Method for rapidly judging position relation between points and polygon in GIS application
A polygon and decision point technology, applied in image data processing, instruments, calculations, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to deal with boundaries, vertices, boundary and ray collinearity, engineers locating faults, wrong decision-making, etc. The effect of fast location relationship, avoiding cumbersome processing, and narrowing the scope
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
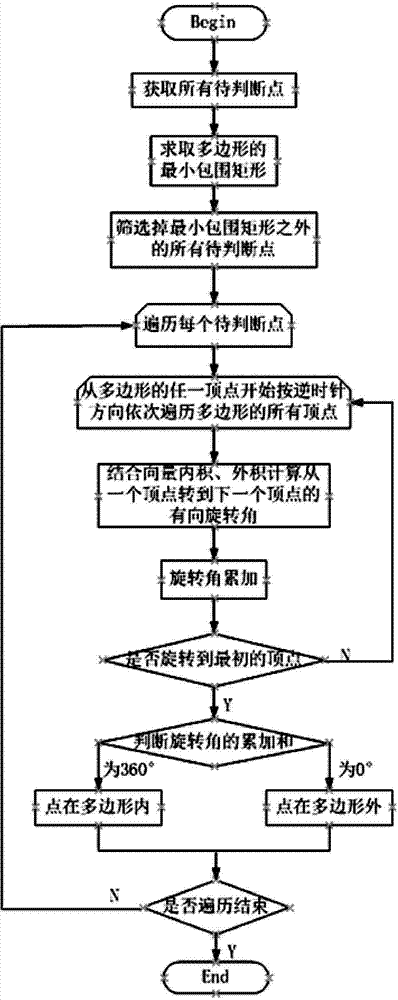
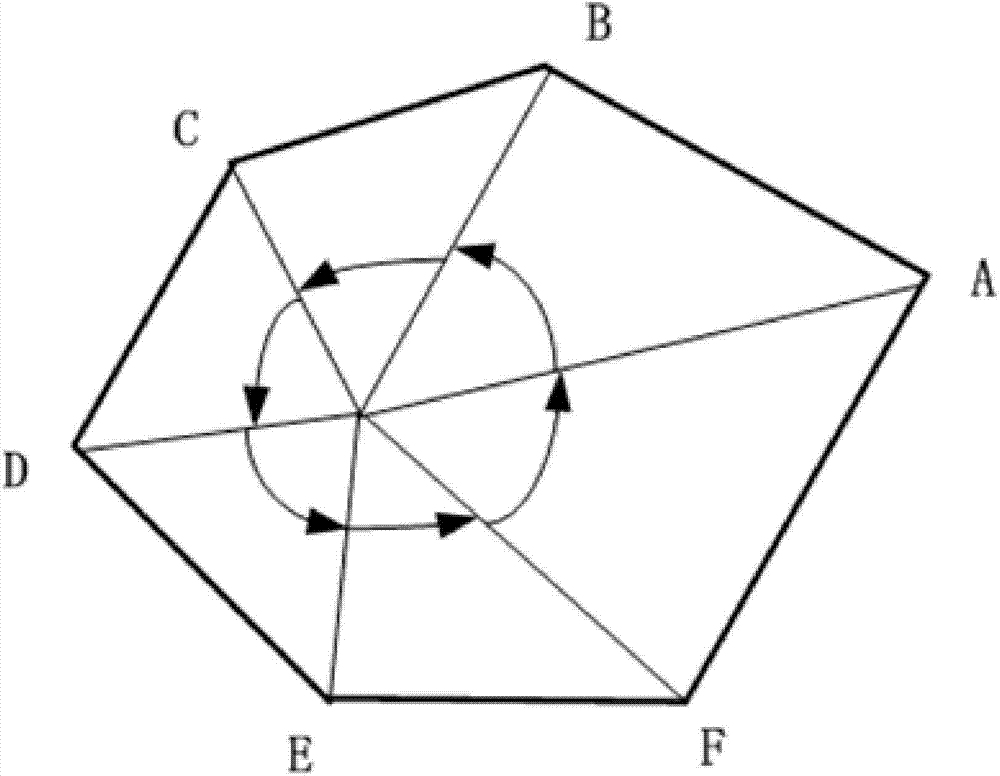
[0040] Embodiment: The following is an example of using the method of the present invention to identify network elements within a certain geographical range when polygons are used to circle network elements within a certain geographical range on a GIS map. The network elements on the map all have the basic geographic information of longitude and latitude. The premise of judging by the method of the present invention is that the latitude and longitude coordinates are converted into coordinates of a plane Cartesian coordinate system through Gaussian projection coordinate conversion. The coordinates of the network element after Gaussian projection coordinate transformation are used means, such as and many more.
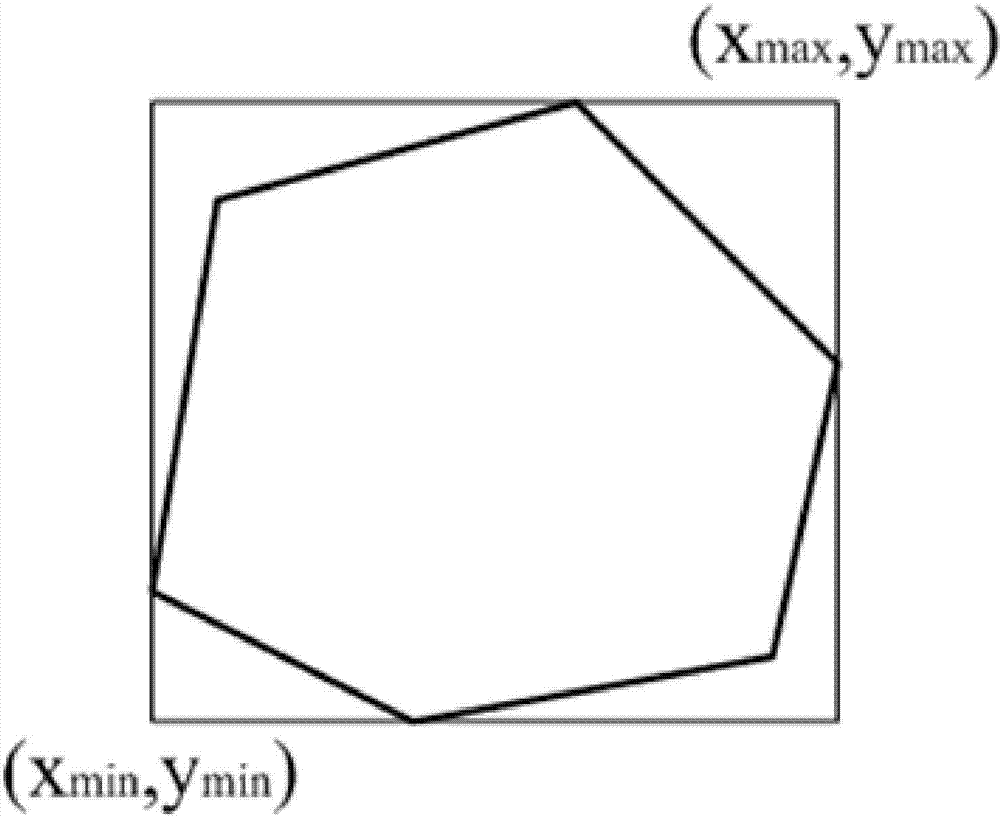
[0041] attached figure 2 The minimum enclosing rectangle of polygons is explained. Number the vertices of the polygon in counterclockwise order to obtain the sequence of polygon vertices: . Calculate the minimum value of the X coordinate in the polygon vertex co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com