Method for determining a crankshaft position of an internal combustion engine
A crankshaft position, internal combustion engine technology, applied in mechanical equipment, engine control, fuel injection control, etc., can solve the problems of uncertain working stroke, distinction, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
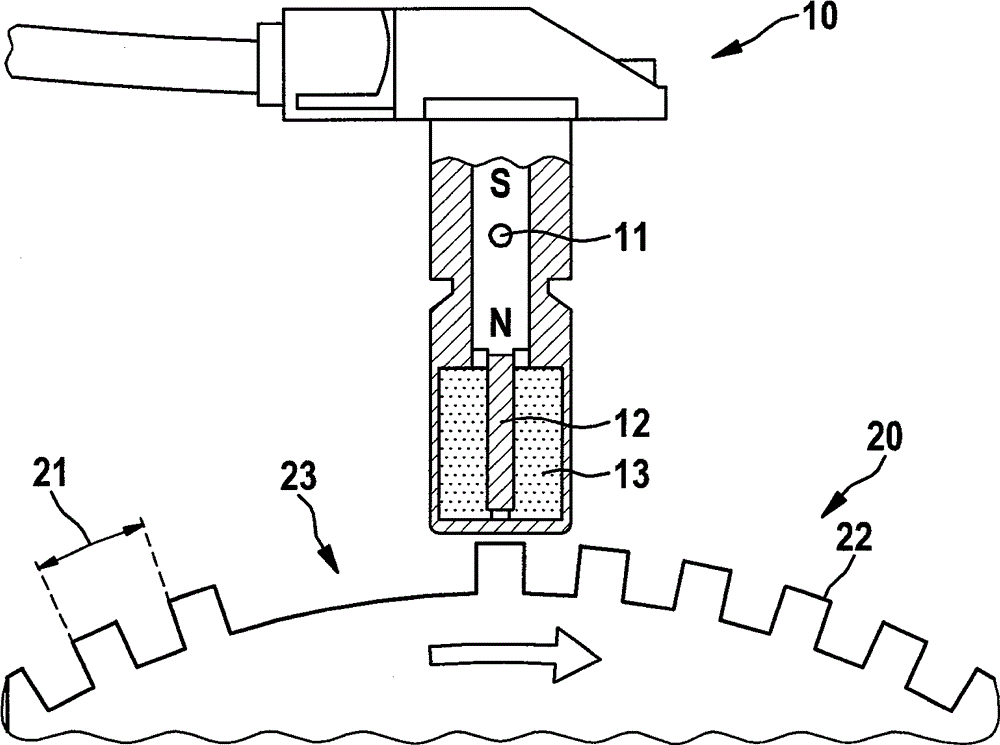
[0026] exist figure 1 A sensor wheel 20 and a corresponding inductive sensor 10 are schematically shown in FIG. 1 , which are used, for example, for determining the rotational speed in the prior art. The sensor wheel 20 is here generally fixedly connected to the crankshaft of the internal combustion engine, and the sensor 10 is fixedly mounted at a suitable location.
[0027] The sensor wheel 20 , usually made of ferromagnetic material, has teeth 22 which are arranged on the outside with a space 21 between them. At a position on the outside, the sensor wheel 20 has a gap 23 of the length of the specified number of teeth. This gap 23 serves as a reference mark for identifying the absolute position of the sensor wheel 20 .
