selectivity in conditions of normal temperature, 1MPa and H2 and causes no dehalogenation reaction. In addition, the catalyst hasstable activity, can be repeatedly used for a plurality of times and can conveniently cause the catalyst to be separated from a product after the reaction. The adoption of the process for preparing the halogenated arylamine can lead to low cost and zero pollution, and has relatively great implementing value and social and economic benefits.
Owner:CHINA WEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Photocatalytic halohydrocarbon dehalogenation conversion method
InactiveCN109438156AHigh economic valueAvoid it happening againPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrocarbon from halogen organic compoundsHalohydrocarbonAlkyne
The invention provides a photocatalytic halohydrocarbon dehalogenation conversion method which comprises the following steps: adding a photocatalyst quantum dot / rod into a solvent to obtain a solutionA; adding halohydrocarbon and an electronic sacrificial body into the solution A to obtain a solution B; utilizing a light source to irradiate the solution B and catalyzing the solution B to performhalohydrocarbon dehalogenation conversion. According to the photocatalytic halohydrocarbon dehalogenation conversion method disclosed by the invention, a nano quantum dot and a nano quantum rod are applied to dehalogenation conversion reaction of alkyl halide, alkenyl halide and alkyne halide for the first time; the reaction conditions are moderate, visible light is utilized as driving energy, a product is hydrocarbon compound, and the whole process has the advantages of environmental protection, conciseness and high efficiency. In addition, higher hydrocarbon of carbon chain growth can be generated after dehalogenation reaction, so that the method has potential application in preparation of higher hydrocarbon. According to the method disclosed by the invention, halohydrocarbon dehalogenation conversion and deuteration marking processes are jointly performed; hydrocarbon deuteration marking can be finished when a halohydrocarbon dehalogenation process is finished. The invention furtherprovides a method for performing deuteration marking on hydrocarbon.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite catalyst for preparing trichlorosilane through catalytic hydrogenation of silicon tetrachloride
ActiveCN103007995ASimple production processHigh catalytic efficiencyMolecular sieve catalystsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystHydrogen atmosphere
The invention discloses composite catalyst for preparing trichlorosilane through catalytic hydrogenation of silicon tetrachloride. The active constituents of the catalyst comprise at least one second main group metallic element and at least one transitional metal element, or a compound of the second main group metallic element and that of the transitional metal element, and can be loaded on a carrier for use. The catalyst can be used for catalytic hydrogenation dehalogenation reaction of silicon tetrachloride in the atmosphere of 700 to 1000 DEG C and 1 to 30 bar hydrogen, has higher catalytic activity and favorable selectivity, and is low in cost, simple to prepare and stable in performance.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Cerium-based carbon-containing nanotube composite RE oxide and its prepn
InactiveCN1432429AImprove thermal stabilityImprove anti-sintering performanceDispersed particle separationCatalyst activation/preparationCeriumInternal combustion engine
