Improvement of Heat Treatment Process for Low Magnitude Coarse Grain and Microstructure of h13 Forgings
A technology of microstructure and process, which is applied in the field of heat treatment process to improve the low-magnification coarse grain and microstructure of H13 forgings, can solve the problems affecting the service life of the mold, mixed crystals, etc., to increase the cooling speed and eliminate the low-magnification coarse grain , Eliminate the effect of uniform microstructure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
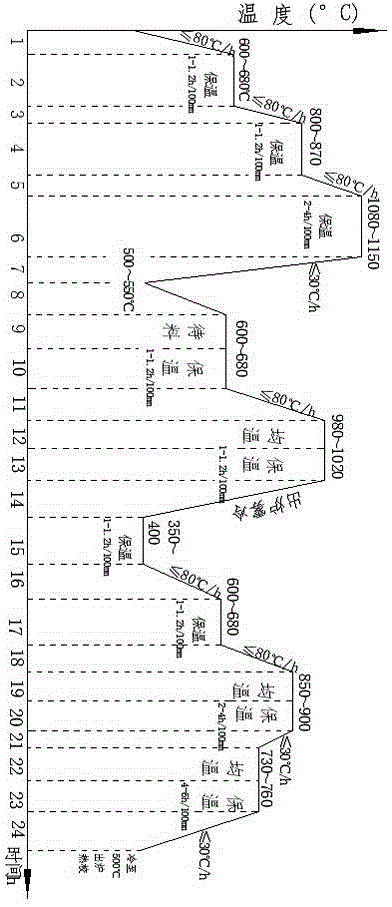
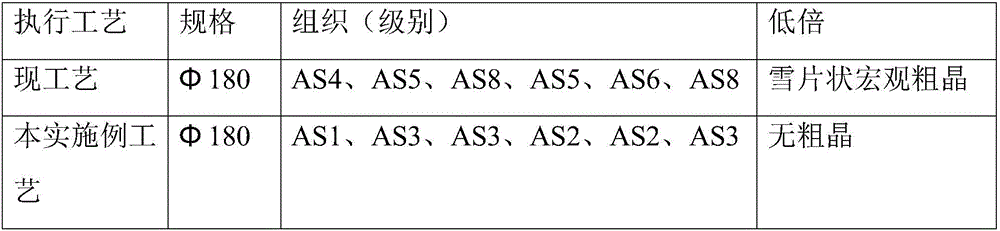
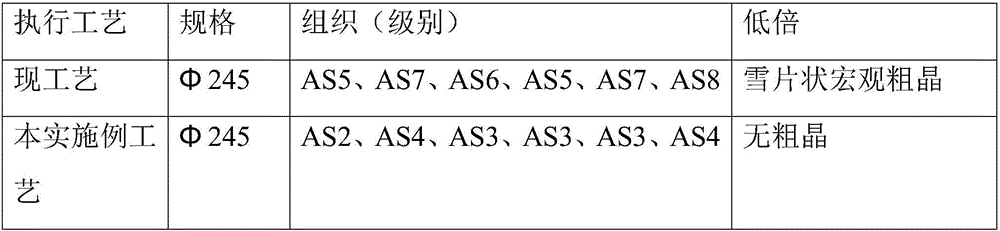
[0011] To improve the heat treatment process of H13 forgings with low magnification coarse grain and microstructure, the selected steel forgings are H13 (4Cr5MoSiV1), C is 0.38-0.43%, Si is 0.80-1.20%, Mn is 0.30-0.50%, and Cr is 4.75% ~5.5%, Mo is 1.10~1.75%, S≤0.020%, P≤0.025%, and the specification is Forgings, including the following processes (such as figure 1 shown):
[0012] Step 1: High-temperature diffusion heating: the first preheating temperature of high-temperature diffusion is 600-680°C, the heating rate is ≤80°C / h, the holding time is 1-1.2 hours / 100mm, the second preheating temperature is 800-870°C, heat The speed is ≤80°C / h, the holding time is 1-1.2 hours / 100mm, the high-temperature diffusion temperature is 1080-1150°C, and the holding time is 2-4h / 100mm;
[0013] Step 2: High-temperature diffusion cooling, after heat preservation, cool to 500-550°C at a rate of ≤30°C / h;
[0014] Step 3: put into the furnace for normalizing heating, the preheating temperat...
Embodiment 2
[0024] To improve the heat treatment process of H13 forgings with low magnification coarse grain and microstructure, the steel forgings are selected as H13, C is 0.38-0.43%, Si is 0.80-1.20%, Mn is 0.30-0.50%, and Cr is 4.75-5.5%. , Mo is 1.10~1.75%, S≤0.020%, P≤0.025%, and the specification is Forgings, including the following processes (such as figure 1 shown):
[0025] Step 1: High-temperature diffusion heating: the first preheating temperature of high-temperature diffusion is 600-680°C, the heating rate is ≤80°C / h, the holding time is 1-1.2 hours / 100mm, the second preheating temperature is 800-870°C, heat The speed is ≤80°C / h, the holding time is 1-1.2 hours / 100mm, the high-temperature diffusion temperature is 1080-1150°C, and the holding time is 2-4h / 100mm;
[0026] Step 2: High-temperature diffusion cooling, after heat preservation, cool to 500-550°C at a rate of ≤30°C / h;
[0027] Step 3: put into the furnace for normalizing heating, the preheating temperature is 600...
Embodiment 3
[0037] To improve the heat treatment process of H13 forgings with low magnification coarse grain and microstructure, the steel forgings are selected as H13, C is 0.38-0.43%, Si is 0.80-1.20%, Mn is 0.30-0.50%, and Cr is 4.75-5.5%. , Mo is 1.10~1.75%, S≤0.020%, P≤0.025%, and the specification is Forgings, including the following processes (such asfigure 1 shown):
[0038] Step 1: High-temperature diffusion heating: the first preheating temperature of high-temperature diffusion is 600-680°C, the heating rate is ≤80°C / h, the holding time is 1-1.2 hours / 100mm, the second preheating temperature is 800-870°C, heat The speed is ≤80°C / h, the holding time is 1-1.2 hours / 100mm, the high-temperature diffusion temperature is 1080-1150°C, and the holding time is 2-4h / 100mm;
[0039] Step 2: High-temperature diffusion cooling, after heat preservation, cool to 500-550°C at a rate of ≤30°C / h;
[0040] Step 3: put into the furnace for normalizing heating, the preheating temperature is 600-6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com