Method and device for accessing mass time sequence data
A technology of time series and data, applied in the field of data cloud storage, can solve the problems of long storage time, high storage frequency, large amount of data, etc., and achieve the effect of improving access efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
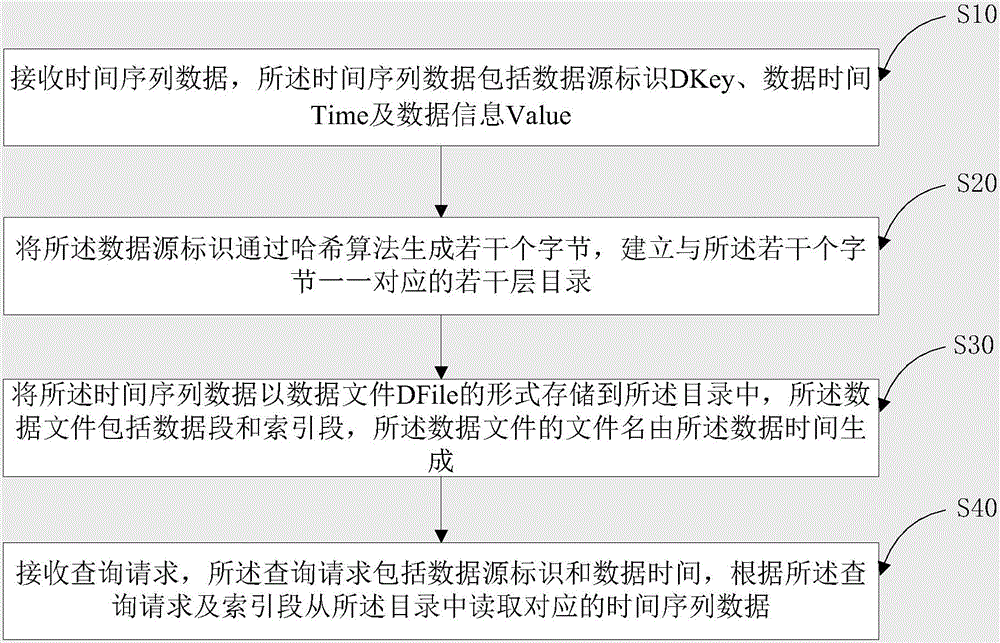
[0052] figure 1 It is a flowchart of a method for accessing massive time series data provided by this embodiment.
[0053] A method for accessing massive time series data, including:
[0054] S10. Receive time series data, the time series data including data source identifier DKey, data time Time and data information Value;
[0055] S20. Generate several bytes of the data source identifier through a hash algorithm, and establish several layers of directories corresponding to the several bytes;
[0056]S30. Store the time series data in the directory in the form of a data file DFile, the data file includes a data segment and an index segment, and the file name of the data file is generated by the data time;
[0057] S40. Receive a query request, where the query request includes a data source identifier and data time, and read corresponding time series data from the directory according to the query request and the index segment.
[0058] In this embodiment, the time-series da...
Embodiment 2
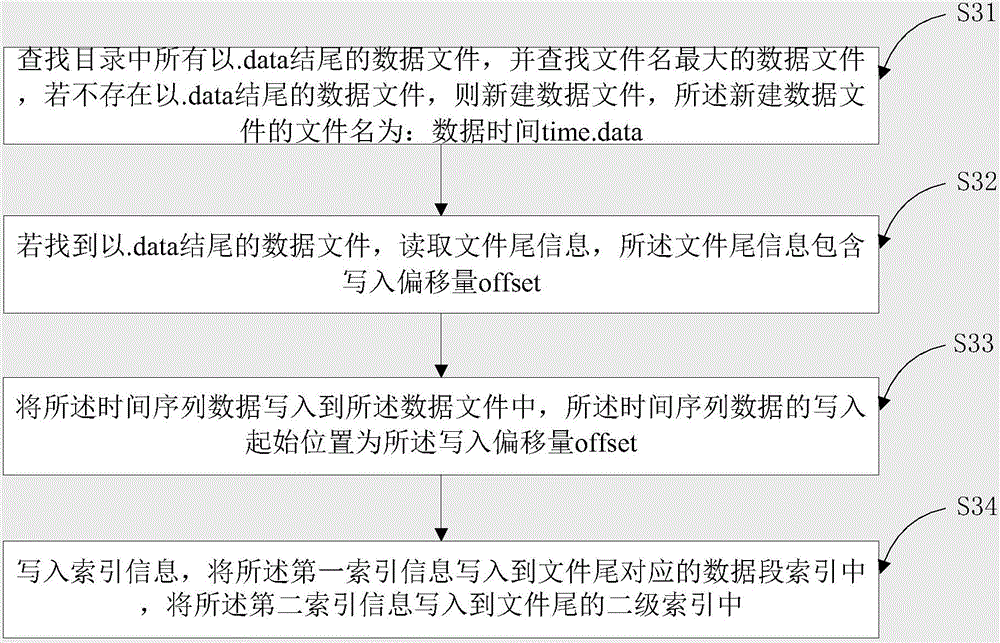
[0074] Such as figure 2 As shown, in this embodiment, the step S30 includes:
[0075] S31, search for all data files ending with .data in the directory, and search for the data file with the largest file name, if there is no data file ending with .data, then create a new data file, the file name of the new data file is: data Time time.data; record the basic information of the file at the tailOffset position of the file {startTime, 0, 0} where the start time is the data time, and the end time is 0 to indicate that it is not over. The current data segment is written to position 0 and recorded in the memory in the data structure of the file handle.