Oxides CeO2, ZrO2, La2O3 and Pr6O11 or their salts are prepared into mixed ionic nitric acid solution; small amount of surfactant and carbon nanotube are added into precipitant solution to prepare mixed precipitant solution; two kinds of solution are made to react to produce precipitate; and the precipitate is incinerated at 400-700 deg.c to obtain quarternary nanometer-level cerium-based carbon nanotube-containing composite RE oxide. The composite oxide has high specific surface area at both low temperature and high temperature and high heat stability. It may be used in various catalytic reaction process, such as hydrosulfurization, hydrodenitrification, dehydrohalogenation, internal combustion engine waste gas treatment and dehydrocyclization of hydrocarbon and other organic matters, and is especially suitable for use in purifying automobile tail gas.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Catalyst used in preparation of fluorine-containing olefin through dehydrohalogenation of halohydrofluoroalkane and preparation method of catalyst
ActiveCN102836722AImprove anti-carbon performanceExtended service lifePreparation by hydrogen halide split-offMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAlkaline earth metalGas phase
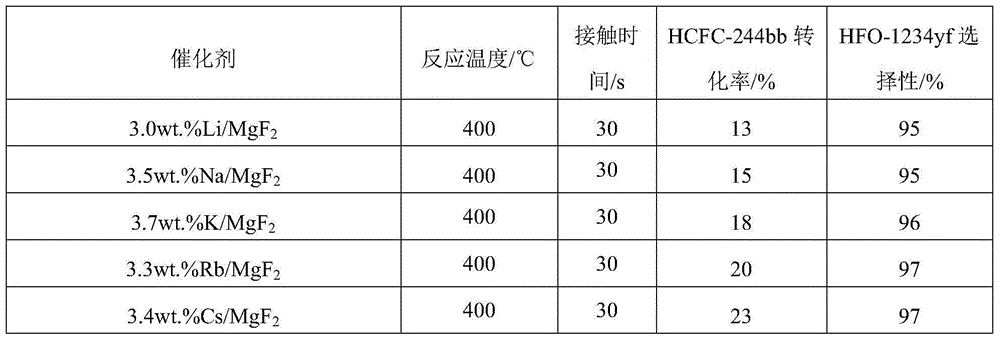
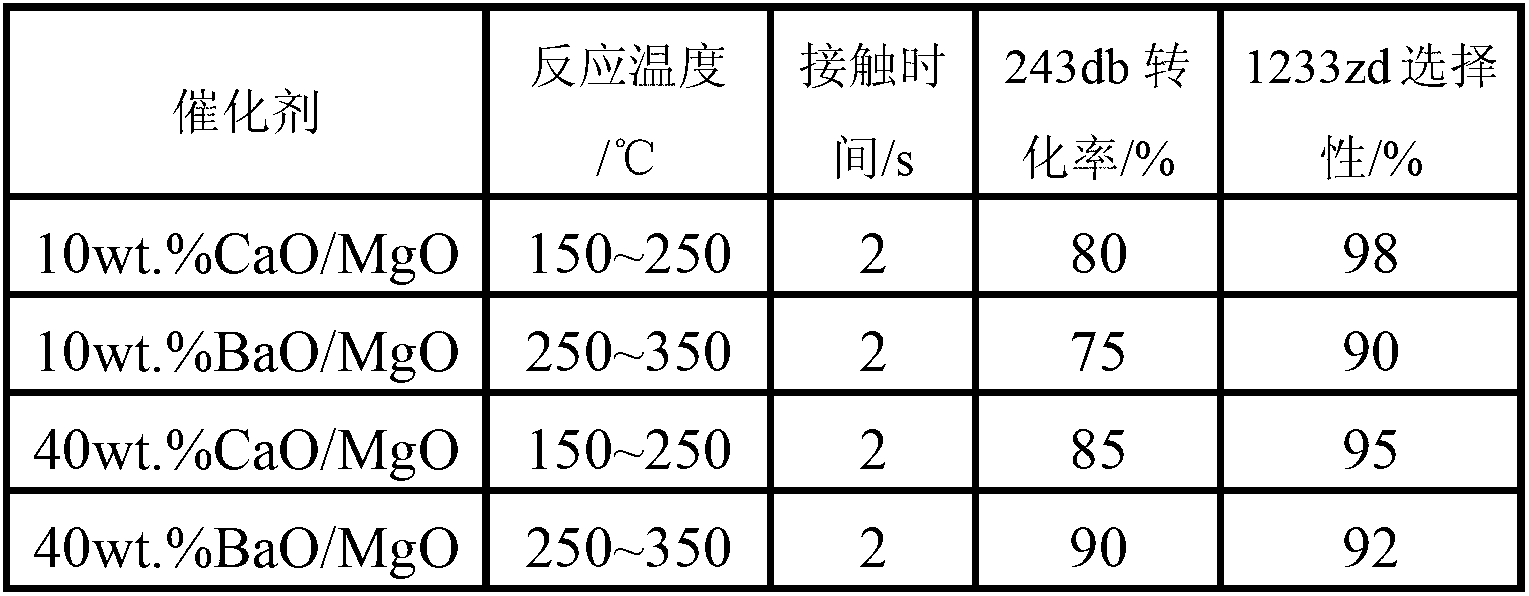
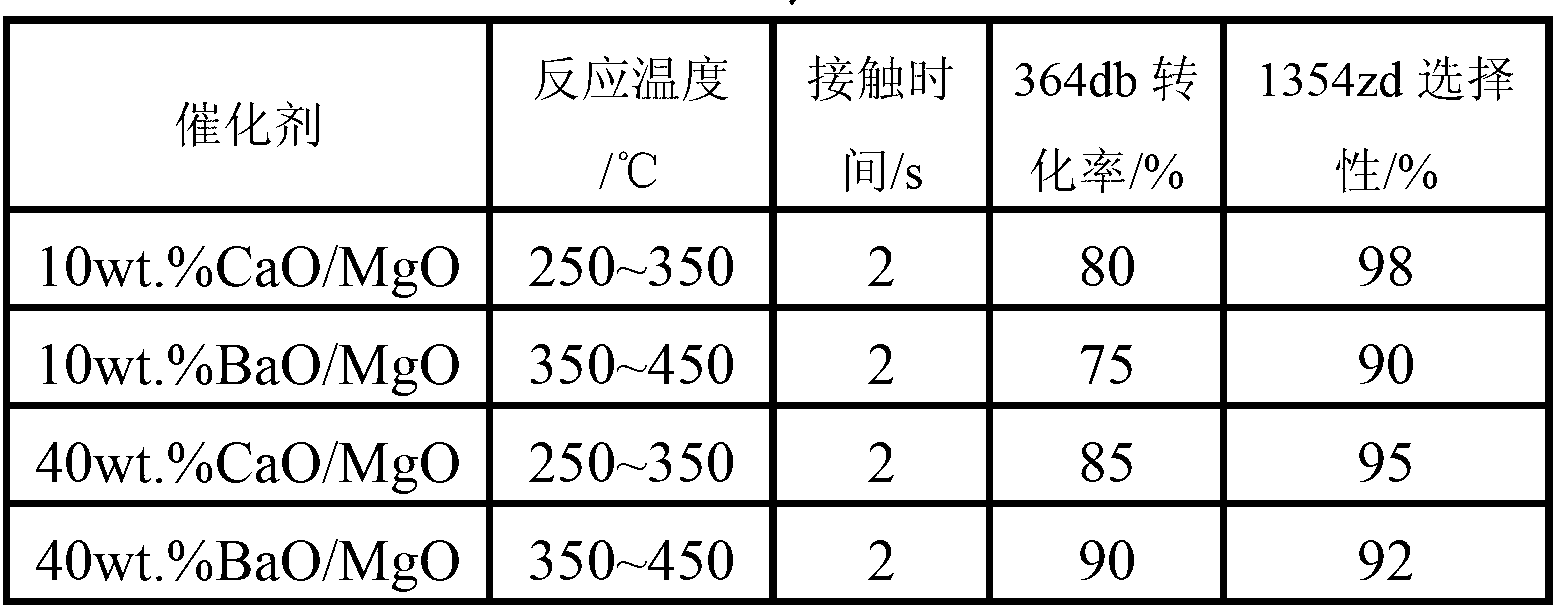
The invention discloses a catalyst used in preparation of fluorine-containing olefin through dehydrohalogenation of halohydrofluoroalkane. The catalyst is represented as nwt. %Y / X, wherein Y represents a catalyst promoter and is one or more selected from alkali metal ions Na<+>, K<+> and Cs<+>, rare earth metal ions La<3+>, Ce<4+>, Y<3+> or high-valence metal ions Al<3+>, Fe<3+>, Ti<4+> and Zr<4+>; X represents a main active ingredient and is one or a mixture of more of alkali metal magnesium, calcium and / or barium oxide; n is the using amount of the catalyst promoter and accounts for 30 percent of the main active ingredient at most; and the catalyst is mainly used for preparation of the fluorine-containing olefin through gas-phase dehydrohalogenation of the halohydrofluoroalkane.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Method for preparing fluorine-containing olefin by selective dehydrohalogenation with halogenated hydrocarbon
ActiveCN102838445AImprove conversion rateHigh dehydrohalogenation selectivityPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsGas phaseEconomic production
The invention discloses a method for preparing fluorine-containing olefin by selective dehydrohalogenation with halogenated hydrocarbon. Halogenated fluorocarbon containing three or more carbon atoms of which at least one hydrogen atom and at least one halogen atom are on the adjacent carbon atoms is used as a raw material. In the presence of a catalyst, a fluorine-containing olefin product is obtained through high temperature gas phase dehydrohalogenation reaction, wherein the reaction temperature is between 150 DEG C and 850 DEG C, the reaction pressure is 0-10atm of absolute pressure, and the contacting time of the reacting raw material and the compound catalyst is 0.3s-14s. The method for preparing fluorine-containing olefin by selective dehydrohalogenation which enables halogenated fluorocarbon to be highly selected has the advantages of high activity of compound catalyst, good stability, less by-product, and being capable of avoiding the complex product separation process and realizing higher economic production of fluorine-containing olefin.
