Friction difference brake method
A technology of friction and friction parts, which is applied in the field of mechanical transmission or braking, can solve the problems of complex control and transmission devices, and achieve the effects of simple structure, wide application range and improved braking accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
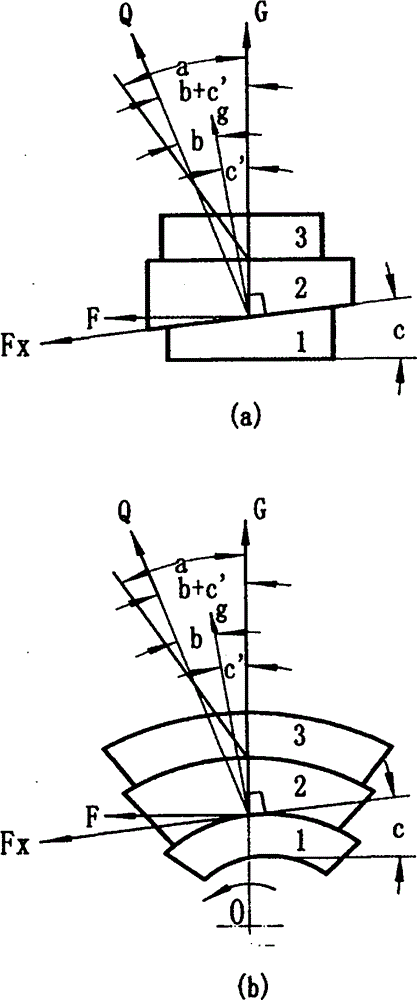
[0063] Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of the friction type linear one-way brake of the present invention: the braking direction is the direction of the reverse driving force angle; the three elements of friction include the driving force part, the friction part and the target part; The moving direction is installed in the frame (brake caliper) in turn; the frame is fixed on the equipment and floats perpendicular to the braking direction; the target part is located between the side of the friction part and the frame; the driving part and the friction part The contact surface is an inclined surface, which is in a constant contact state; the contact surface between the friction part and the target part is a plane; the friction coefficient between the friction part and the target part is generally more than 1 times that between the friction part and the driving part ; b+c≤a or 90°>b+c>a and it is a certain value; where a is the friction angle between the friction part and the...
Embodiment 2
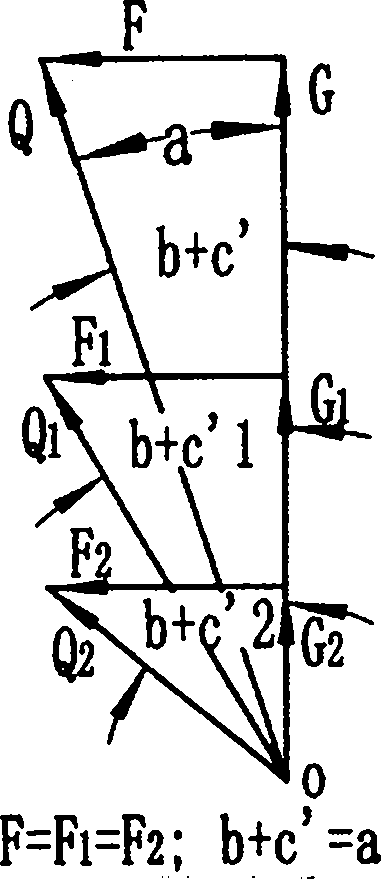
[0067] Figure 6 It is a schematic diagram of a friction-type linear one-way brake outsourcing type 3 (guide rail): the braking direction is the direction of the reverse driving force angle; the three elements of friction include the driving force component, the friction component and the target component; Installed on the frame (not shown), the friction part is installed against the driving part; the frame is fixed on the equipment and floats perpendicular to the braking direction; the two wings of the target part are located on both sides of the driving part and the friction part; The contact surface between the driving force part and the friction part is a slope, which is in a constant contact state; the contact surface between the driving part, the friction part and the target part is a plane; the friction coefficient between the friction part and the target part is generally greater than that between the friction part and the target part. The friction coefficient between ...
Embodiment 3
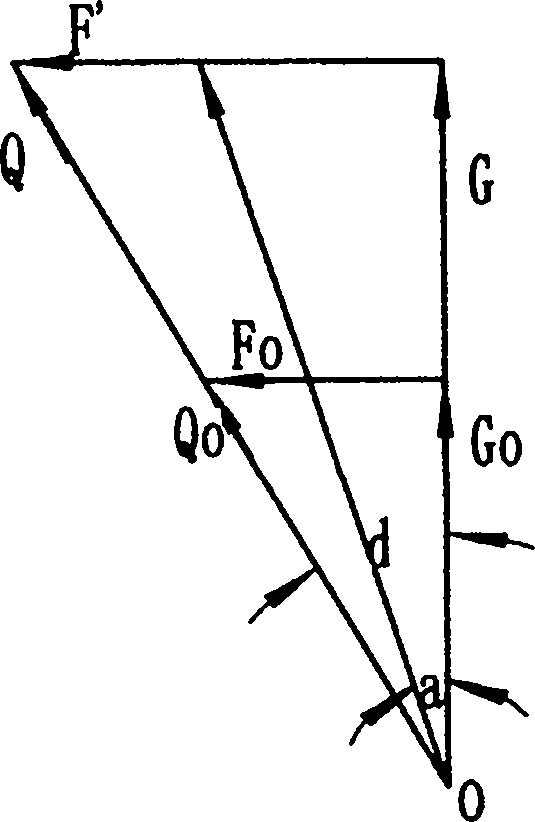
[0070] Figure 7 It is a schematic diagram of a friction-type linear bidirectional brake capable of split-directional control in the present invention: it is equal to the embodiment 1 Figure 5 The two one-way friction self-locking devices shown are opposite and reversely combined; the frame (brake caliper) 8 floats perpendicular to the braking direction; three working conditions can be realized through the control of their respective controllers 7: 1) one-sided During work, action process is the same as embodiment one Figure 5 As shown, at this moment, the friction part 2 on the other side is rigidly constrained by the frame, thereby clamping the target part; when the reverse movement, the part 2 on the working side is in an unlocked sliding state, and the part 2 on the other side is restricted by the controller 7 And will not produce action - this is a one-way braking condition. 2) Both sides work at the same time——when both controllers 7 are released, both directions are...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com