[0076] S32. If a data file ending with .data is found, read the end of file information, which includes the write offset offset; read the end of file record information {startTime, 0, offset}, wherein the start time is Data time, the end time is 0 means it is not over, the current data segment is written to the position offset, an...
Embodiment 3
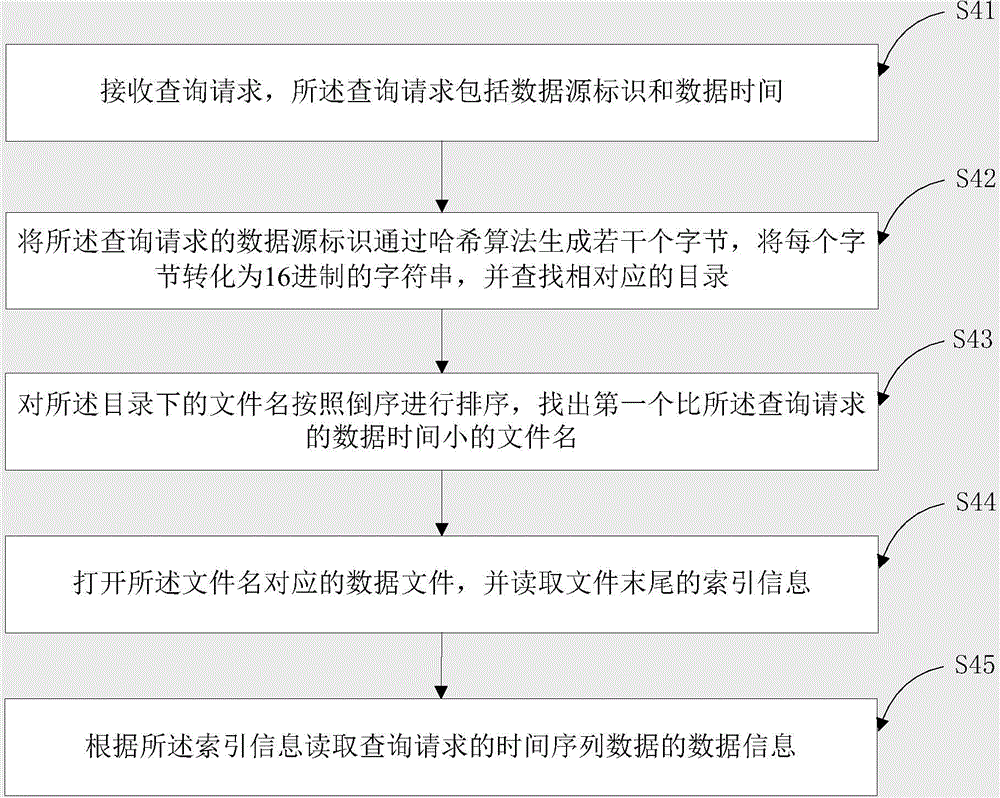
[0082] Such as image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, the step S40 includes:
[0083] S41. Receive a query request, where the query request includes a data source identifier and a data time;
[0084] S42. Generate several bytes of the data source identifier of the query request through a hash algorithm, convert each byte into a hexadecimal string, and search for the corresponding directory;
[0085] S43. Sort the file names in the directory in reverse order, and find the first file name that is shorter than the data time of the query request;
[0086] S44. Open the data file corresponding to the file name, and read the index information at the end of the file;
[0087] S55. Read the data information of the time series data requested by the query according to the index information.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com