Owner:山东华安近代环保科技有限公司
Synthesis method of allyl oxetane compound for ultraviolet light curing
InactiveCN104892549AIncrease profitThe feeding process is simple and easyOrganic chemistrySynthesis methodsReaction temperature
The invention relates to a synthesis method of an allyl oxetane compound for ultraviolet light curing. The synthesis method comprises: in the presence of an aqueous solution or suspension of an alkali, under continuous vigorous stirring, adding a 3-hydroxymethyl oxetane compound and 3-halo-propylene, adding an appropriate amount of a phase transfer catalyst, carrying out a phase transfer catalysis reaction for 24-30 h at a reaction temperature of -5-5 DEG C, and then carrying out dehydrohalogenation esterification so as to obtain the product. According to the present invention, the allyl oxetane compound having extremely low viscosity and capable of concurrently being used for free radical and cation curing can be prepared, and the synthesis method has characteristics of simple and easy-performing related reactions, no requirement of heating, less by-products, environmental protection, high yield, high equipment utilization rate, and easy large-scale industrial production of the allyl oxetane compound.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Preparation of fluorinated olefins via catalytic dehydrohalogenation of halogenated hydrocarbons
ActiveUS9040759B2Preparation by hydrogen halide split-offPhysical/chemical process catalystsHalohydrocarbonHydrogen atom
A process for making a fluorinated olefin having the step of dehydrochlorinating a hydrochlorofluorocarbon having at least one hydrogen atom and at least one chlorine atom on adjacent carbon atoms, preferably carried out in the presence of a catalyst selected from the group consisting of (i) one or more metal halides, (ii) one or more halogenated metal oxides, (iii) one or more zero-valent metals / metal alloys, (iv) a combination of two or more of the foregoing.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Reaction product of phosphine and protonated haloaryl compound and use as epoxy curing accelerator
InactiveUS20090005480A1Improve the overall coefficientImprove conductivityGreenhouse cultivationCultivating equipmentsHigh temperature storageHydrogen halide
The invention relates to a curing accelerator for a curing resin obtained by reacting a phosphine compound (a) with a compound (b) having at least one halogen atom substituted on an aromatic ring and at least one proton atom which can be discharged, and subjecting the reaction product to dehydrohalogenation, a curing resin composition containing the curing accelerator, and an electronic component device having a device component encapsulated with the curing resin composition. The curing accelerator exhibits superior curability under moisture absorption, flow properties, reflow cracking resistance and high-temperature storage characteristics.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
Method for making photocurable halofluorinated acrylates
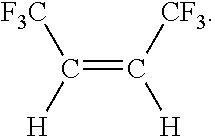
InactiveUS6166156AEconomical and efficient to practiceSuperior optical waveguiding characteristicPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offPreparation from carboxylic acid halidesCarboxylic acidDehydrohalogenation
Halofluorinated alkylene monomers are made by a method comprising the steps of: (a) subjecting a first polymer which is the reaction product of a fluorinated vinyl monomer and a vinyl comonomer to dehydrohalogenation to form a second polymer; (b) treating the second polymer with an oxidizing agent to form an oxidation product consisting of a alpha , omega -dicarboxylic acid or an ester derivative thereof; and (c) treating said oxidation product with a reducing agent to form a reduction product consisting of a a alpha , omega -diol. Preferably, the first polymer has a structure of -[CH2CYZ(CF2CFX)n]m- wherein X and Y=F, Cl or Br; X and Y may be the same or different; Z=H, F, Cl, Br, alkyl or perfluoroalkyl containing from about 1 to about 10 carbon atoms; n=an integer larger than about 1; and m is an integer between about 2 and about 105. The alpha , omega -dicarboxylic acids and alpha , omega -diols produced herein can be directly used as polycondensation monomers. Alternatively, the alpha , omega -dicarboxylic acids and alpha , omega -diols can be further derivitized to tri-, tetra- or other multifunctional alcohols which may be directly used as condensation monomers or they may be converted to acrylates which may be photocured in the presence of a radical photoinitiator into transparent polymers which are useful as optical waveguiding materials.
