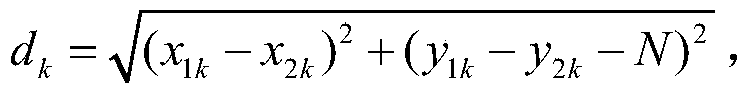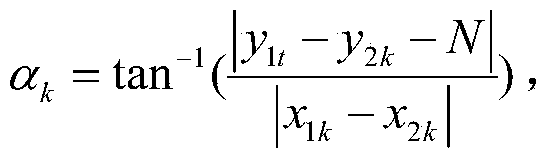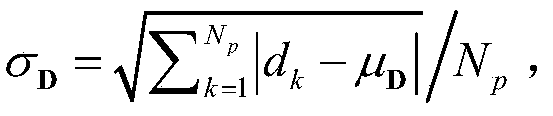Method for registering synthetic aperture radar image with change area based on point pair constraint and Delaunay
A synthetic aperture radar and triangular network technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as low positioning accuracy and failure to find a suitable matching template
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0081] refer to figure 1 , the SAR image registration method based on the point-to-constraint and triangular network of the present invention, the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0082] (1) Input the SAR image I acquired by the same sensor for the same area at two different times 1 and I 2 , the size is M×N, which can be expressed as I t ={I t (x,y)|t=1,2;1
[0083] (2) Separately for image I 1 and I 2Carry out the Pretest filter that the neighborhood block size is b×b, the search window size is w×w, obtain floating image F and reference image R, wherein, the value range of neighborhood block size b is 3~9, in the example of the present invention The value is 3; the value range of the search window size w i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com