Self-biased ultra wideband low-power-consumption low-noise amplifier (LNA)
A low-noise amplifier, ultra-wideband technology, applied in the direction of improving amplifiers to expand bandwidth, improving amplifiers to reduce noise effects, and control of amplification, which can solve difficult broadband input matching, difficult to achieve high flat gain, and large chip area. and other problems, to achieve the effect of realizing ultra-wideband power and noise matching, optimizing broadband input power matching, and optimizing high-frequency noise performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
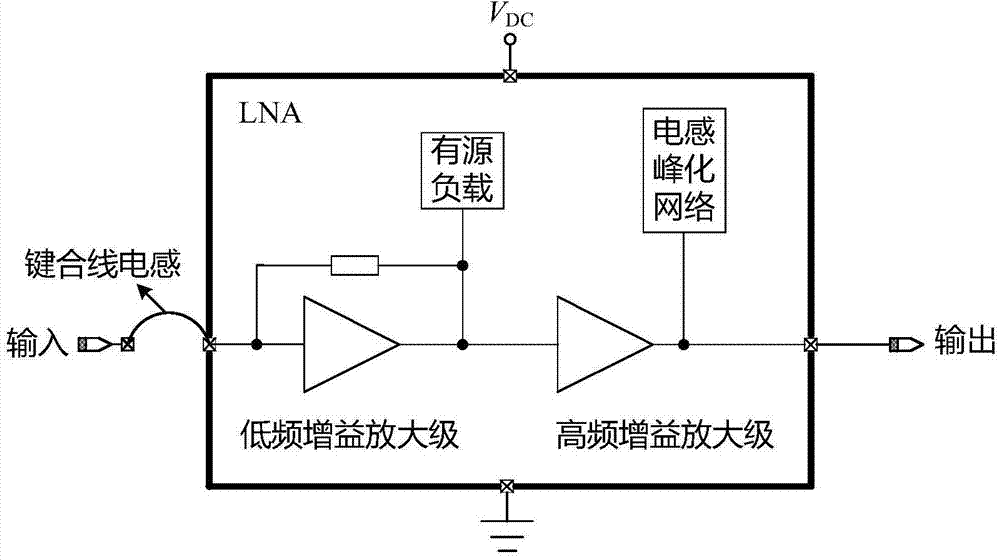
[0018] The LNA of the present invention adopts figure 1 The two-stage cascaded topology is shown. The first stage is a low-frequency gain amplification stage, which uses active devices as loads and resistor negative feedback technology; the second stage is a high-frequency gain amplification stage, which uses a Cascode structure as the basic amplification unit and an inductance peaking network as the load.
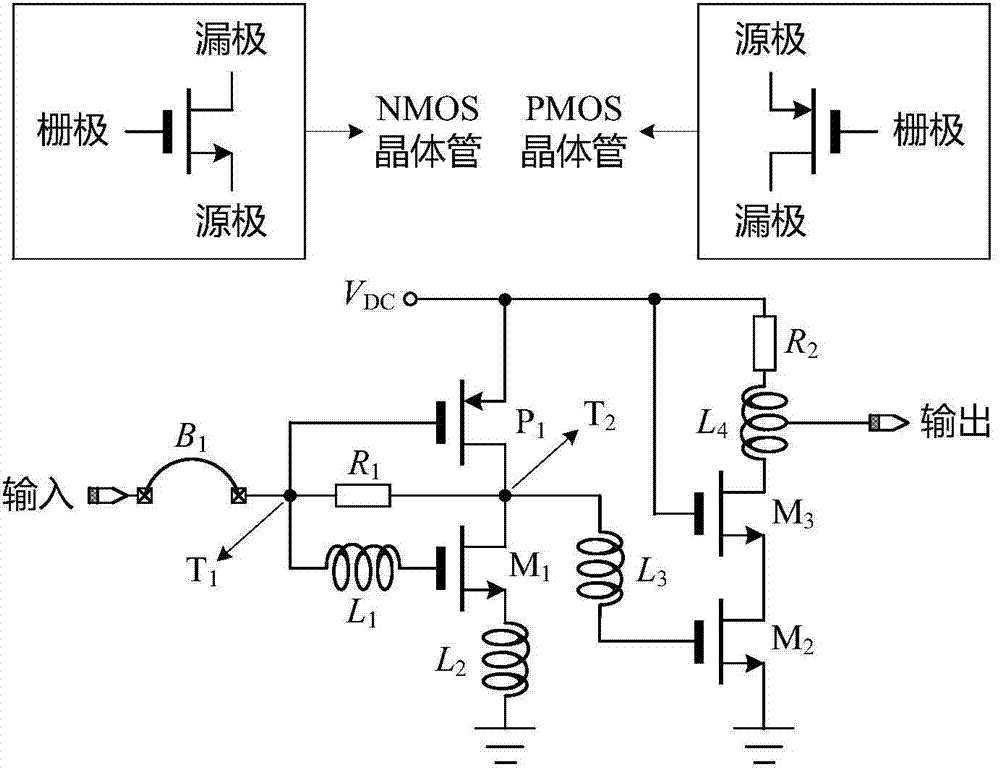
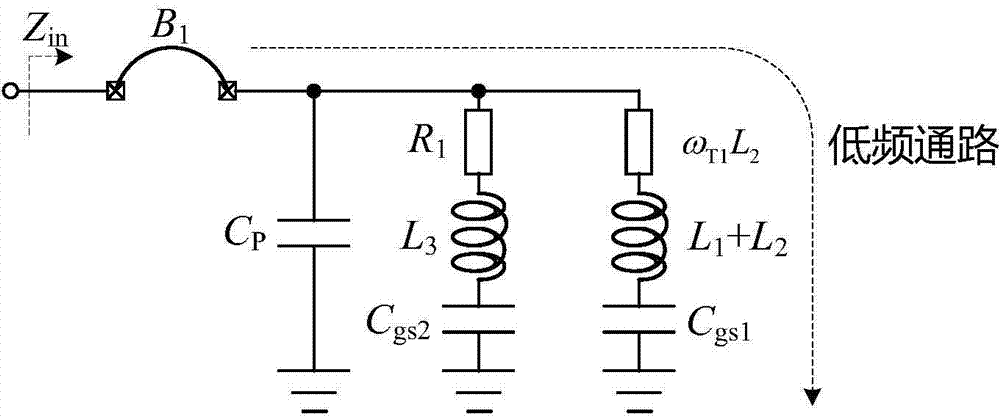
[0019] see figure 2 , the present invention utilizes three NMOS transistors, one PMOS transistor, five passive inductors, and two resistors to realize the circuit design of self-biased ultra-wideband low-power LNA. where the NMOS transistor M 1 , PMOS transistor P 1 , On-chip spiral inductor L 1 , L 2 and resistor R 1 Makes up the first stage of the LNA; NMOS transistor M 2 , M 3 , On-chip spiral inductor L 3 , On-chip ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com