Owner:ENABLENCE TECH USA
Process for dehydrohalogenation of halogenated alkanes
InactiveUS20110269999A1Improve production yieldHigh selectivityPreparation by dehalogenationPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offHydrogen halideAlkane
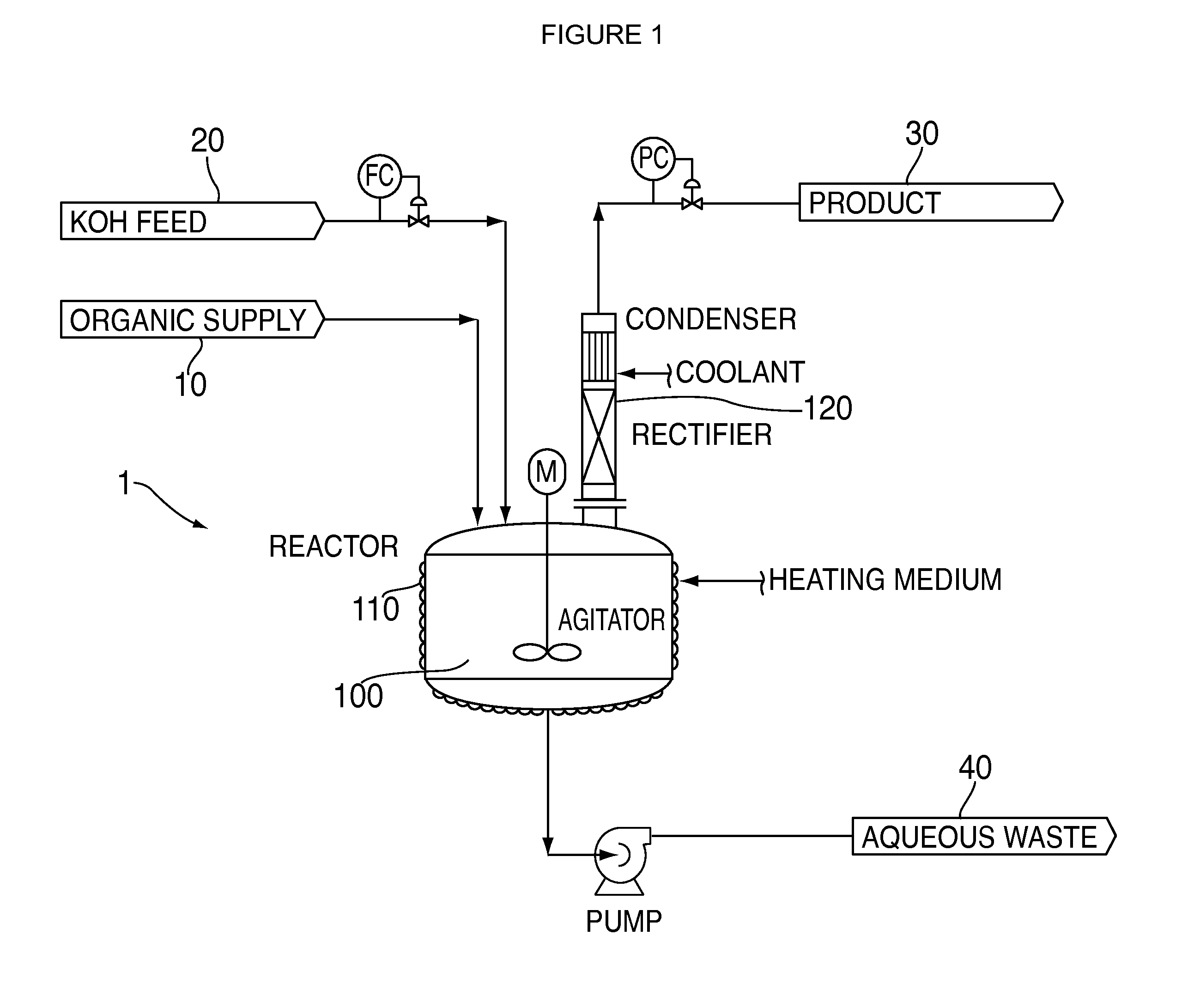
A process for the manufacture of halogenated olefins in semi-batch mode by dehydrohalogenation of halogenated alkanes in the presence of an aqueous base such as KOH which simultaneously neutralizes the resulting hydrogen halide. During the process, aqueous base is continuously added to the haloalkane which results in better yields, lower by-product formation and safer / more controllable operation.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Process for preparing fluorohalogenethers
ActiveCN1986512APreparation by dehalogenationPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offHydrogenHalogen
A process for preparing perfluorovinylethers having general formula: R f O-CF=CF 2 (IA) wherein R f is a C 1 -C 3 alkyl perfluorinated substituent; comprising the following steps: 1a) fluorination with fluorine of olefins of formula: CY''Y=CY'Cl (II) wherein Y, Y' and Y'', equal to or different from each other, are H, Cl, Br, with the proviso that Y, Y' and Y'' are not contemporaneously hydrogen; and obtainment of fluorohalogencarbons of formula: FCY''Y-CY'ClF (III) wherein Y, Y' and Y'' are as above; 2a) dehalogenation or dehydrohalogenation of the fluorohalogencarbons (III) and obtainment of fluorohalogen olefins of formula: FCY I =CY II F (IV) wherein Y I and Y II , equal to or different from each other, have the meaning of H, Cl, Br with the proviso that Y I and Y II are not both H; 3a) reaction between a hypofluorite of formula R f OF and a fluorohalogenolefin (IV), obtaining the fluorohalogenethers of formula: RfO-CFY I -CF 2 Y II (I) wherein Y I , Y II , equal to or different from each other, are Cl, Br, H with the proviso that Y I and Y II cannot be contemporaneously equal to H; 4a) dehalogenation or dehydrohalogenation of the compounds (I) and obtainment of the perfluorovinylethers (IA).
