G protein-coupled receptor topology calculation prediction method based on feedback type conditional random field
A technology of conditional random field and coupled receptors, which is applied in computing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
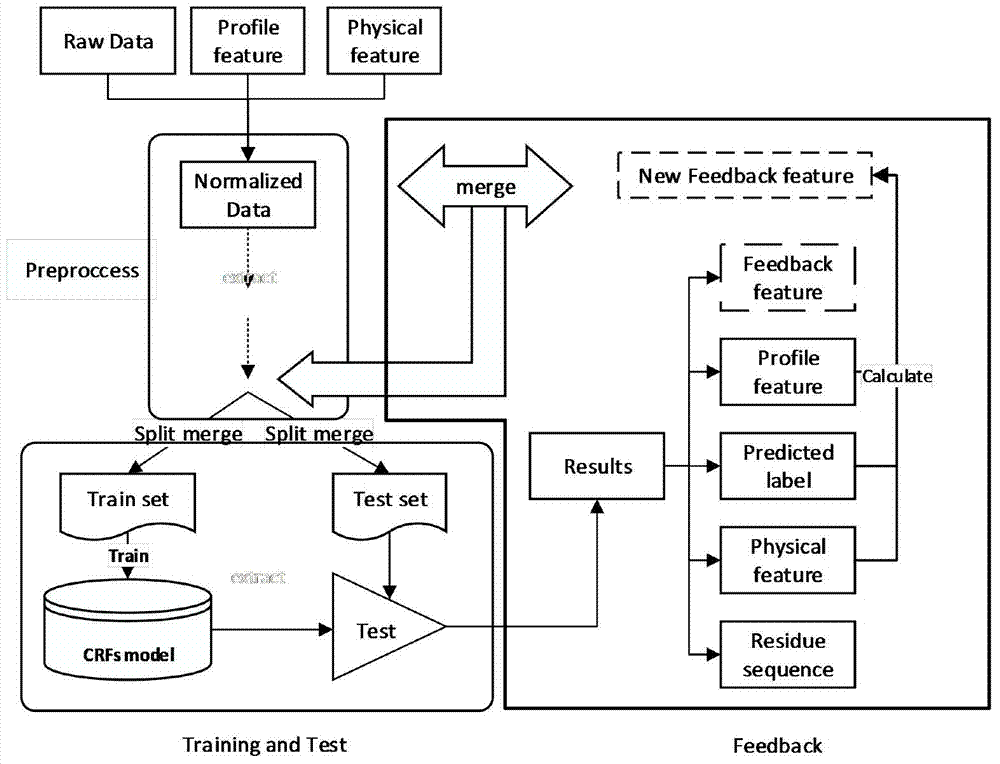
[0053] This embodiment discloses a method for predicting the topological calculation of G protein-coupled receptors based on feedback conditional random fields. The prediction method includes:
[0054] (1) Data set preparation: Prepare two data sets, TMPDB_FB and PDBTM_FB, the TMPDB_FB contains 106 different α-helix chains selected from TMPB, and the PDBTM_FB contains 472 non-redundant α-helix chains selected from PDBTM chain.
[0055] (2) Data preprocessing: normalize the data set, and map the value ranges of the physical attribute values and contour feature attribute values of the residues to the [0,1] interval.