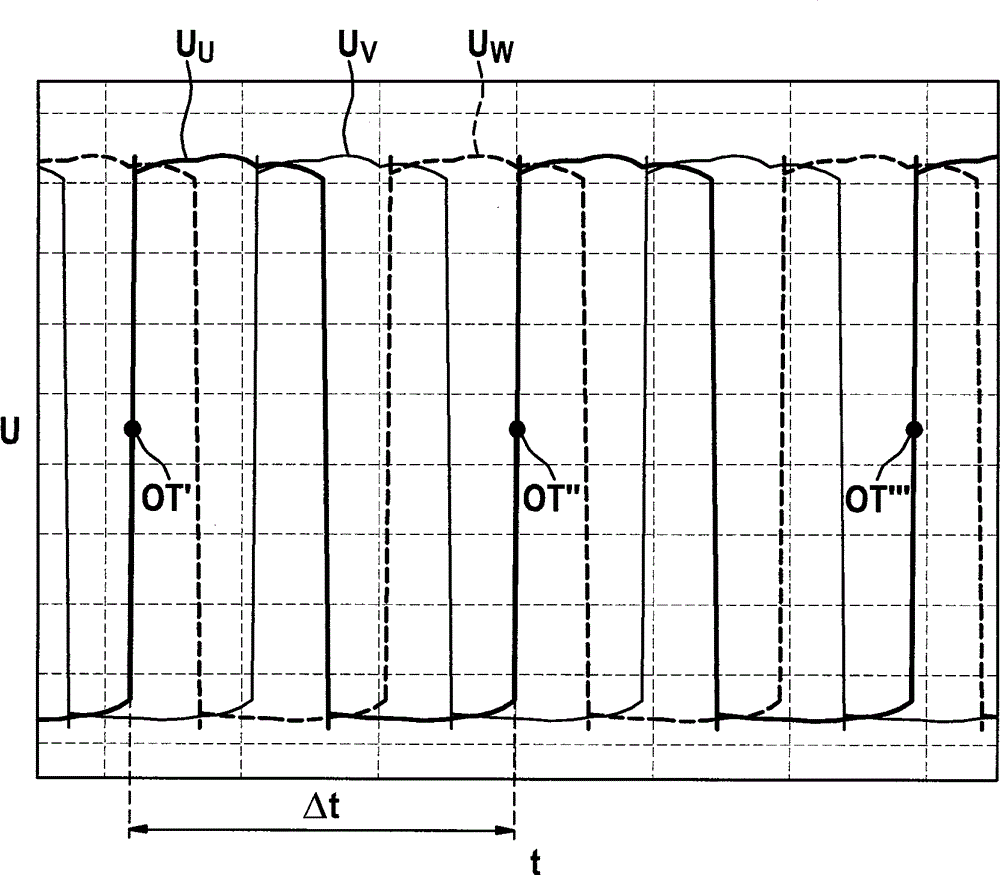
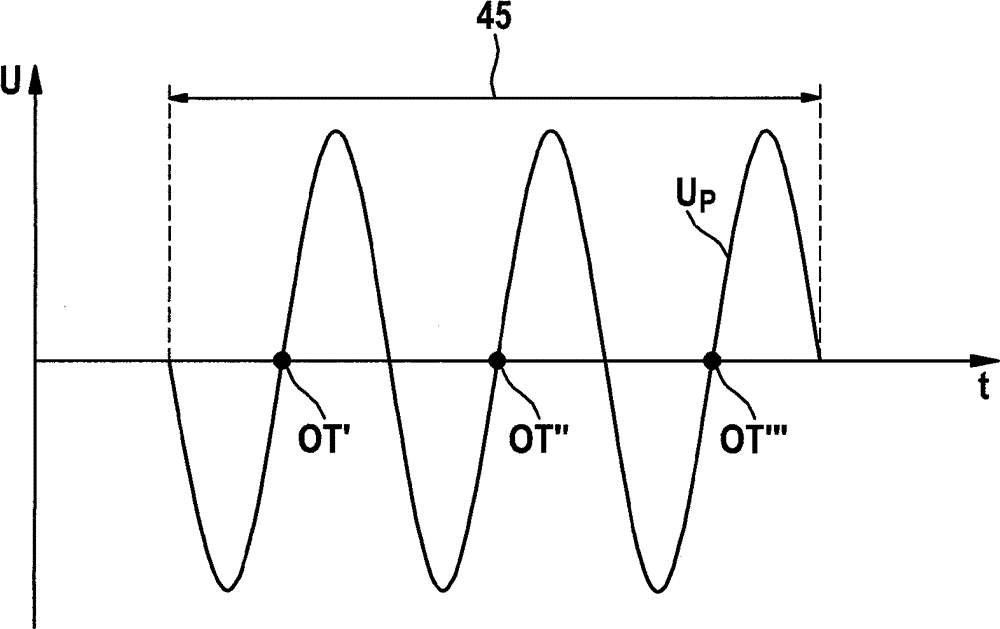
[0028] The sensor 10 has a bar magnet 11 on which a soft-magnetic pole pin 12 is mounted. The pole pin 12 is in turn surrounded by an induction coil 13 . When the sensor wheel 20 rotates, the teeth 22 and the gap between every two teeth alternately pass ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com