Owner:SOLVAY SOLEXIS
Photochlorination And Dehydrohalogenation Process For Preparation Of Olefinic Compounds
InactiveUS20080076950A1Preparation by hydrogen halide split-offHydrocarbonsHydrogen halideHalohydrocarbon
A process is disclosed for producing an olefinic compound from a least one compound selected from hydrocarbons and halohydrocarbons containing at least two carbon atoms and at least two hydrogen atoms. The process involves (a) directing light from a light source through the wall of a reactor to interact with reactants comprising chlorine and said at least one compound in said reactor, thereby producing a saturated halogenated hydrocarbon having increased chlorine content by photochlorination, and (b) dehydrohalogenating said saturated halogenated hydrocarbon produced by the photochlorination in (a); and is characterized by the light directed through the reactor wall being directed through a poly(perhaloolefin) polymer.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
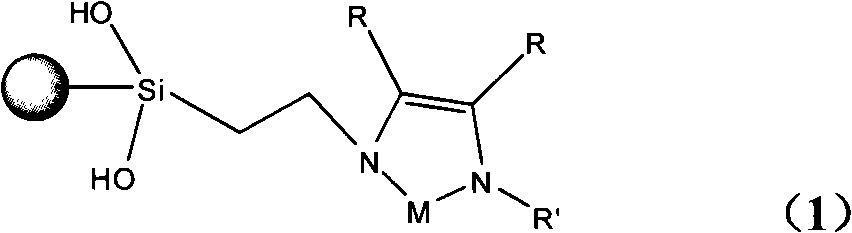
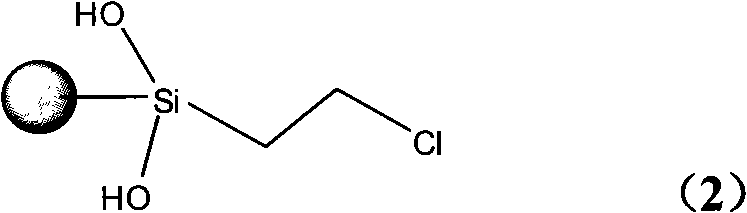
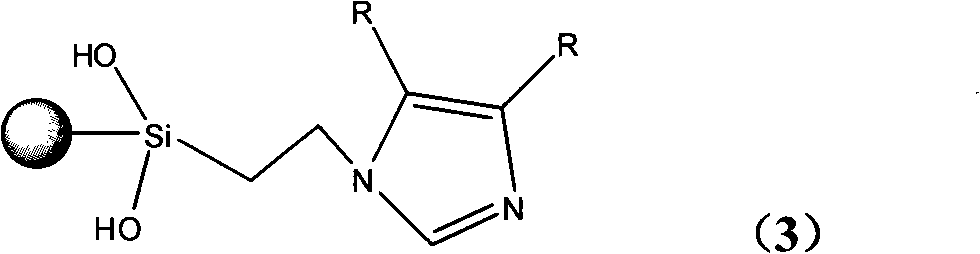
Glyoxaline ligand metallic catalyst supported on silica-gel and process for synthesizing the same
InactiveCN101279293AHigh activityImprove catalytic performanceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsWater/sewage treatmentStructural formulaSilica gel
The present invention discloses a silica solid-carrying imidazole ligand metal catalyst with a structural formula on the right; wherein, the group on the left is a silica solid-carrying agent, R is selected from H atom and methyl; R' is selected from phenmethyl and aryl; M is selected from metal palladium or nickel. The catalyst uses imidazole carbine and transition metals to form a ligand compound. The catalyst can be used for degradation and dehalogenation of the organic halides in water; the reaction conditions of the catalyst are gentle and no secondary pollution is generated. The present invention provides an effective method for the treatment of waste water with organic halides included. The present invention also applies for a synthesizing method for the catalyst provided by the present invention.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Catalytic hydrogenation method for preparing halogenated aromatic amine from halogenated arene nitro compounds
