Joint perception method for perceiving belief propagation in heterogeneous cellular network
A technology of belief propagation and cellular network, applied in the field of joint perception of cognitive belief propagation, can solve the problems of reducing system robustness, flexibility and scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
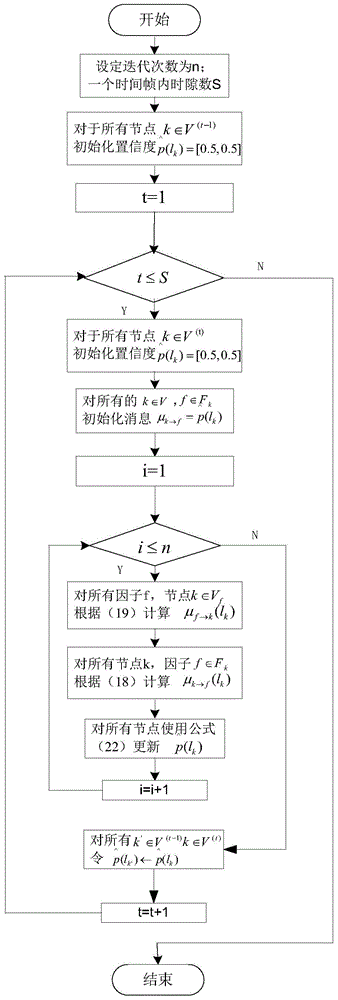
[0032] General steps of the present invention of embodiment 1
[0033] A joint perception method for cognitive belief propagation in a heterogeneous cellular network of the present invention has the modeling of the Markov random field of each time slot network topology, the conversion of the probability graph model into a factor graph, and the use of a unified complex weighted belief propagation algorithm Realize the three steps of reasoning and estimating the probability that a specific wireless channel is occupied by an authorized user.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 Modeling of Markov Random Fields of Each Time Slot Network Topology
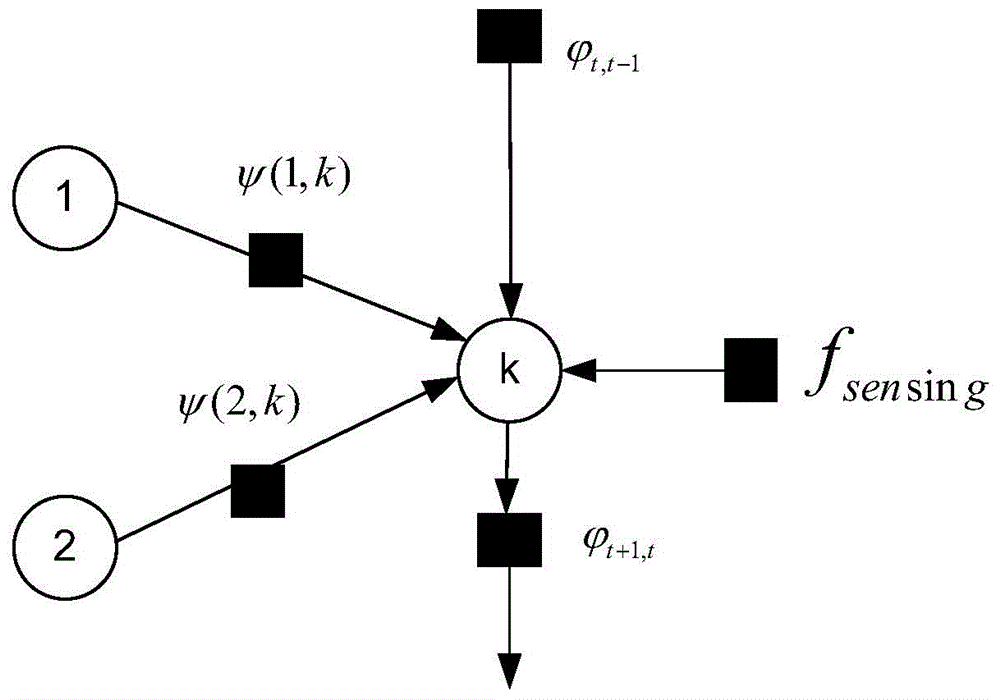
[0035] Assuming that there are K nodes in a distributed cognitive network, the time is divided into 0-S time slots, and the variable Represents the state of each cognitive node in time slot t: 0 indicates that the corresponding channel is idle; 1 indicates that the channel is occupied by authorized users, and the vector is a variable representing the state of K nodes at time t. make Represents the test statistic of the corresponding channel obtained by node k after performing a local spectrum sensing at time t. At time t, the test statistic of all K nodes is Wherein, the network node may adopt any single-node spectrum sensing method. For the sake of simplicity, it is assumed that the cognitive nodes all adopt the energy detection algorithm, then the test statistic It is about the signal sampling vector The function:
[0036] T k ...
Embodiment 3
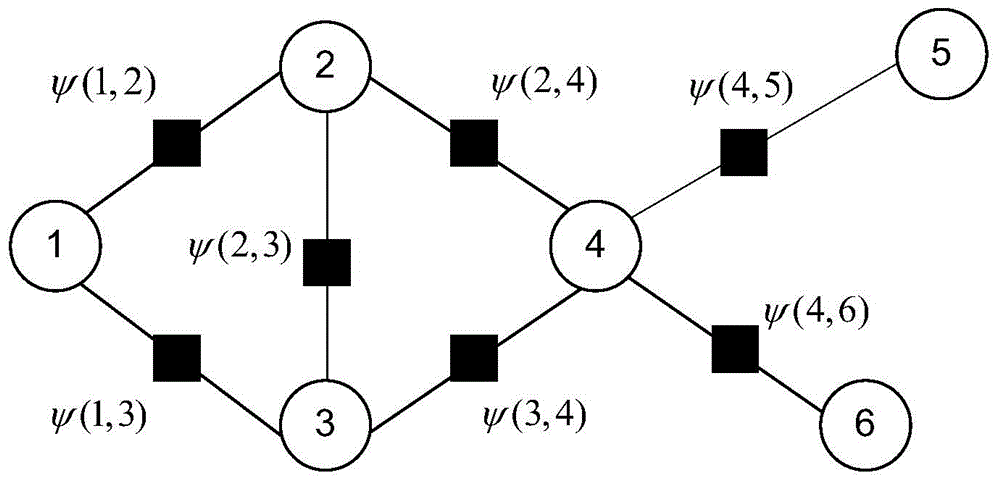
[0053] Example 3 Converting the probability graph model into a factor graph
[0054] A probabilistic graphical model is actually a graph composed of nodes and edges, where each node represents a (or a group of) random variables, and the edges connecting the nodes represent the probability relationship between random variables. Such a graph expresses a mathematical relationship—how the joint distribution over all random variables breaks down into a product of factors that depend on only some of the random variables.
[0055] In order to effectively solve inference problems, probabilistic graphical models are often transformed into a general graphical model called factor graph. A factor graph is a unified representation of Bayesian networks and Markov networks, which explicitly describes the decomposition of the joint probability distribution on the graph by introducing factor nodes. Let {x 1 ,x 2 ,...,x n} is a variable set, where the element x i Belongs to some symbol s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com