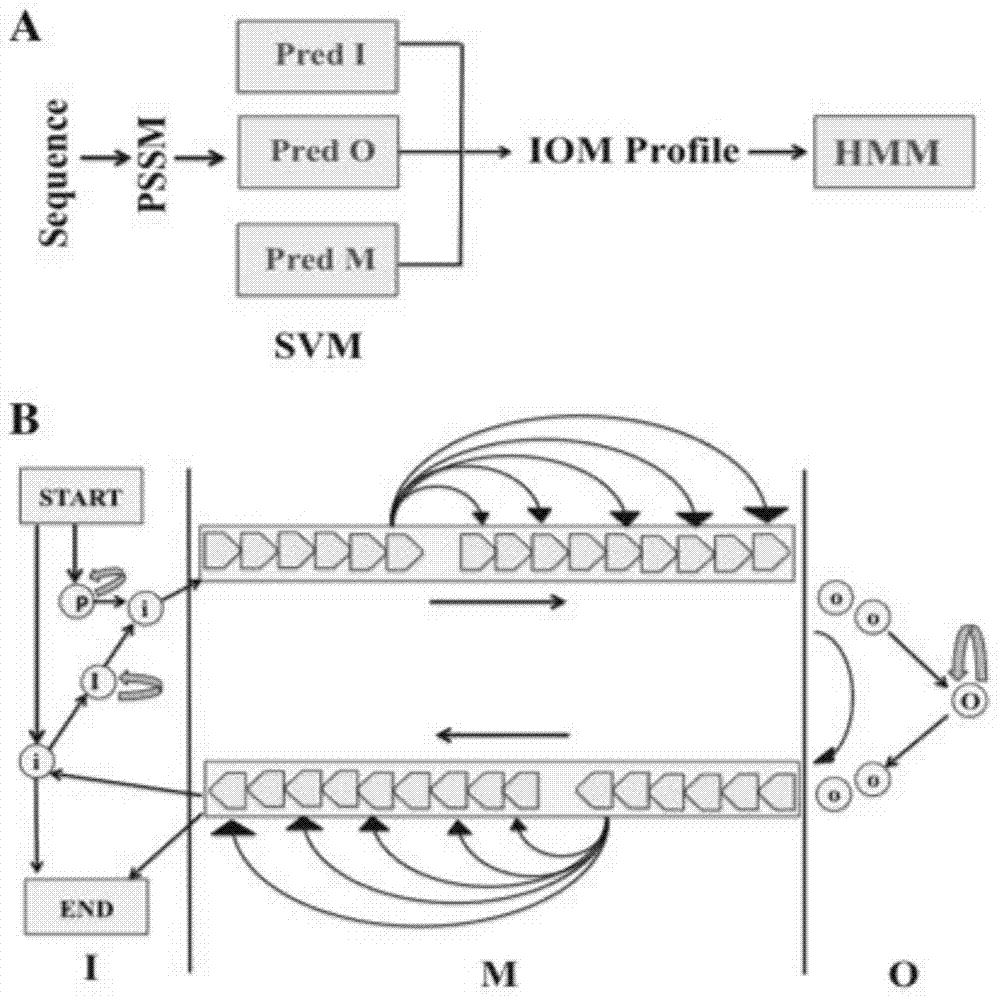
[0056] (3) Feedback conditional random field, including three stages:
[0057] (31) Basic conditional random field model: conditional random field theory, the conditional probability distribution between the marker sequence Y and the given observation sequence X is shown in formula (1):
[0058] P ( Y | ...
Embodiment 2
[0114] In this embodiment, the feedback CRF in Embodiment 1 is compared with the non-feedback CRF. Correct protein helix position and protein helix number are two very important indicators for studying GPCR. The correct rate of protein helical positions is equal to the ratio of the number of amino acid chains with correct helical positions to the total number of amino acid chains, and the correct rate of protein helical numbers is equal to the ratio of the number of amino acid chains with correct helical numbers to the total ratio of numbers.
[0115] In the data set PDBTM_FB, the relationship between the above two indicators and the window size and the number of feedbacks is shown in Table 2 and 3. In the two tables, the size of the window is (11,13,15), no feedback means no feedback, because when the basic conditional random field model is first constructed, there is no low-level prediction result to generate feedback features , feedback 1 means the first feedback.
[011...
Embodiment 3
[0122] This embodiment compares the feedback type conditional random field in embodiment 1 with the existing method. In order to further verify the performance of the feedback type basic conditional random field model, in this embodiment, the accuracy of this method is compared with other methods. Ten well-known GPCR topology prediction methods are compared. They are MEMSATS-SVM, OCTOPUS, MEMSAT3, ENSEMBLE, PHOBIUS, HMMTOP, PRODIV, SVMTOP, TMHMM, PHDhtm, the data set used is TMPDB_FB, the results are as follows Figure 4 shown.
[0123] Figure 4 "Correct protein helix count" in the table indicates the correct rate of protein helix number, and "Correct helix location" indicates the correct rate of helix position. The correct rate of helix position here is different from the correct rate of protein helix position. The correct rate of helix position It refers to the ratio of the correct number of helices predicted by the helix position in the entire data set to the total numbe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com