ActiveCN101265194AEliminate pollutionEasy to separateOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationNitro compoundHalogen
The invention relates to a method of preparing halogen aromatic amine by catalyzing aryl halide nitrocompound through selective hydrogenation. The method comprises the following steps: in scCO2, a non-noble metal Ni catalyst is adopted to catalyze the aryl halide nitrocompound and prepare the halogen aromatic amine through selective hydrogenation under the low temperature ranging from 31 to 100 DEG C; in the scCO2, the hydrogenation speed of -NO2 group in the aryl halide nitrocompound is higher than the speed in ethanol obviously, and the dehalogenation reaction is markedly inhibited, so that the selectivity of the halogen aromatic amine is more than 99 percent is realized. The cost of the Ni catalyst is lower than a noble metal catalyst; the Ni catalyst has ferromagnetism at the same time, thereby providing the possibility to the reactor operation and the catalyst separating by adopting an external magnetic field.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Process for producing 2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene
The present invention provides a process for producing 2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene represented by the chemical formula: CF3CCl=CH2, comprising mixing a fluorine-containing alkane, in a liquid state, represented by the formula: CF3CHClCH2X, wherein X is halogen, with an aqueous solution containing at least one metal hydroxide selected from the group consisting of alkali metal hydroxides and alkali earth metal hydroxides in the presence of a catalyst to perform a dehydrohalogenation reaction of the fluorine-containing alkane. According to the present invention, 2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene (HCFO-1233xf) can be obtained at a very high yield at a relatively low reaction temperature.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Method for preparing vinylene carbonate
ActiveCN101210006AEasy to separate and purifyRaw materials are easy to getOrganic chemistryDistillationDehydrohalogenation
The invention relates to a preparation method of vinylene carbonate, which comprises halogenated ethylene carbonate and dehydrohalogenation agent which are subject to contact reaction. The dehydrohalogenation agent is ammonia with a purity of not less than 99.9 percent. The yield of the vinylene carbonate prepared by adopting the method provided by the invention reaches as high as 85 percent, resultant can be quite easily separated and purified, and the purity of the resultant can reach 99.5 percent (GC) through general distillation and a crystallization method. Raw materials of the dehydrohalogenation agent can be easily obtained at low price; furthermore, excessive ammonia can be recycled, so the production cost is greatly reduced compared with using organic amine as the dehydrohalogenation agent. In addition, molecular weight of the ammonia that is used as the dehydrohalogenation agent is small, thus greatly reducing the weight of side products under the same situation.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
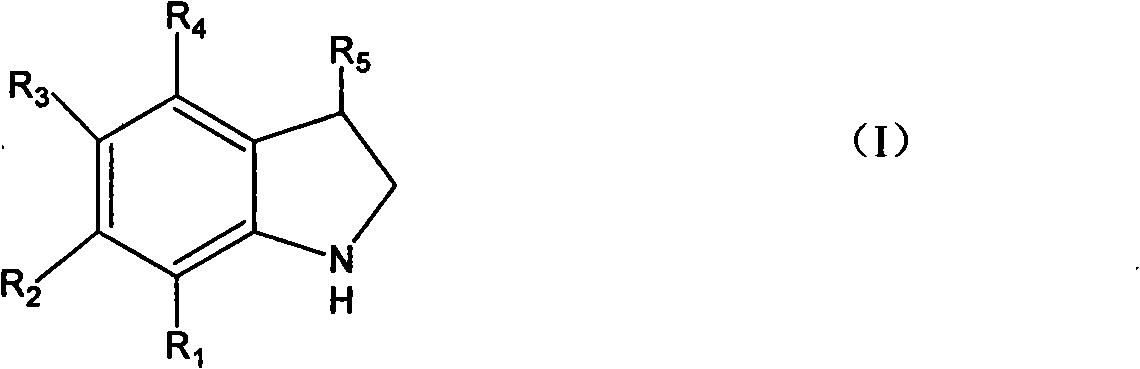
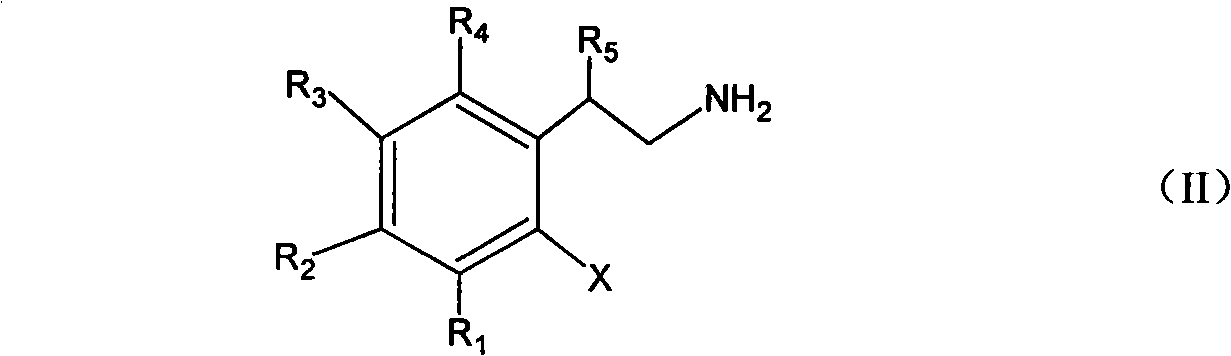
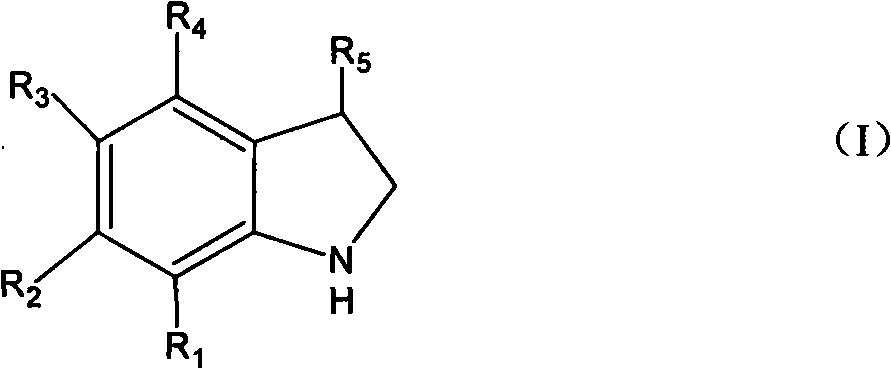
Method for synthesizing indoline and derivates thereof
InactiveCN101328144AEasy to recycleAvoid problems that have to be pressurizedOrganic chemistryMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHydrogenIndoline
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing indoline in formula (I) and a derivative thereof. Titanium dioxide laden copper of Cu / TiO2 with a charge number between 5 and 15 weight percent is taken as a catalyst. The a compound in formula (II) and the catalyst have condensation reaction under the action of a dehydrohalogenation agent to produce the indoline, wherein R1, R2, R3 and R4 represent hydrogen, C1 to C4 represent alkyl, C1 to C4 represent alkoxyl group and nitryl, and C1 to C4 represent hydroxyalkyl; and R5 represents hydrogen, and C1 and C2 represent alkyl. The method avoids the operation at high pressure, avoids the use of raw materials such as organic amine and the catalyst with high price and great toxicity, lowers the cost, improves the operating environment, is easy to reclaim the catalyst and has high yield of the product.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Method for producing fluorine-containing olefin
ActiveUS7973202B2Reduce the amount requiredHigh selectivityPreparation by hydrogen halide split-offOrganic halogenationDehydrohalogenationReaction step
The present invention aims to reduce an amount of by-products generated in a reaction step for obtaining fluorine-containing olefin, and thereby to obtain fluorine-containing olefin as a target substance with a higher selectivity than that in the conventional method.In a reaction step for generating fluorine-containing olefin by a dehydrohalogenation reaction from fluorine-containing halogenated propane expressed by a general formula CF3CH(2-n)XnCH(3-m)Xm (wherein n=0, 1 or 2; m=1, 2 or 3; and n+m≦3; and X is selected from F, Cl and Br, independently), fluorochromium oxide having a fluorine content not less than 30% by weight is used as a catalyst.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
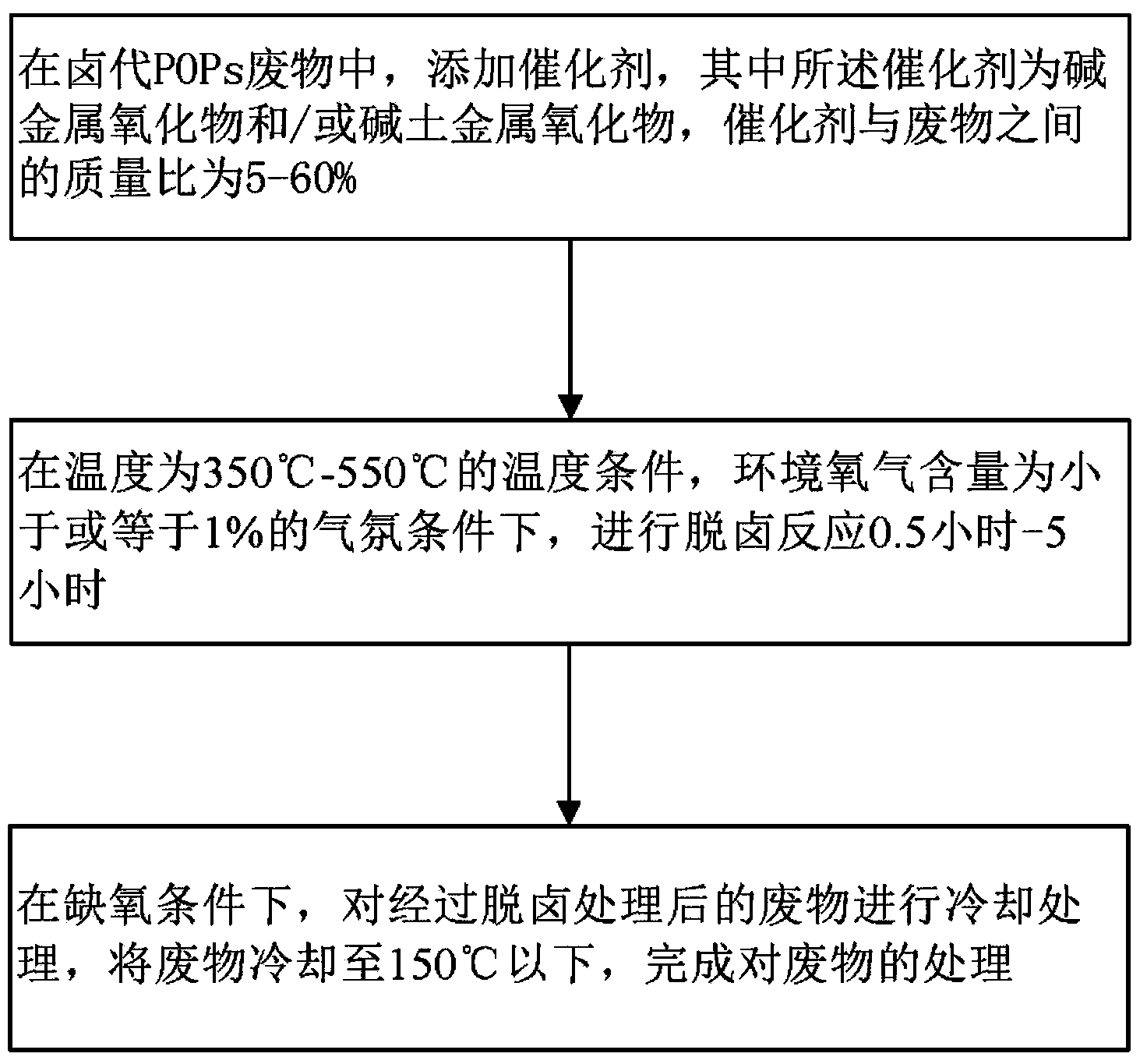
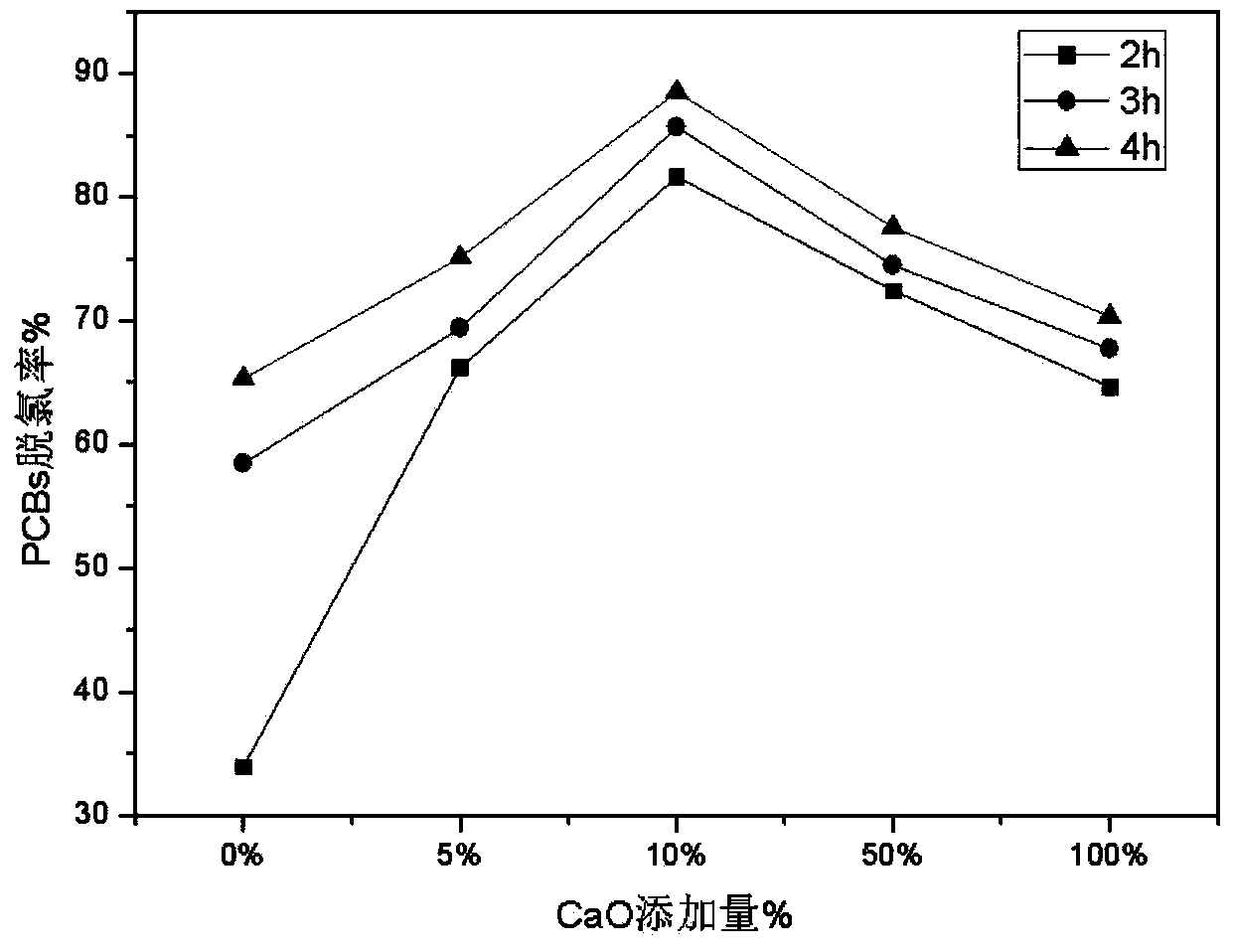
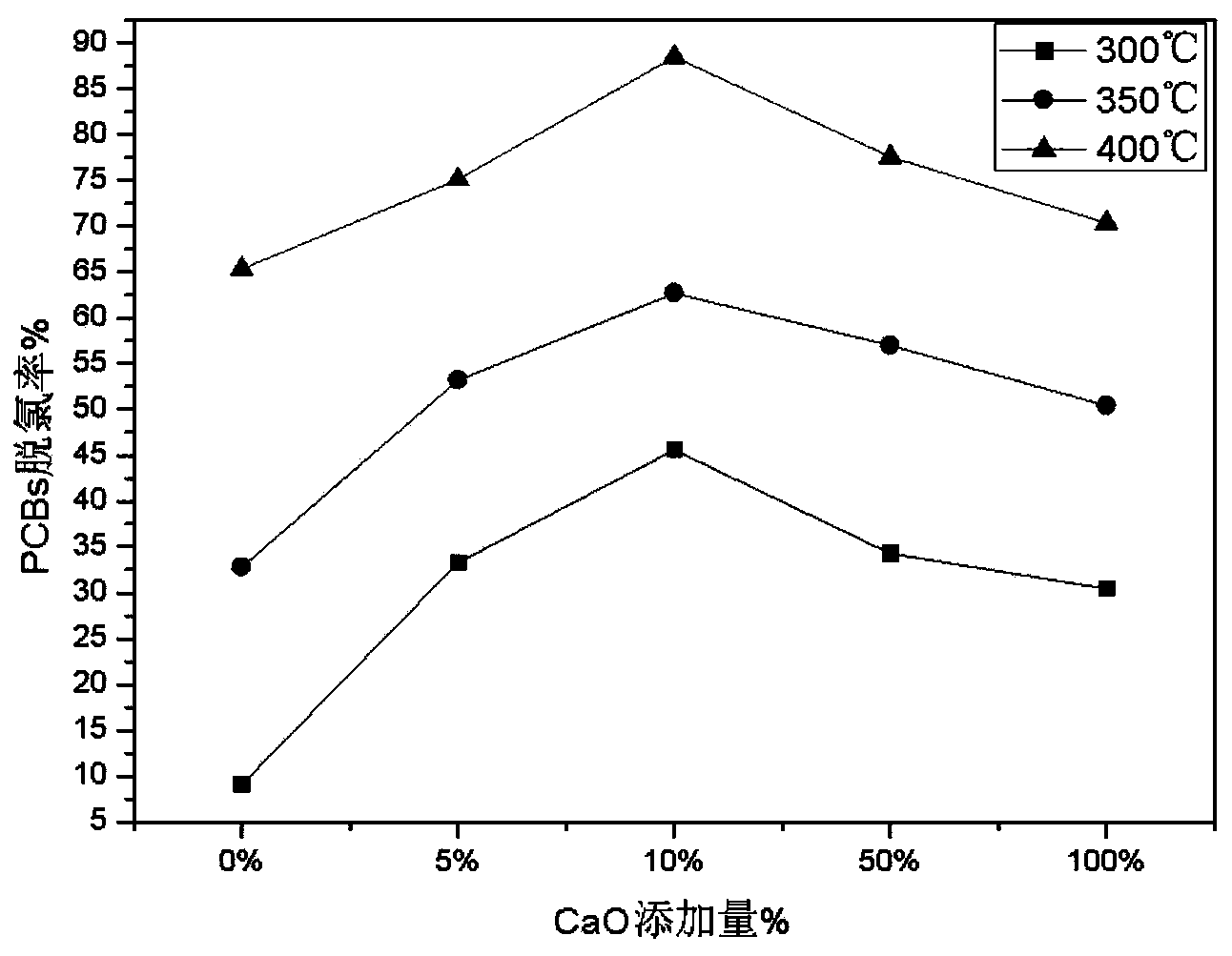
Method and system for processing wastes of halogenated POPs (Persistent Organic Pollutants)
ActiveCN103752583AEfficient removalRealize processingSolid waste disposalAlkali metal oxidePersistent organic pollutant
The invention provides a method and a system for processing wastes of halogenated POPs (Persistent Organic Pollutants). The method comprises the steps of adding catalysts into the wastes of the POPs, wherein the catalysts are alkali metal oxides and / or alkaline earth metal oxides; performing dehalogenation for 0.5-5 hours at the temperature of 250-600 DEG C under an atmosphere condition that the content of oxygen in the environment is less than or equal to 1%; and cooling the wastes after dehalogenation under an anoxic atmosphere condition, and cooling the wastes to below 150 DEG C, thus finishing treatment of the wastes. Meanwhile, the invention also provides a method for implementing the method. Through the technical scheme of the method and the system, the wastes of the halogenated POPs can be effectively subjected to dehalogenation, processing efficiency is good, the processing process is easily-controllable, the cost is low, and the method and the system are applicable to treatment of the wastes of the industrial POPs.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com